SLVSEM1A March 2019 – September 2019 LM76202-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 8.3.2 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 8.3.3 Reverse Battery Protection
- 8.3.4 Hot Plug-In and In-Rush Current Control
- 8.3.5 Overload and Short Circuit Protection
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Orderable Information
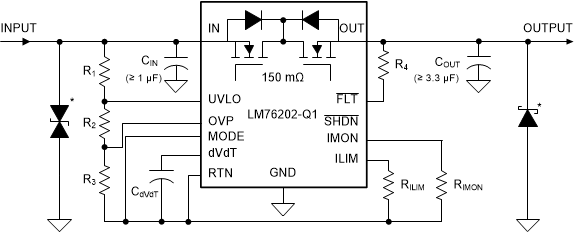
10.1 Transient Protection
In case of short circuit and over load current limit, when the device interrupts current flow, input inductance generates a positive voltage spike on the input and output inductance generates a negative voltage spike on the output. The peak amplitude of voltage spikes (transients) is dependent on value of inductance in series to the input or output of the device. Such transients can exceed the Absolute Maximum Ratings of the device if steps are not taken to address the issue.
Typical methods for addressing transients include:
- Minimizing lead length and inductance into and out of the device
- Using large PCB GND plane
- Schottky diode across the output to absorb negative spikes
- A ceramic capacitor at input (C(IN)) with value more than 1µF to absorb the energy and dampen the transients.
The approximate value of input capacitance can be estimated with Equation 14.
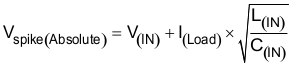
where
- V(IN) is the nominal supply voltage
- I(LOAD) is the load current
- L(IN) equals the effective inductance seen looking into the source
- C(IN) is the capacitance present at the input
Automotive applications could require additional Transient Voltage Suppressor (TVS) to prevent transients from exceeding the Absolute Maximum Ratings of the device. These transients include ISO 7637 Pulse 1, Output short to battery, Output short to GND and reverse battery at input.
The circuit implementation with optional protection components (TVS Diode at Input and schottky diode at output) is shown in Figure 48. For protection from automotive transients similar to ISO 7637 Pulse 1, Output short to battery , output short to GND and reverse battery, use CIN ≥ 1 µF and COUT ≥ 3.3 µF. For selection of TVS diode and other components, see Application Information.