SNAS264D April 2006 – February 2024 LM94
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2
Feature Description
- 6.2.1 Monitoring Cycle Time
- 6.2.2 ΣΔ A/D Inherent Averaging
- 6.2.3 Temperature Monitoring
- 6.2.4 Event Errors for Fan Boost
- 6.2.5 Voltage Monitoring
- 6.2.6 Recommended External Scaling Resistors for +12V Power Rails
- 6.2.7 Recommended External Scaling Circuit for −12V Power Input
- 6.2.8 Adding External Scaling Resistors to Other Analog Inputs
- 6.2.9 Dynamic Vccp Monitoring Using VID
- 6.2.10 Monitoring Analog Temperature Sensors
- 6.2.11 VREF Output
- 6.2.12 PROCHOT Background Information
- 6.2.13 PROCHOT Monitoring
- 6.2.14 PROCHOT Output Control
- 6.2.15 Fan Speed Measurement
- 6.2.16 Smart Fan Speed Measurement
- 6.2.17 Inputs/Outputs
- 6.2.18
Fan Control
- 6.2.18.1 Automatic Fan Control Methods
- 6.2.18.2 LUT Fan Control Duty Cycles
- 6.2.18.3 Alternate LUT PWM Mapping
- 6.2.18.4 Fan Control Priorities
- 6.2.18.5 PWM to 100% Conditions
- 6.2.18.6 VRDx_HOT Ramp-Up/Ramp-Down
- 6.2.18.7 PROCHOT Ramp-Up/Ramp-Down
- 6.2.18.8 Manual PWM Override
- 6.2.18.9 Fan Spin-Up Control
- 6.2.19 XOR TREE TEST
- 6.3
Programming
- 6.3.1
SMBus Interface
- 6.3.1.1 SMBus ADDRESSING
- 6.3.1.2 DIGITAL NOISE EFFECT ON SMBus COMMUNICATION
- 6.3.1.3 GENERAL SMBus TIMING
- 6.3.1.4 SMBus ERROR SAFETY FEATURES
- 6.3.1.5 Serial Interface Protocols
- 6.3.1.6 READING AND WRITING 16-BIT REGISTERS
- 6.3.1
SMBus Interface
- 6.4
Registers
- 6.4.1 Regsiter Warnings
- 6.4.2 Register Summary Table
- 6.4.3 Factory Registers 00h–04h
- 6.4.4 Value Registers Section 1
- 6.4.5 PWM Duty Cycle Overide Registers
- 6.4.6
Extended Resolution Value Registers
- 6.4.6.1 Registers 10h - 17h Zone 1 (CPU1) and Zone 2 (CPU2) Extended Resolution Unfiltered Temperature Value Registers, Most and Least Significant Bytes
- 6.4.6.2 Registers 18h – 1Fh Zone 1 (CPU1) and Zone 2 (CPU2) Extended Resolution Filtered Value Registers, Most and Least Significant Bytes
- 6.4.6.3 Registers 20h – 23h Zone 3 and Zone 4 Extended Resolution Value Registers, Most and Least Significant Bytes
- 6.4.7
PI Loop Fan Control Setup Registers
- 6.4.7.1 Register 31h Internal/External Temperature Source Select
- 6.4.7.2 Register 32h PWM Filter Settings
- 6.4.7.3 Register 33h PWM1 Filter Shutoff Threshold
- 6.4.7.4 Register 34h PWM2 Filter Shutoff Threshold
- 6.4.7.5 Register 35h PI/LUT Fan Control Bindings
- 6.4.7.6 Register 36h PI Controller Minimum PWM and Hysteresis
- 6.4.7.7 Registers 37h and 38h Zone 1 and 2 PI Controller Target Temperature (Tcontrol)
- 6.4.7.8 Register 39h and 3Ah Zone 1 and 2 PI Fan Control Off Temperature (Toff)
- 6.4.7.9 Register 3Bh Proportional Coefficient
- 6.4.7.10 Register 3Ch Integral Coefficient
- 6.4.7.11 Register 3Dh PI Coefficient Exponents
- 6.4.8 Device Identification Registers (3Eh-3Fh)
- 6.4.9
BMC Error Status Registers 40h–47h
- 6.4.9.1 Register 40h B_Error Status 1
- 6.4.9.2 Register 41h B_Error Status 2
- 6.4.9.3 Register 42h B_Error Status 3
- 6.4.9.4 Register 43h B_Error Status 4
- 6.4.9.5 Register 44h B_ P1_PROCHOT Error Status
- 6.4.9.6 Register 45h B_P2_PROCHOT Error Status
- 6.4.9.7 Register 46h B_GPI Error Status
- 6.4.9.8 Register 47h B_Fan Error Status
- 6.4.10
Host Error Status Registers
- 6.4.10.1 Register 48h H_Error Status 1
- 6.4.10.2 Register 49h H_Error Status 2
- 6.4.10.3 Register 4Ah H_Error Status 3
- 6.4.10.4 Register 4Bh H_Error Status 4
- 6.4.10.5 Register 4Ch H_P1_PROCHOT Error Status
- 6.4.10.6 Register 4Dh B_P2_PROCHOT Error Status
- 6.4.10.7 Register 4Eh H_GPI Error Status
- 6.4.10.8 Register 4Fh H_Fan Error Status
- 6.4.11
Value Registers
- 6.4.11.1 Registers 50–53h Unfiltered Temperature Value Registers
- 6.4.11.2 Registers 54–55h Filtered Temperature Value Registers
- 6.4.11.3 Register 56–65h A/D Channel Voltage Registers
- 6.4.11.4 Register 67h Current P1_PROCHOT
- 6.4.11.5 Register 68h Average P1_PROCHOT
- 6.4.11.6 Register 69h Current P2_PROCHOT
- 6.4.11.7 Register 6Ah Average P2_PROCHOT
- 6.4.11.8 Register 6Bh Current GPI State
- 6.4.11.9 Register 6Ch P1_VID
- 6.4.11.10 Register 6Dh P2_VID
- 6.4.11.11 Register 6E–75h Fan Tachometer Readings
- 6.4.12
Limit Registers
- 6.4.12.1 Registers 78–7Fh Temperature Limit Registers
- 6.4.12.2 Registers 80–83h Fan Boost Temperature Registers
- 6.4.12.3 Register 84h Zone1, and Zone2 Hysteresis for Limit Comparisons
- 6.4.12.4 Register 85h Zone3 and Zone4 Hysteresis for Limit Comparisons
- 6.4.12.5 Registers 8E–8Fh Zone 1b and Zone 2b Temperature Reading Adjustment Registers
- 6.4.12.6 Registers 90–AFh Voltage Limit Registers
- 6.4.12.7 Register B0–B1h PROCHOT User Limit Registers
- 6.4.12.8 Register B2–B3h Dynamic Vccp Limit Offset Registers
- 6.4.12.9 Register B4–BBh Fan Tach Limit Registers
- 6.4.13
Setup Registers
- 6.4.13.1 Register BCh Special Function Control 1 (Voltage Hysteresis and Fan Control Filter Enable)
- 6.4.13.2 Register BDh Special Function Control 2 (Smart Tach Mode Enable, Fan Control Temperature Resolution Control and VID Mode Select)
- 6.4.13.3 Register BEh GPI/VID Level Control
- 6.4.13.4 Register BFh PWM Ramp Control
- 6.4.13.5 Register C0h Fan Boost Hysteresis (Zones 1/2)
- 6.4.13.6 Register C1h Fan Boost Hysteresis (Zones 3/4)
- 6.4.13.7 Register C2h Zones 1/2 Spike Smoothing Control
- 6.4.13.8 Register C3h LUT 1/2 MinPWM and Hysteresis
- 6.4.13.9 Register C4h LUT 3/4 MinPWM and Hysteresis
- 6.4.13.10 Register C5h GPO
- 6.4.13.11 Register C6h PROCHOT Control
- 6.4.13.12 Register C7h PROCHOT Time Interval
- 6.4.13.13 Register C8h PWM1 Control 1
- 6.4.13.14 Register C9h PWM1 Control 2
- 6.4.13.15 Register CAh PWM1 Control 3
- 6.4.13.16 Register CBh PWM1 Control 4
- 6.4.13.17 Register CCh PWM2 Control 1
- 6.4.13.18 Register CDh PWM2 Control 2
- 6.4.13.19 Register CEh PWM2 Control 3
- 6.4.13.20 Register CFh PWM2 Control 4
- 6.4.13.21 Register D0h–D3h LUT 1 to 4 Base Temperatures
- 6.4.13.22 Register D4h–DFh Lookup Table Steps—LUT 1/2 and LUT 3/4 Offset Temperature
- 6.4.13.23 Register E0h Special Function TACH to PWM Binding
- 6.4.13.24 Register E1h Tachometer Fan Boost Control Register
- 6.4.13.25 Register E2h LM94 Status Control
- 6.4.13.26 Register E3h LM94 Configuration
- 6.4.14
Sleep State Control and Mask Registers
- 6.4.14.1 Register E4h Sleep State Control
- 6.4.14.2 Register E5h S1 GPI Mask
- 6.4.14.3 Register E6h S1 Tach Mask
- 6.4.14.4 Register E7h S3 GPI Mask
- 6.4.14.5 Register E8h S3 Tach Mask
- 6.4.14.6 Register E9h S3 Temperature/Voltage Mask
- 6.4.14.7 Register EAh S4/5 GPI Mask
- 6.4.14.8 Register EBh S4/5 Temperature/Voltage Mask
- 6.4.15 Other Mask Registers
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGG|56
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
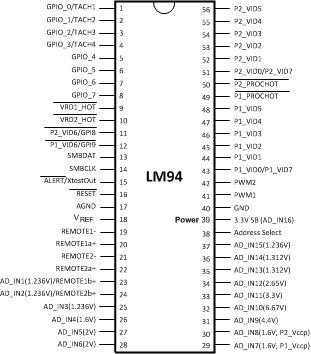 Figure 4-1 56 Pin TSSOP Package See
Package Number DGG0056A TOP VIEW
Figure 4-1 56 Pin TSSOP Package See
Package Number DGG0056A TOP VIEWTable 4-1 Pin Descriptions(1)
| Symbol | Pin No. | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPIO_0/TACH1 | 1 | Digital I/O (Open-Drain) | Can be configured as fan tach input or a general purpose open-drain digital I/O. |
| GPIO_1/TACH2 | 2 | Digital I/O (Open-Drain) | Can be configured as fan tach input or a general purpose open-drain digital I/O. |
| GPIO_2/TACH3 | 3 | Digital I/O (Open-Drain) | Can be configured as fan tach input or a general purpose open-drain digital I/O. |
| GPIO_3/TACH4 | 4 | Digital I/O (Open-Drain) | Can be configured as fan tach input or a general purpose open-drain digital I/O.. |
| GPIO_4 / P1_THERMTRIP | 5 | Digital I/O (Open-Drain) | A general purpose open-drain digital I/O. Can be configured to monitor a CPU's THERMTRIP signal to mask other errors. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| GPIO_5 / P2_THERMTRIP | 6 | Digital I/O (Open-Drain) | A general purpose open-drain digital I/O. Can be configured to monitor a CPU's THERMTRIP signal to mask other errors. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| GPIO_6 | 7 | Digital I/O (Open-Drain) | Can be used to detect the state of CPU1 IERR or a general purpose open-drain digital I/O. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| GPIO_7 | 8 | Digital I/O (Open-Drain) | Can be used to detect the state of CPU2 IERR or a general purpose open-drain digital I/O. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| VRD1_HOT | 9 | Digital Input | CPU1 voltage regulator HOT. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| VRD2_HOT | 10 | Digital Input | CPU2 voltage regulator HOT. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P2_VID6/ GPI8 | 11 | Digital Input | CPU2 VID6 input. Could also be used as a general purpose input to trigger an error event. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P1_VID6/ GPI9 | 12 | Digital Input | CPU1 VID6 input. Could also be used as a general purpose input to trigger an error event. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| SMBDAT | 13 | Digital I/O (Open-Drain) | Bidirectional System Management Bus Data. Output configured as 5V tolerant open-drain. SMBus 2.0 compliant. |
| SMBCLK | 14 | Digital Input | System Management Bus Clock. Driven by an open-drain output, and is 5V tolerant. SMBus 2.0 Compliant. |
| ALERT/XtestOut | 15 | Digital Output (Open-Drain) | Open-drain ALERT output used in an interrupt driven system to signal that an error event has occurred. Masked error events do not activate the ALERT output. When in XOR tree test mode, functions as XOR Tree output. |
| RESET | 16 | Digital I/O (Open-Drain) | Open-drain reset output when power is first applied to the LM94. Used as a reset for devices powered by 3.3V stand-by. After reset, this pin becomes a reset input. See Section 7.1.2 for more information. If this pin is not used, connection to an external resistive pull-up is required to prevent LM94 malfunction. |
| AGND | 17 | GROUND Input | Analog Ground. Digital ground and analog ground need to be tied together at the chip then both taken to a low noise system ground. A voltage difference between analog and digital ground may cause erroneous results. |
| VREF | 18 | Analog Output | 2.5V used for external ADC reference, or as a VREF reference voltage |
| REMOTE1− | 19 | Remote Thermal Diode_1- Input (CPU 1 THERMDC) | This is the negative input (current sink) from both of the CPU1 thermal diodes. Connected to THERMDC pin of Pentium processor or the emitter of a diode connected MMBT3904 NPN transistor. Serves as the negative input into the A/D for thermal diode voltage measurements. A 100 pF capacitor is optional and can be connected between REMOTE1− and REMOTE1+. |
| REMOTE1a+ | 20 | Remote Thermal Diode_1+ I/O (CPU1 THERMDA1) | This is a positive connection to the first CPU1 thermal diode. Serves as the positive input into the A/D for thermal diode voltage measurements. It also serves as a current source output that forward biases the thermal diode. Connected to THERMDA pin of Pentium processor or the base of a diode connected MMBT3904 NPN transistor. A 100 pF capacitor is optional and can be connected between REMOTE1− and each REMOTE1+. |
| REMOTE2− | 21 | Remote Thermal Diode_2 - Input (CPU2 THERMDC) | This is the negative input (current sink) from both of the CPU2 thermal diodes. Connected to THERMDC pins of Pentium processor or the emitter of a diode connected MMBT3904 NPN transistor. Serves as the negative input into the A/D for thermal diode voltage measurements. A 100 pF capacitor is optional and can be connected between REMOTE2− and each REMOTE2+. |
| REMOTE2a+ | 22 | Remote Thermal Diode_2 + I/O (CPU2 THERMDA1) | This is a positive connection to the first CPU2 thermal diode. Serves as the positive input into the A/D for thermal diode voltage measurements. It also serves as a current source output that forward biases the thermal diode. Connected to THERMDA pin of Pentium processor or the base of a diode connected MMBT3904 NPN transistor. A 100 pF capacitor is optional and can be connected between REMOTE2− and REMOTE2+. |
| AD_IN1/REMOTE1b+ | 23 | Analog Input (+12V1 or CPU1 THERMDA2) | Analog Input for +12V Rail 1 monitoring, for CPU1 voltage regulator. External attenuation resistors required such that 12V is attenuated to 0.927V for nominal ¾ scale reading. This pin may also serve as the second positive thermal diode input for CPU1. |
| AD_IN2/REMOTE2b+ | 24 | Analog Input (+12V2 or CPU2 THERMDA2) | Analog Input for +12V Rail 2 monitoring, for CPU2 voltage regulator. External attenuation resistors required such that 12V is attenuated to 0.927V for nominal ¾ scale reading. This pin may also serve as the second positive thermal diode input for CPU2. |
| AD_IN3 | 25 | Analog Input (+12V3) | Analog Input for +12V Rail 3, for Memory/3GIO slots. External attenuation resistors required such that 12V is attenuated to 0.927V for nominal ¾ scale reading. |
| AD_IN4 | 26 | Analog Input (FSB_Vtt) | Analog input for 1.2V monitoring, nominal ¾ scale reading |
| AD_IN5 | 27 | Analog Input (3GIO / PXH / MCH_Core) | Analog input for 1.5V monitoring, nominal ¾ scale reading |
| AD_IN6 | 28 | Analog Input (ICH_Core) | Analog input for 1.5V monitoring, nominal ¾ scale reading |
| AD_IN7 (P1_Vccp) | 29 | Analog Input (CPU1_Vccp) | Analog input for +Vccp (processor voltage) monitoring. |
| AD_IN8 (P2_Vccp) | 30 | Analog Input (CPU2_Vccp) | Analog input for +Vccp (processor voltage) monitoring. |
| AD_IN9 | 31 | Analog Input (+3.3V) | Analog input for +3.3V monitoring, nominal ¾ scale reading |
| AD_IN10 | 32 | Analog Input (+5V) | Analog input for +5V monitoring silver box supply monitoring, nominal ¾ scale reading |
| AD_IN11 | 33 | Analog Input (SCSI_Core) | Analog input for +2.5V monitoring, nominal ¾ scale reading. This pin may also be used to monitor an analog temperature sensor such as the LM60, since readings from this input can be routed to the fan control logic. |
| AD_IN12 | 34 | Analog Input (Mem_Core) | Analog input for +1.969V monitoring, nominal ¾ scale reading. |
| AD_IN13 | 35 | Analog Input (Mem_Vtt) | Analog input for +0.984V monitoring, nominal ¾ scale reading. |
| AD_IN14 | 36 | Analog Input (Gbit_Core) | Analog input for +0.984V S/B monitoring, nominal ¾ scale reading. |
| AD_IN15 | 37 | Analog Input (-12V) | Analog input for -12V monitoring. External resistors required to scale to positive level. Full scale reading at 1.236V, , nominal ¾ scale reading. This pin may also be used to monitor an analog temperature sensor such as the LM60, since readings from this input can be routed to the fan control logic. |
| Address Select | 38 | 3 level analog input | This input selects the lower two bits of the LM94 SMBus slave address. |
| 3.3V SB (AD_IN16) | 39 | POWER (VDD) +3.3V standby power | VDD power input for LM94. Generally
this is connected to +3.3V standby power. The LM94 can be powered by +3.3V if monitoring in low power states is not required, but power should be applied to this input before any other pins. This pin also serves as the analog input to monitor the 3.3V stand-by (SB) voltage. It is necessary to bypass this pin with a 0.1 µF in parallel with 100 pF. A bulk capacitance of 10 µF should be in the near vicinity. The 100 pF should be closest to the power pin. |
| GND | 40 | GROUND | Digital Ground. Digital ground and analog ground need to be tied together at the chip then both taken to a low noise system ground. A voltage difference between analog and digital ground may cause erroneous results. |
| PWM1 | 41 | Digital Output (Open-Drain) | Fan control output 1. |
| PWM2 | 42 | Digital Output (Open-Drain) | Fan control output 2 |
| P1_VID0/P1_VID7 | 43 | Digital Input | Voltage Identification signal from the processor. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P1_VID1 | 44 | Digital Input | Voltage Identification signal from the processor. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P1_VID2 | 45 | Digital Input | Voltage Identification signal from the processor. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P1_VID3 | 46 | Digital Input | Voltage Identification signal from the processor. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P1_VID4 | 47 | Digital Input | Voltage Identification signal from the processor. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P1_VID5 | 48 | Digital Input | Voltage Identification signal from the processor. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P1_PROCHOT | 49 | Digital I/O (Open-Drain) | Connected to CPU1 PROCHOT (processor hot) signal through a bidirectional level shifter. Supports TTL input logic level. |
| P2_PROCHOT | 50 | Digital I/O (Open-Drain) | Connected to CPU2 PROCHOT (processor hot) signal through a bidirectional level shifter. Supports TTL input logic level. |
| P2_VID0/P2_VID7 | 51 | Digital Input | Voltage Identification signal from the processor. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P2_VID1 | 52 | Digital Input | Voltage Identification signal from the processor. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P2_VID2 | 53 | Digital Input | Voltage Identification signal from the processor. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P2_VID3 | 54 | Digital Input | Voltage Identification signal from the processor. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P2_VID4 | 55 | Digital Input | Voltage Identification signal from the processor. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
| P2_VID5 | 56 | Digital Input | Voltage Identification signal from the processor. Supports TTL input logic levels and AGTL compatible input logic levels. |
(1) The over-score indicates the signal is active low (“Not”).