SNIS146B March 2007 – October 2017 LM95214
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: Temperature-to-Digital Converter
- 6.6 Logic Electrical Characteristics: Digital DC Characteristics
- 6.7 Switching Characteristics: SMBus Digital
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- NHL|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)(3)(4)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| Voltage at SMBDAT, SMBCLK, TCRIT1, TCRIT2, TCRIT3 |
–0.5 | 6 | V | |
| Voltage at other pins | –0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V | |
| D− Input current | ±1 | mA | ||
| Input current at all other pins (2) | ±5 | mA | ||
| Package input current (2) | 30 | mA | ||
| SMBDAT, TCRIT1, TCRIT2, TCRIT3 output sink current |
10 | mA | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) When the input voltage (VI) at any pin exceeds the power supplies (VI < GND or VI > VDD), the current at that pin must be limited to 5 mA. Parasitic components and or ESD protection circuitry are shown in the table below for the LM95214's pins.
(3) Soldering process must comply with reflow temperature profile specifications. Refer to http://www.ti.com/packaging
(4) Reflow temperature profiles are different for packages containing lead (Pb) than for those that do not.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge(3) | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1000 | |||
| Machine Model | ±200 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(3) Human-body model, 100-pF discharged through a 1.5-kΩ resistor. Machine model, 200-pF discharged directly into each pin. Charged-device model (CDM) simulates a pin slowly acquiring charge (such as from a device sliding down the feeder in an automated assembler) then rapidly being discharged.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operating temperature | –40 | 140 | °C | ||
| Supply voltage (VDD) | 3 | 3.6 | V | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LM95214 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NHL (WSON) | |||
| 14 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 38.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 27.5 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 16.7 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.3 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 16.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 3.2 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics: Temperature-to-Digital Converter
minimum and maximum specifications are over –40°C to +125°C and V+ = +3 V to 3.6 V (unless otherwise noted); typical specifications are at TA = TJ = 25°C and V+ = 3.3 V| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature error using local diode | TA = –40°C to +125°C, (1) | –2 | ±1 | +2 | °C | ||
| Temperature error using an MMBT3904 transistor remote diode(2) | TA = +25°C to +85°C TD = +60°C to +100°C |
–1.1 | +1.1 | °C | |||
| TA = +25°C to +85°C TD = –40°C to +125°C |
–1.3 | +1.3 | °C | ||||
| TA = –40°C to +85°C TD = –40°C to +125°C |
–3 | +3 | °C | ||||
| TA = –40°C to +85°C TD = 125°C to +140°C |
–3.3 | +3.3 | °C | ||||
| Local diode measurement resolution | 11 | Bits | |||||
| 0.125 | °C | ||||||
| Remote diode measurement resolution | Digital filter off | 11 | Bits | ||||
| 0.125 | °C | ||||||
| Digital filter on (Remote Diodes 1 and 2 only) | 13 | Bits | |||||
| 0.03125 | °C | ||||||
| Conversion time of all temperatures at the fastest setting(4) | All channels are enabled in default state | 1100 | 1210 | ms | |||
| 1 external channel | 31 | 34 | ms | ||||
| Local only | 30 | 33 | ms | ||||
| Quiescent current (3) | SMBus inactive, 1-Hz conversion rate, channels in default state | 570 | 800 | µA | |||
| Shutdown | 360 | µA | |||||
| D− Source voltage | 0.4 | V | |||||
| Remote diode source current | High level | 160 | 230 | µA | |||
| Low level | 10 | ||||||
| Power-On reset threshold | Measured on VDD input, falling edge | 1.6 | 2.8 | V | |||
| TCRIT1 pin temperature threshold | Default diodes 1 and 2 only | 110 | °C | ||||
| TCRIT2 pin temperature threshold | Default all channels | 85 | °C | ||||
| TCRIT3 pin temperature threshold | Default diodes 3 and 4 only | 85 | °C | ||||
(1) Local temperature accuracy does not include the effects of self-heating. The rise in temperature due to self-heating is the product of the internal power dissipation of the LM95214 and the thermal resistance. See under Recommended Operating Conditions table for the thermal resistance to be used in the self-heating calculation.
(2) The accuracy of the LM95214CISD is ensured when using a typical MMBT3904 diode-connected transistor. For further information on other thermal diodes see applications Diode Non-Ideality.
(3) Quiescent current will not increase substantially with an SMBus communication.
(4) This specification is provided only to indicate how often temperature data is updated. The LM95214 can be read at any time without regard to conversion state (and will yield last conversion result).
6.6 Logic Electrical Characteristics: Digital DC Characteristics
Unless otherwise noted all limits are specified for VDD = +3 Vdc to 3.6 Vdc, TA= TJ = +25°C.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMBDAT, SMBCLK INPUTS | |||||||
| VIN(1) | Logical 1 input voltage | 2.1 | V | ||||
| VIN(0) | Logical 0 input voltage | 0.8 | V | ||||
| VIN(HYST) | SMBDAT and SMBCLK digital input hysteresis | 400 | mV | ||||
| IIN(1) | Logical 1 input current | VIN = VDD | 0.005 | 10 | µA | ||
| IIN(0) | Logical 0 input current | VIN = 0 V | −0.005 | –10 | µA | ||
| CIN | Input capacitance | 5 | pF | ||||
| A0 DIGITAL INPUT | |||||||
| VIH | Input high voltage | 0.90 × VDD | V | ||||
| VIM | Input middle voltage | 0.43 × VDD | 0.57 × VDD | V | |||
| V | |||||||
| VIL | Input low voltage | 0.10 × VDD | V | ||||
| IIN(1) | Logical 1 input current | VIN = VDD | VIN = VDD | –0.005 | –10 | µA | |
| IIN(0) | Logical 0 input current | VIN = 0 V | VIN = 0 V | 0.005 | 10 | µA | |
| CIN | Input capacitance | 5 | pF | ||||
| SMBDAT, TCRIT1, TCRIT2, TCRIT3 DIGITAL OUTPUTS | |||||||
| IOH | High level output current | VOH = VDD | 10 | µA | |||
| VOL(SMBDAT) | SMBus low level output voltage | IOL = 4 mA | 0.4 | V | |||
| IOL = 6 mA | 0.6 | V | |||||
| VOL(TCRIT) | TCRIT1, TCRIT2, TCRIT3 low level output voltage | IOL = 6 mA | 0.4 | V | |||
| COUT | Digital output capacitance | 5 | pF | ||||
6.7 Switching Characteristics: SMBus Digital
Unless otherwise noted, these specifications apply for VDD=+3.0 Vdc to +3.6 Vdc, CL (load capacitance) on output lines = 80 pF, TA = TJ = +25°C.
The switching characteristics of the LM95214 fully meet or exceed the published specifications of the SMBus version 2.0. The following parameters are the timing relationships between SMBCLK and SMBDAT signals related to the LM95214. They adhere to but are not necessarily the SMBus bus specifications.
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fSMB | SMBus clock frequency | 10 | 100 | kHz | |||
| tLOW | SMBus clock low time | from VIN(0)max to VIN(0)max | 4.7 | µs | |||
| 25 | ms | ||||||
| tHIGH | SMBus clock high time | from VIN(1)min to VIN(1)min | 4.0 | µs | |||
| tR,SMB | SMBus rise time | See (1) | 1 | µs | |||
| tF,SMB | SMBus fall time | See (2) | 0.3 | µs | |||
| tOF | Output fall time | CL = 400 pF, IO = 3 mA(2) |
250 | ns | |||
| tTIMEOUT | SMBDAT and SMBCLK time low for reset of serial interface | 25 | 35 | ms | |||
| tSU;DAT | Data in setup time to SMBCLK high | 250 | ns | ||||
| tHD;DAT | Data out stable after SMBCLK low | 300 | 1075 | ns | |||
| tHD;STA | Start condition SMBDAT low to SMBCLK low (Start condition hold before the first clock falling edge) | 100 | ns | ||||
| tSU;STO | Stop condition SMBCLK high to SMBDAT low (Stop condition setup) | 100 | ns | ||||
| tSU;STA | SMBus repeated start-condition setup time, SMBCLK high to SMBDAT low | 0.6 | µs | ||||
| tBUF | SMBus free time between stop and start conditions | 1.3 | µs | ||||
(1) The output rise time is measured from (VIN(0)max − 0.15 V) to (VIN(1)min + 0.15 V).
(2) The output fall time is measured from (VIN(1)min + 0.15 V) to (VIN(0)max − 0.15 V).
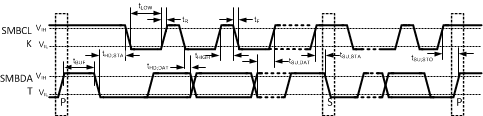 Figure 1. SMBus Communication
Figure 1. SMBus Communication
6.8 Typical Characteristics
 Figure 2. Conversion Rate Effect on Average Power Supply Current
Figure 2. Conversion Rate Effect on Average Power Supply Current
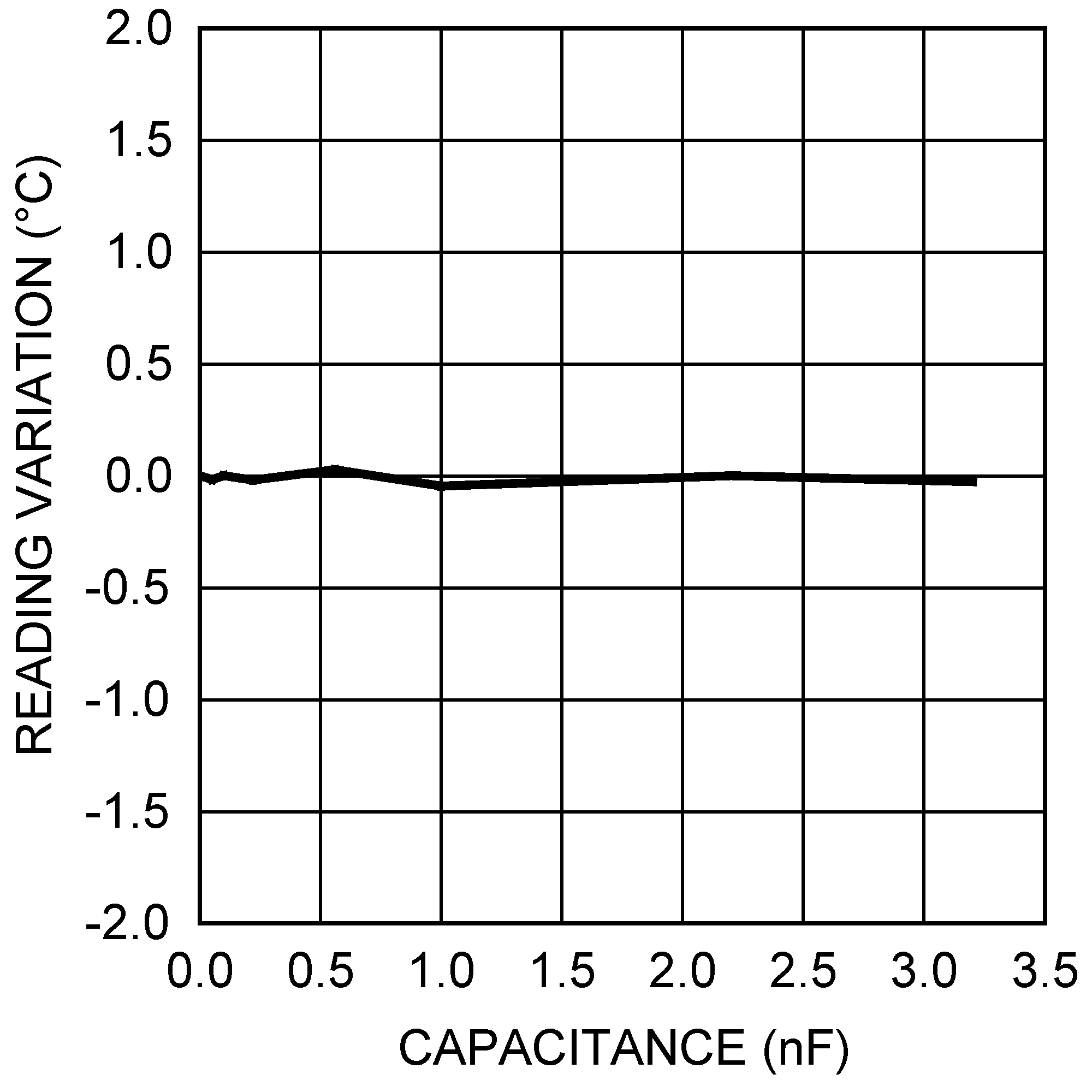 Figure 4. Remote Temperature Reading Sensitivity to Thermal Diode Filter Capacitance
Figure 4. Remote Temperature Reading Sensitivity to Thermal Diode Filter Capacitance
 Figure 6. Remote 1 Temperature Error, TA = TD
Figure 6. Remote 1 Temperature Error, TA = TD
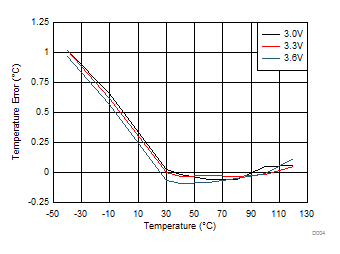 Figure 8. Remote 3 Temperature Error, TA = TD
Figure 8. Remote 3 Temperature Error, TA = TD
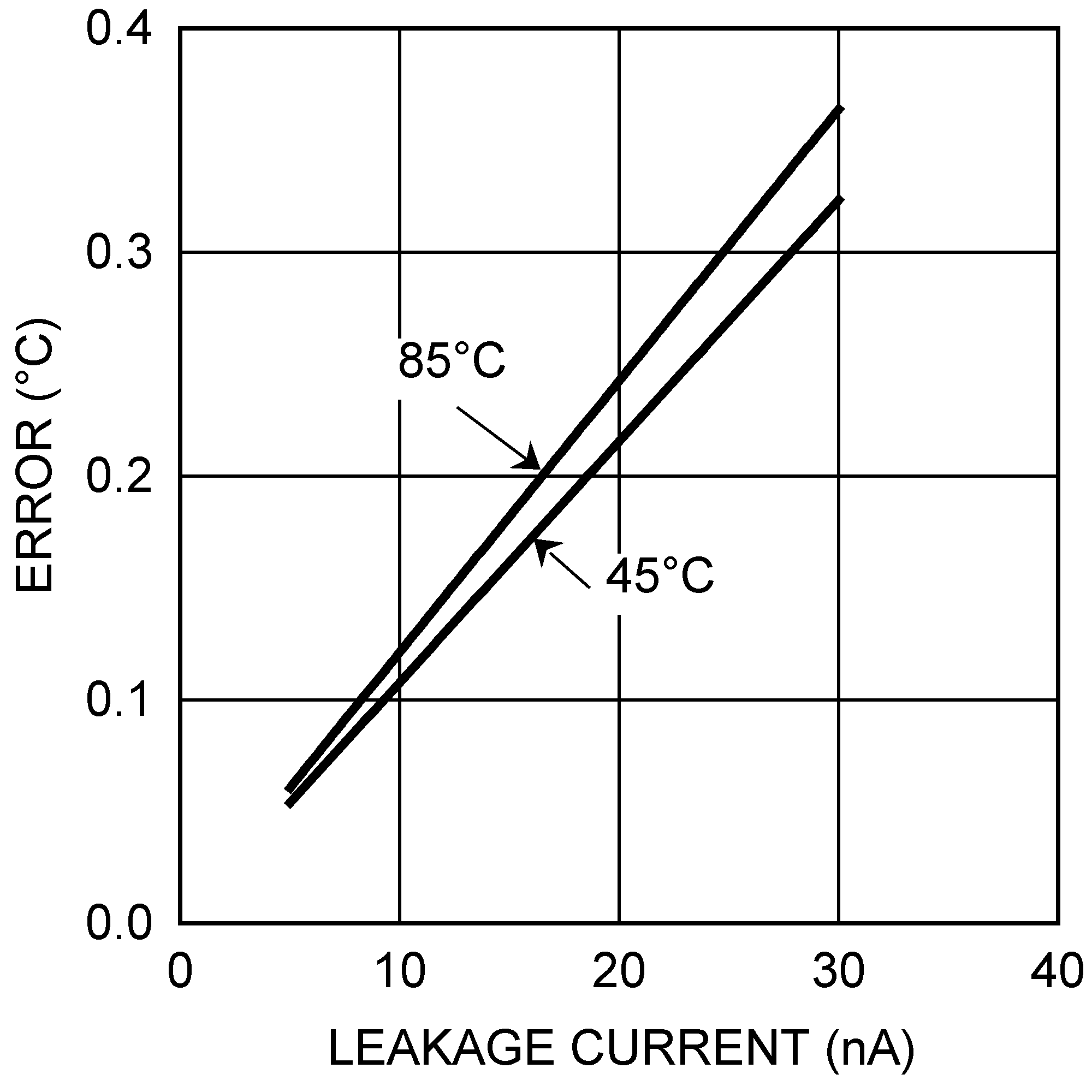 Figure 3. Thermal Diode Capacitor or PCB Leakage Current Effect on Remote Diode Temperature Reading
Figure 3. Thermal Diode Capacitor or PCB Leakage Current Effect on Remote Diode Temperature Reading
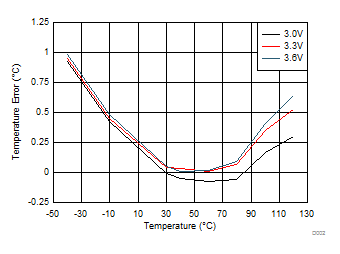 Figure 5. Local Temperature Error, TA = TD
Figure 5. Local Temperature Error, TA = TD
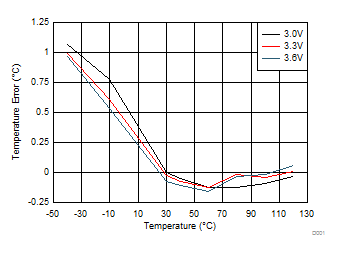 Figure 7. Remote 2 Temperature Error, TA = TD
Figure 7. Remote 2 Temperature Error, TA = TD
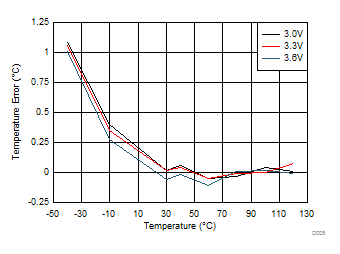 Figure 9. Remote 4 Temperature Error, TA = TD
Figure 9. Remote 4 Temperature Error, TA = TD