SNOS724F August 2000 – February 2024 LMC6492 , LMC6494
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1Features
- 2Applications
- 3Description
- 4Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5Specifications
- 6Application and Implementation
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Revision History
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5.6 Typical Characteristics
at VS = +15V, single supply, and TA = 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
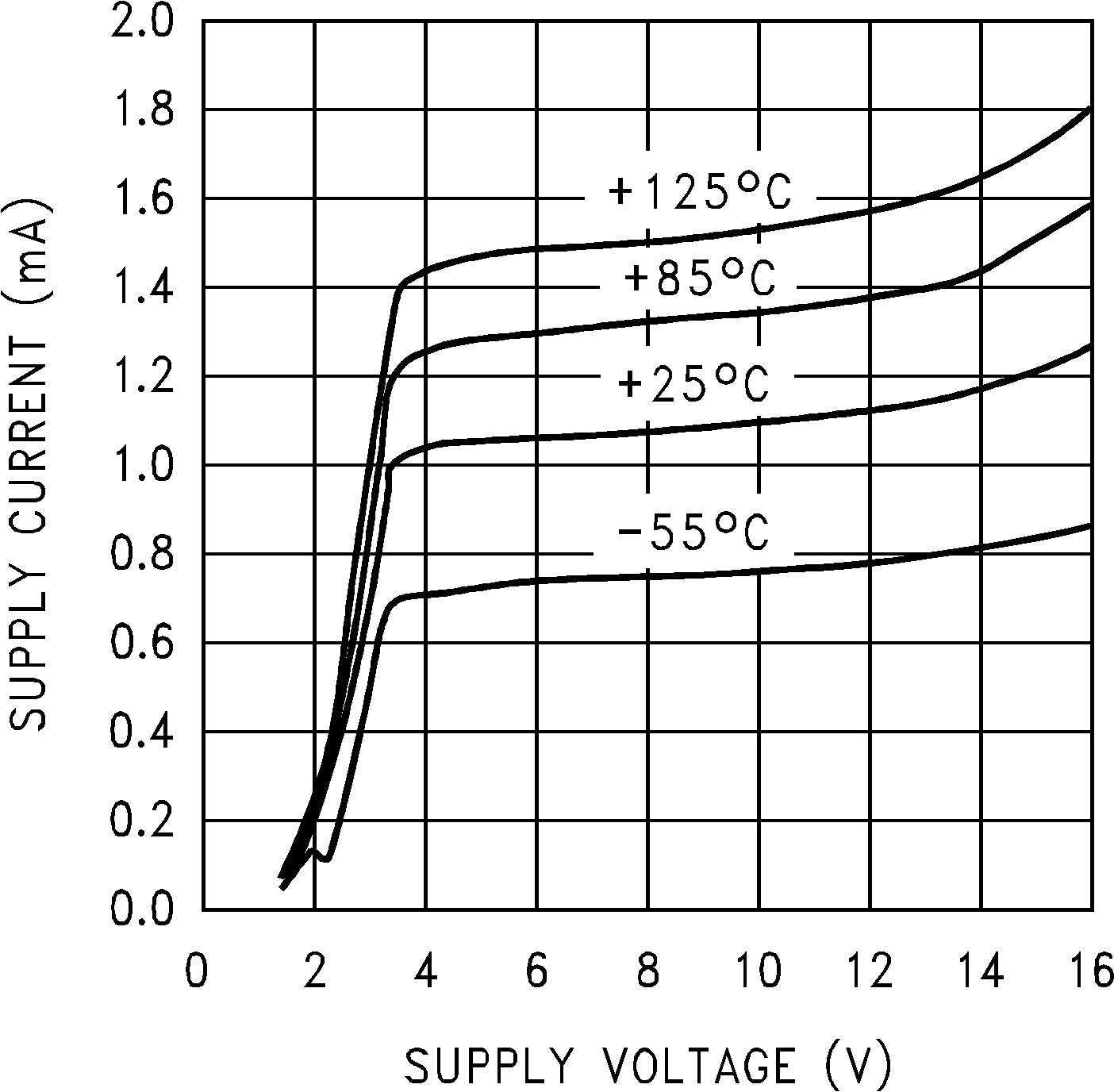 Figure 5-1 Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 5-1 Supply Current vs Supply Voltage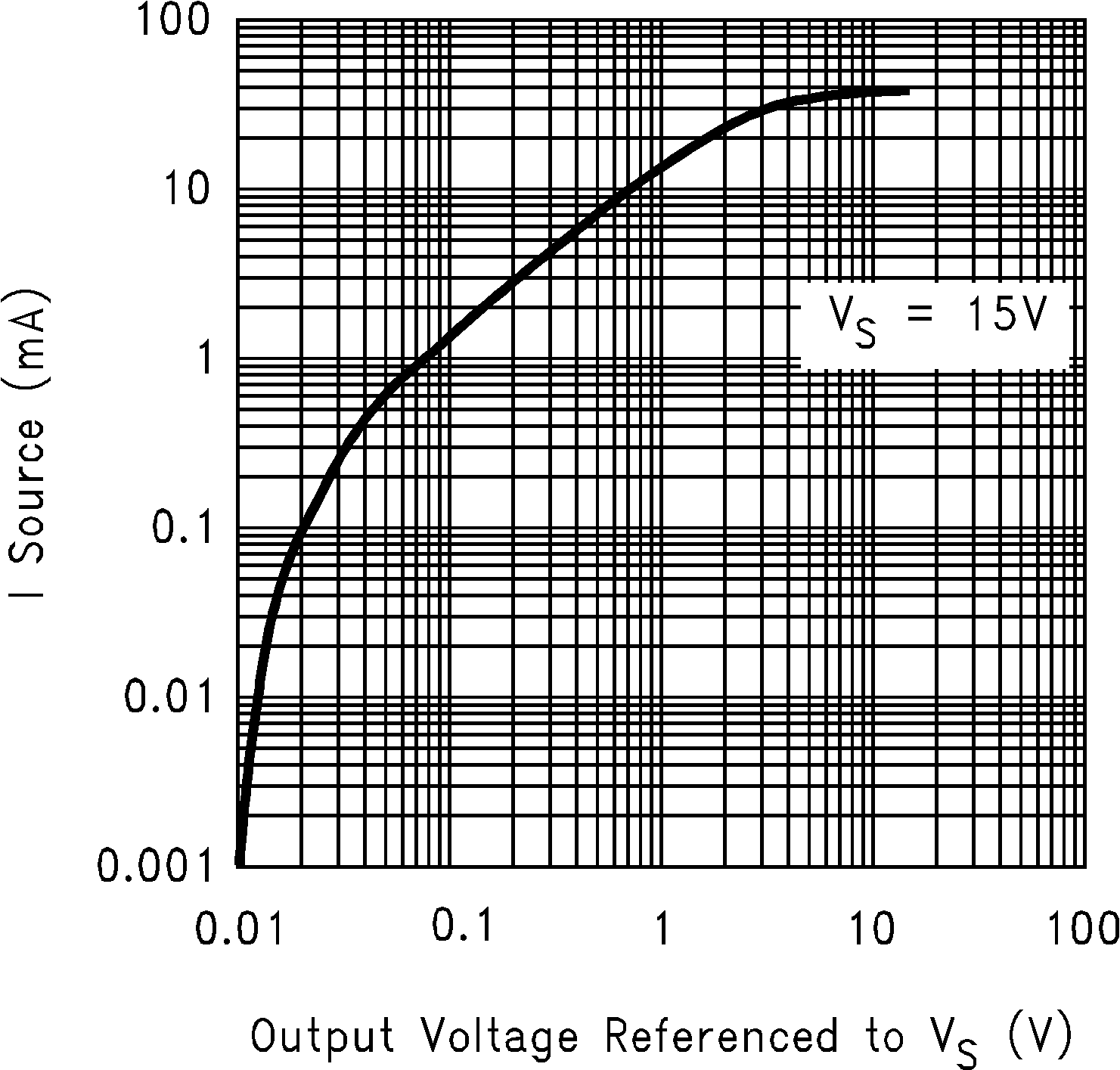 Figure 5-3 Sourcing Current vs Output Voltage
Figure 5-3 Sourcing Current vs Output Voltage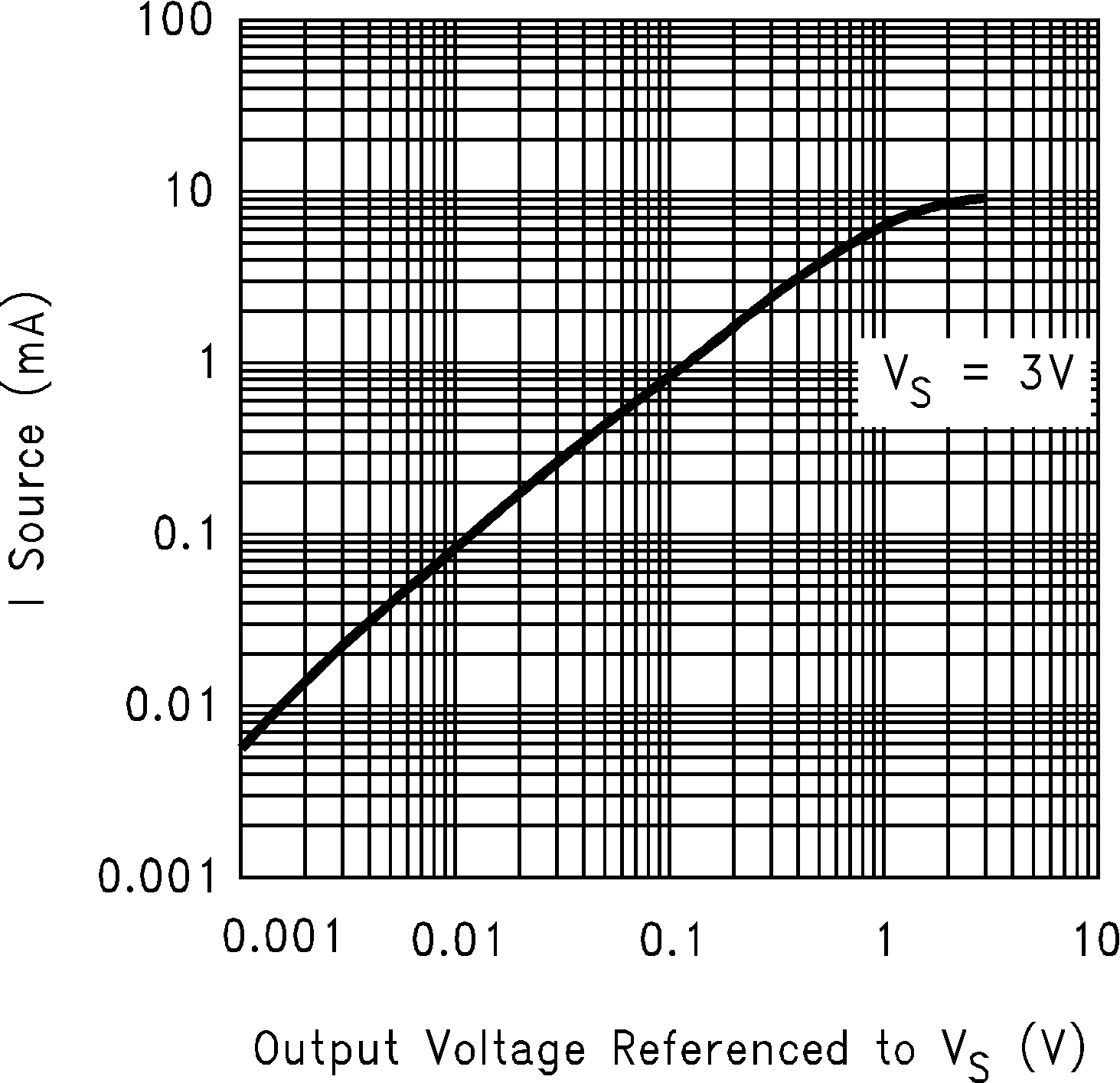 Figure 5-5 Sourcing Current vs Output Voltage
Figure 5-5 Sourcing Current vs Output Voltage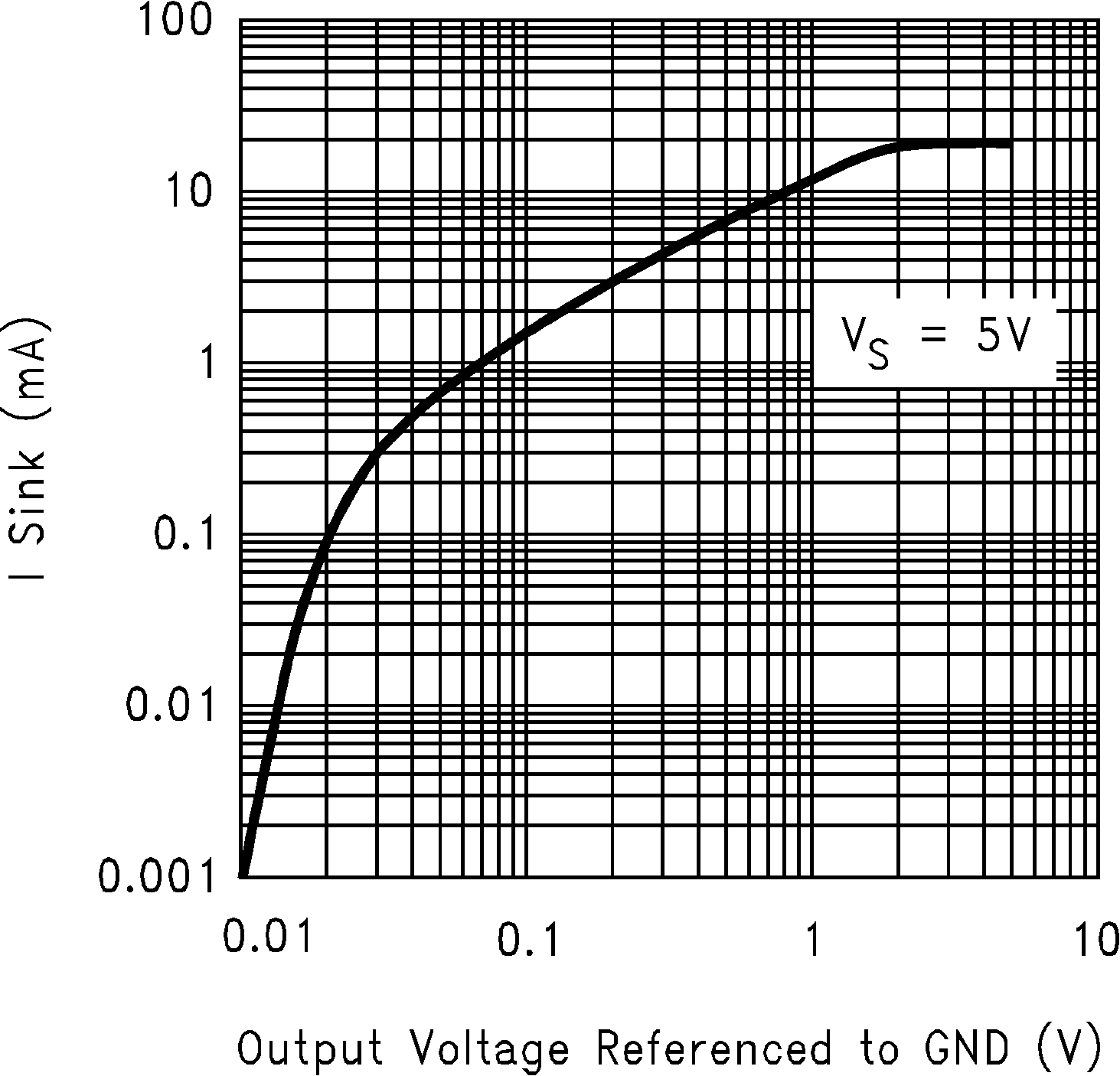 Figure 5-7 Sinking Current vs Output Voltage
Figure 5-7 Sinking Current vs Output Voltage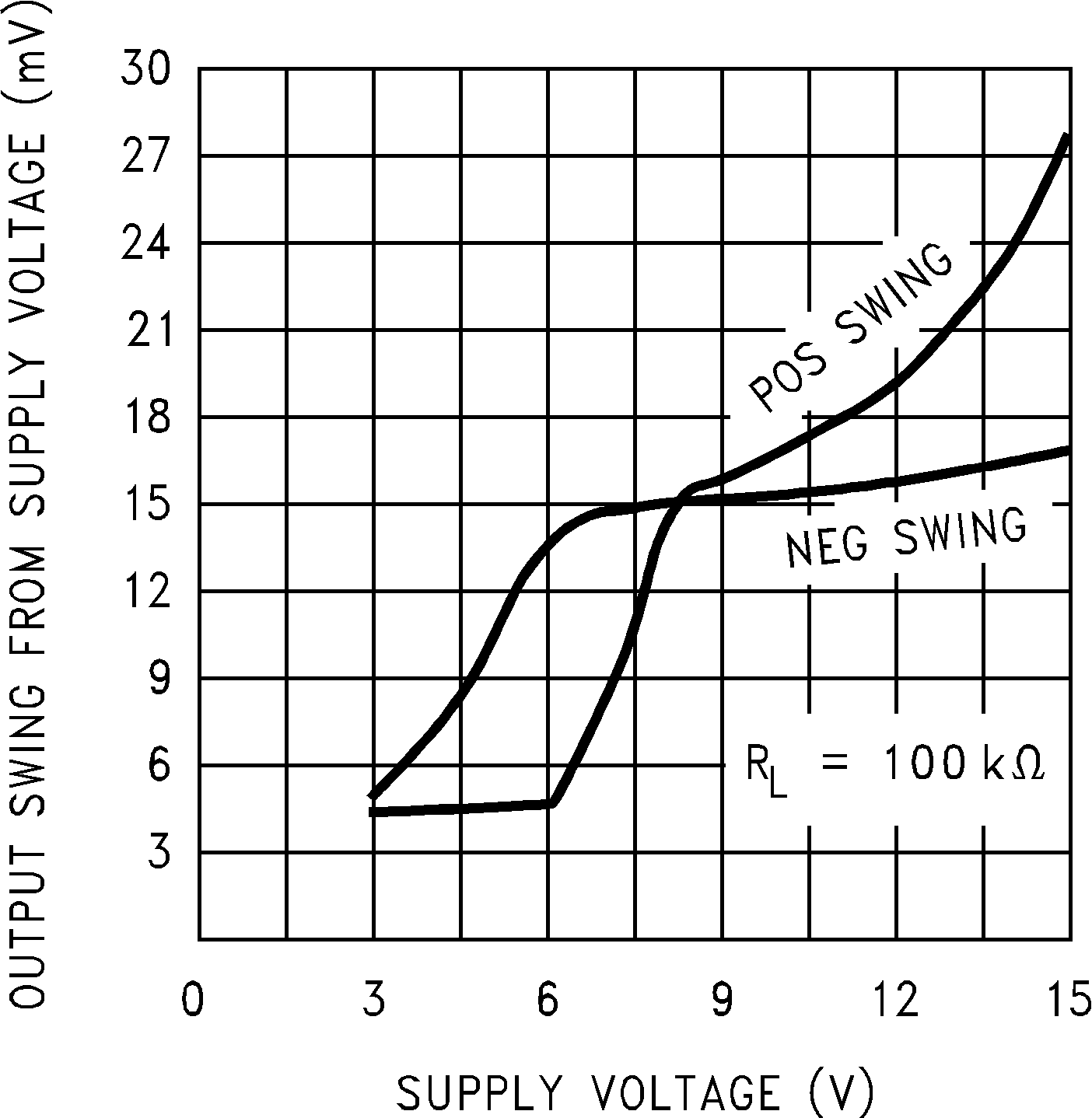 Figure 5-9 Output Voltage Swing vs Supply Voltage
Figure 5-9 Output Voltage Swing vs Supply Voltage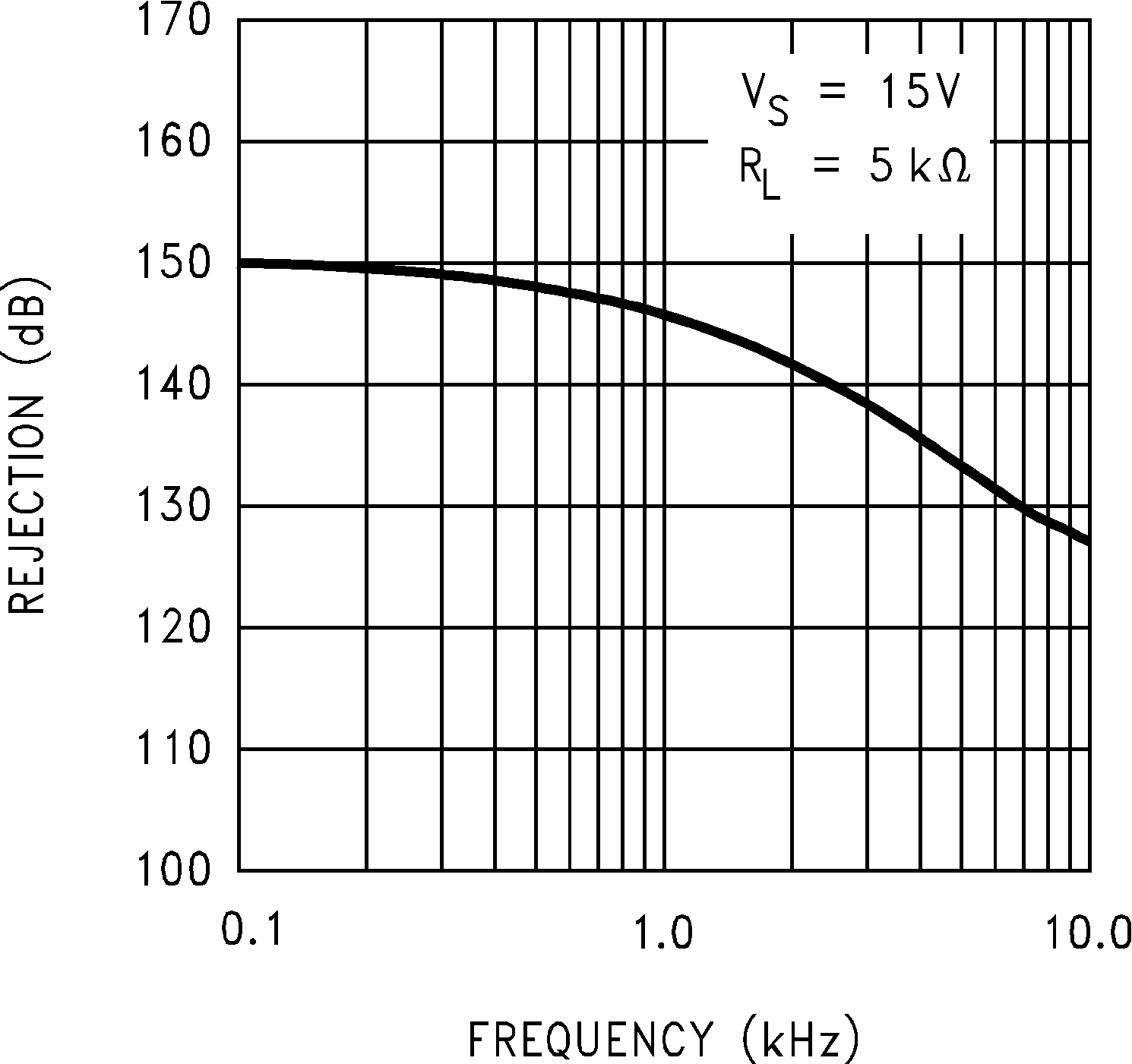 Figure 5-11 Crosstalk Rejection vs Frequency
Figure 5-11 Crosstalk Rejection vs Frequency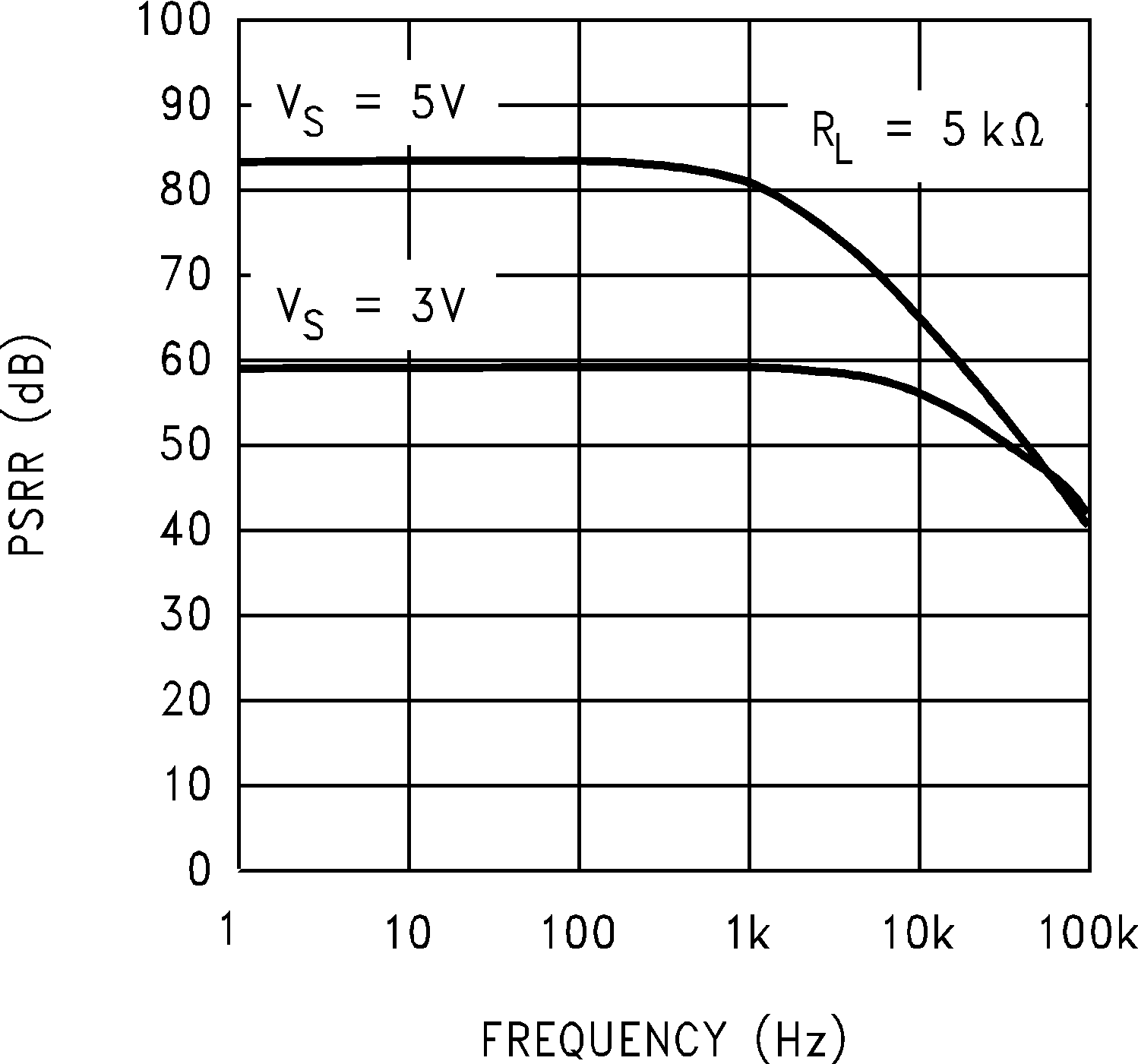 Figure 5-13 Positive PSRR vs Frequency
Figure 5-13 Positive PSRR vs Frequency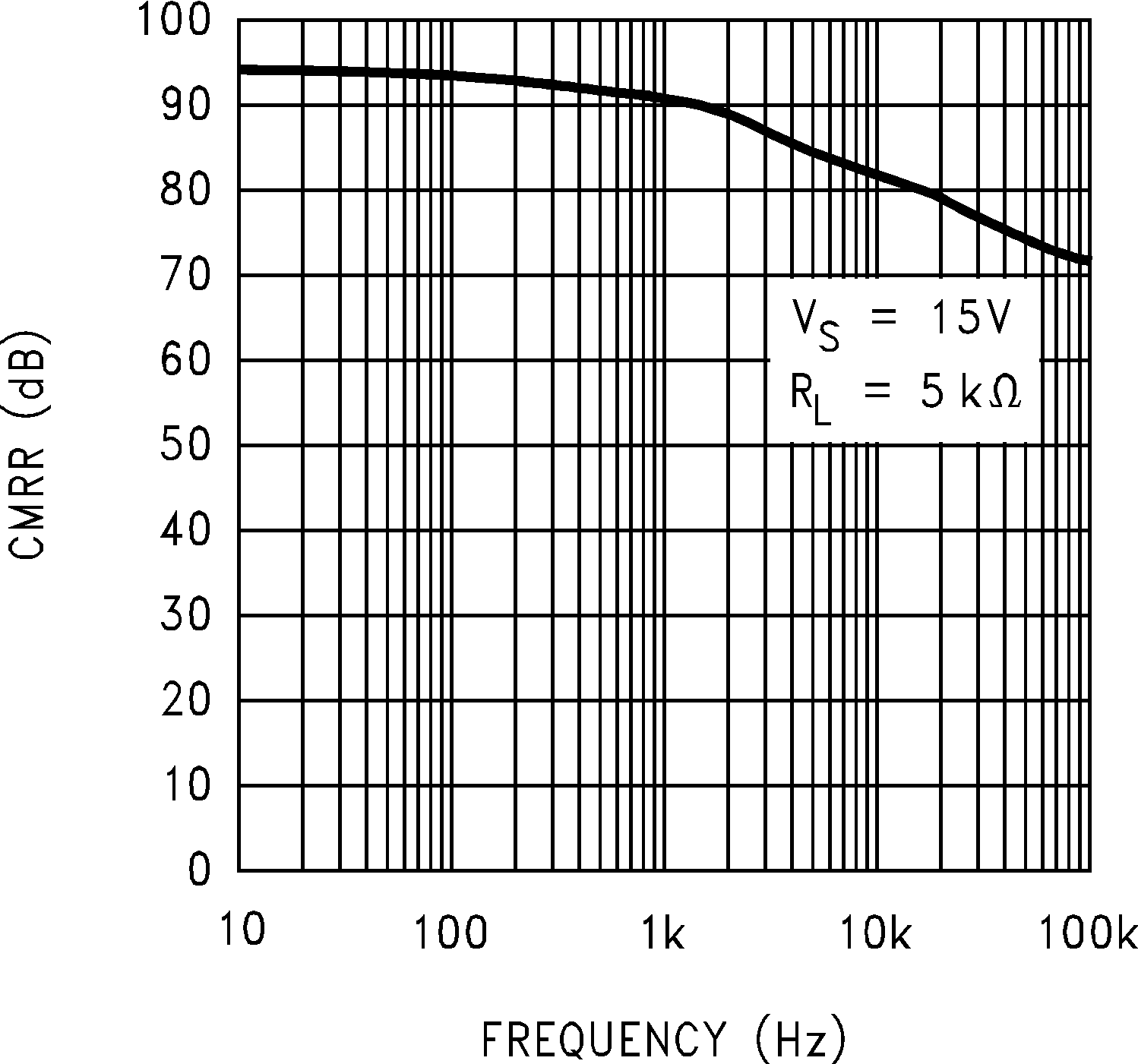 Figure 5-15 CMRR vs Frequency
Figure 5-15 CMRR vs Frequency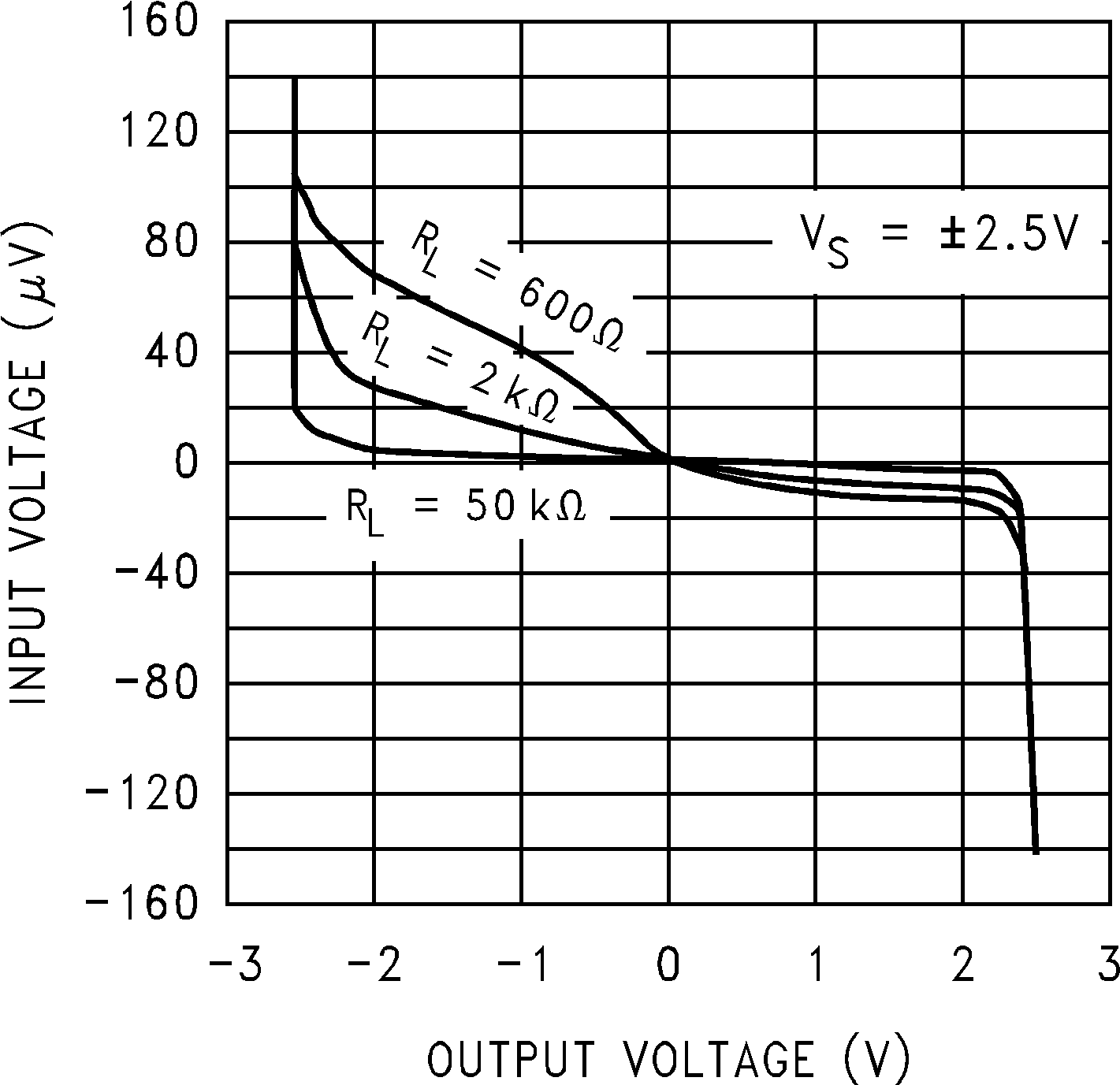 Figure 5-17 Input Voltage vs Output Voltage
Figure 5-17 Input Voltage vs Output Voltage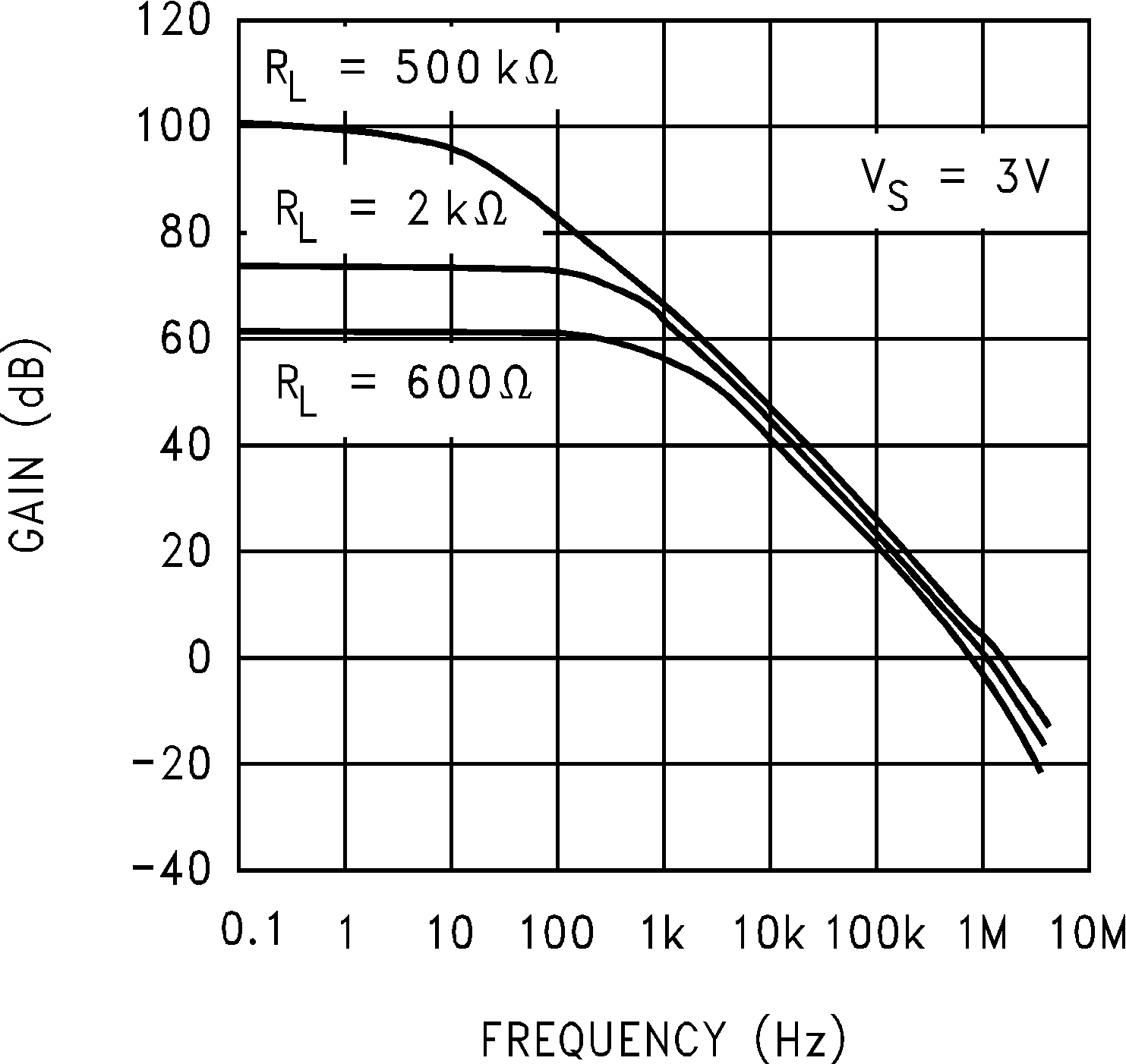 Figure 5-19 Open Loop Frequency Response
Figure 5-19 Open Loop Frequency Response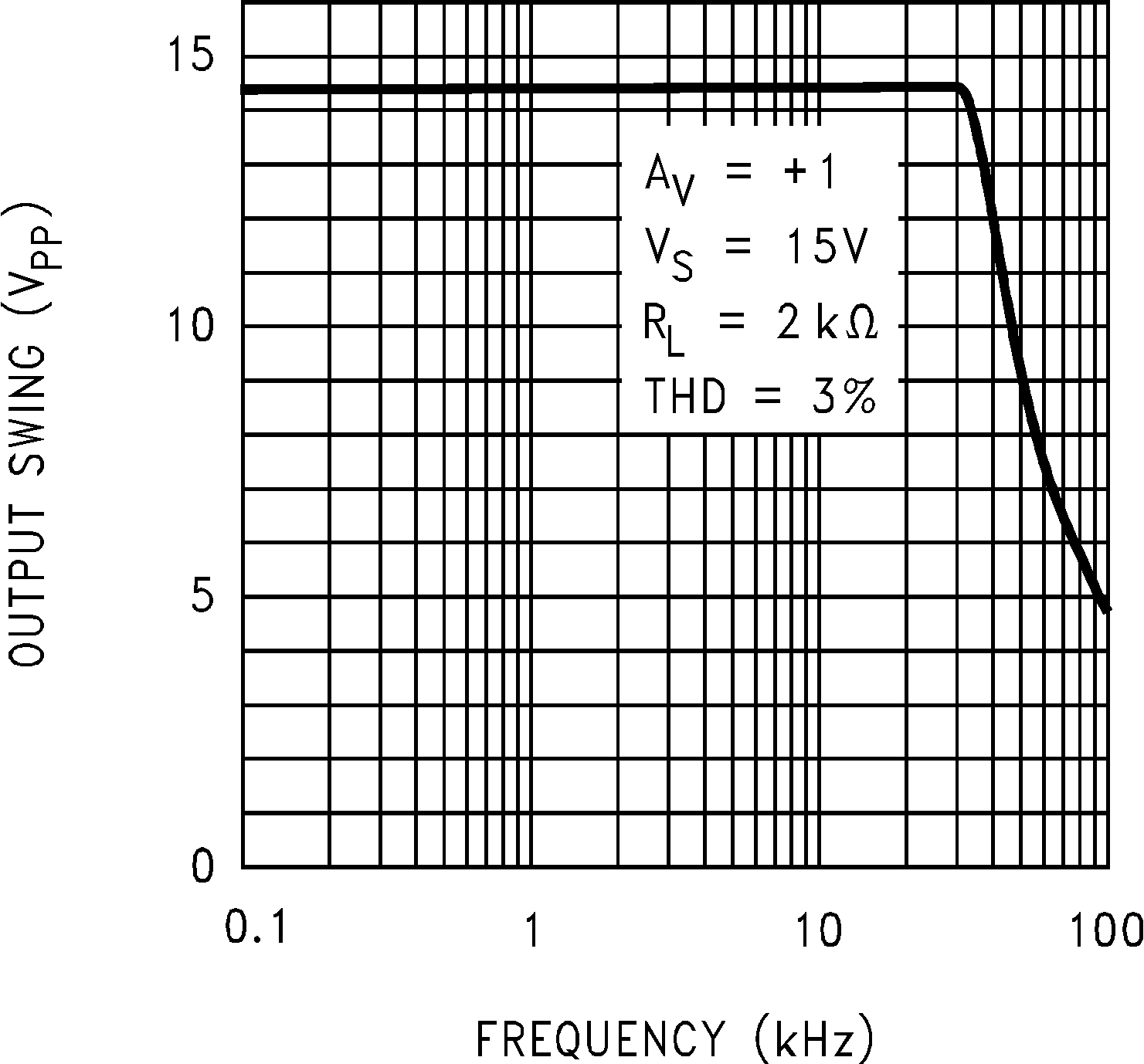 Figure 5-21 Maximum Output Swing vs Frequency
Figure 5-21 Maximum Output Swing vs Frequency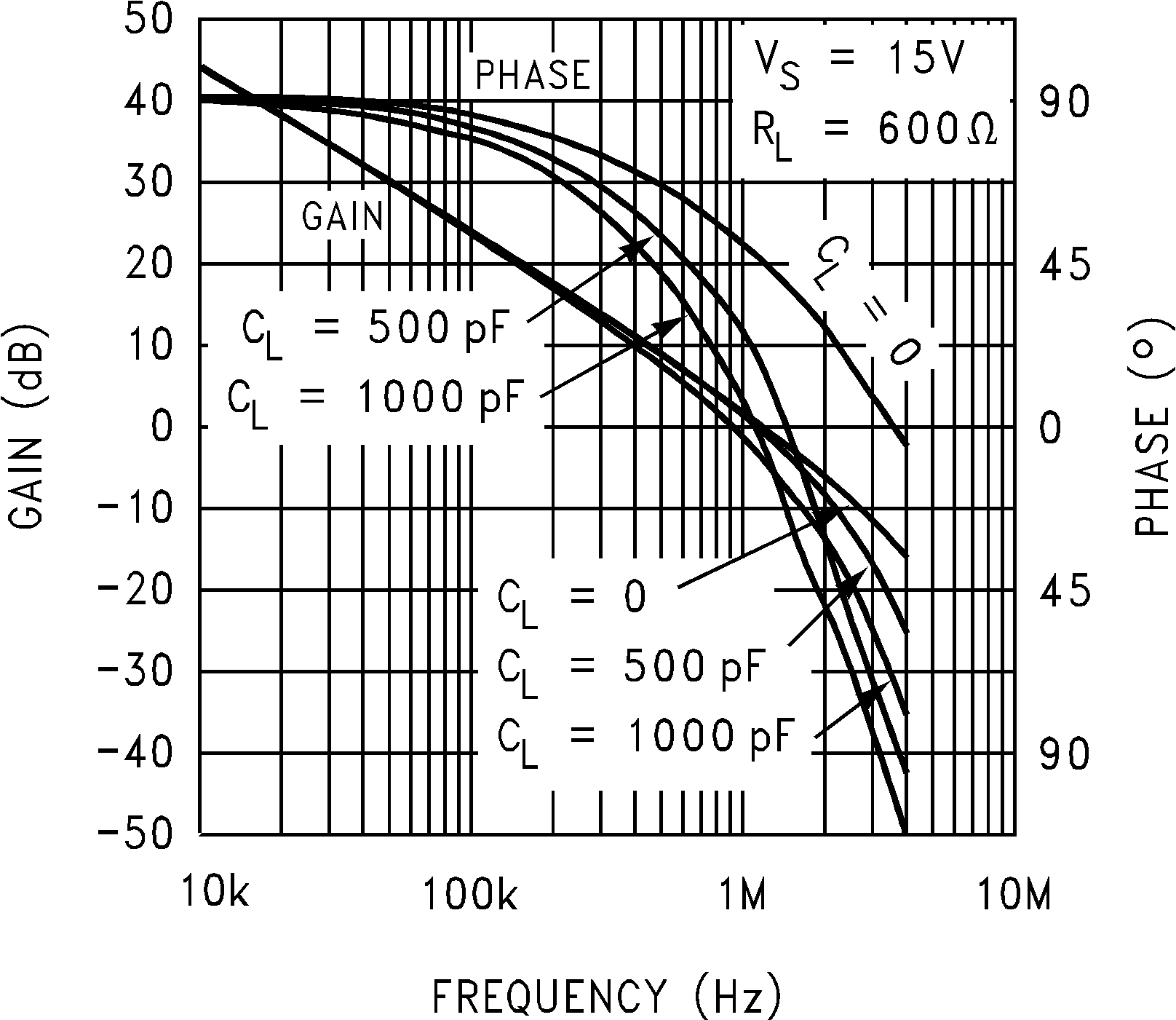 Figure 5-23 Gain and Phase vs Capacitive Load
Figure 5-23 Gain and Phase vs Capacitive Load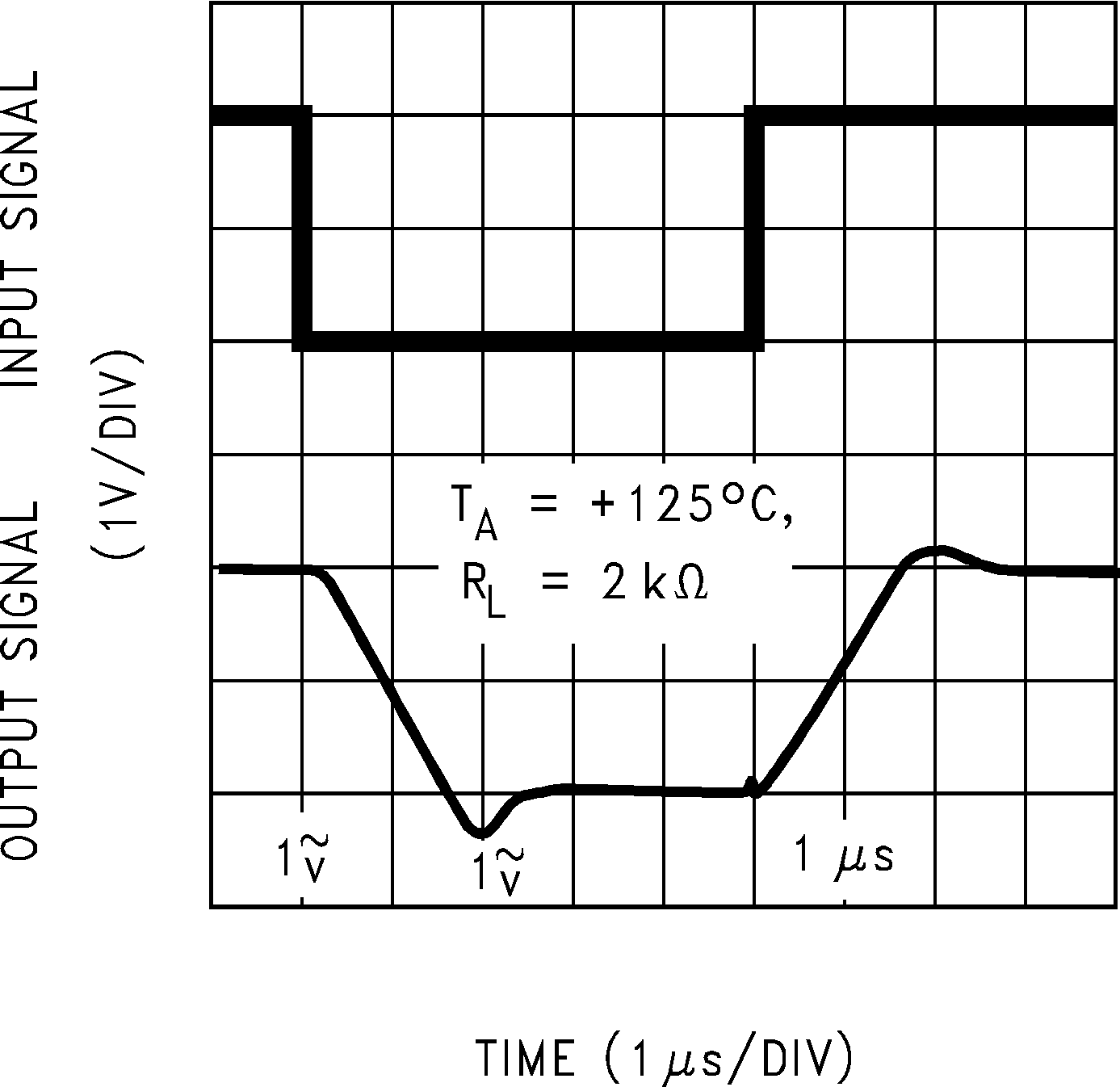 Figure 5-25 Non-Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response
Figure 5-25 Non-Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response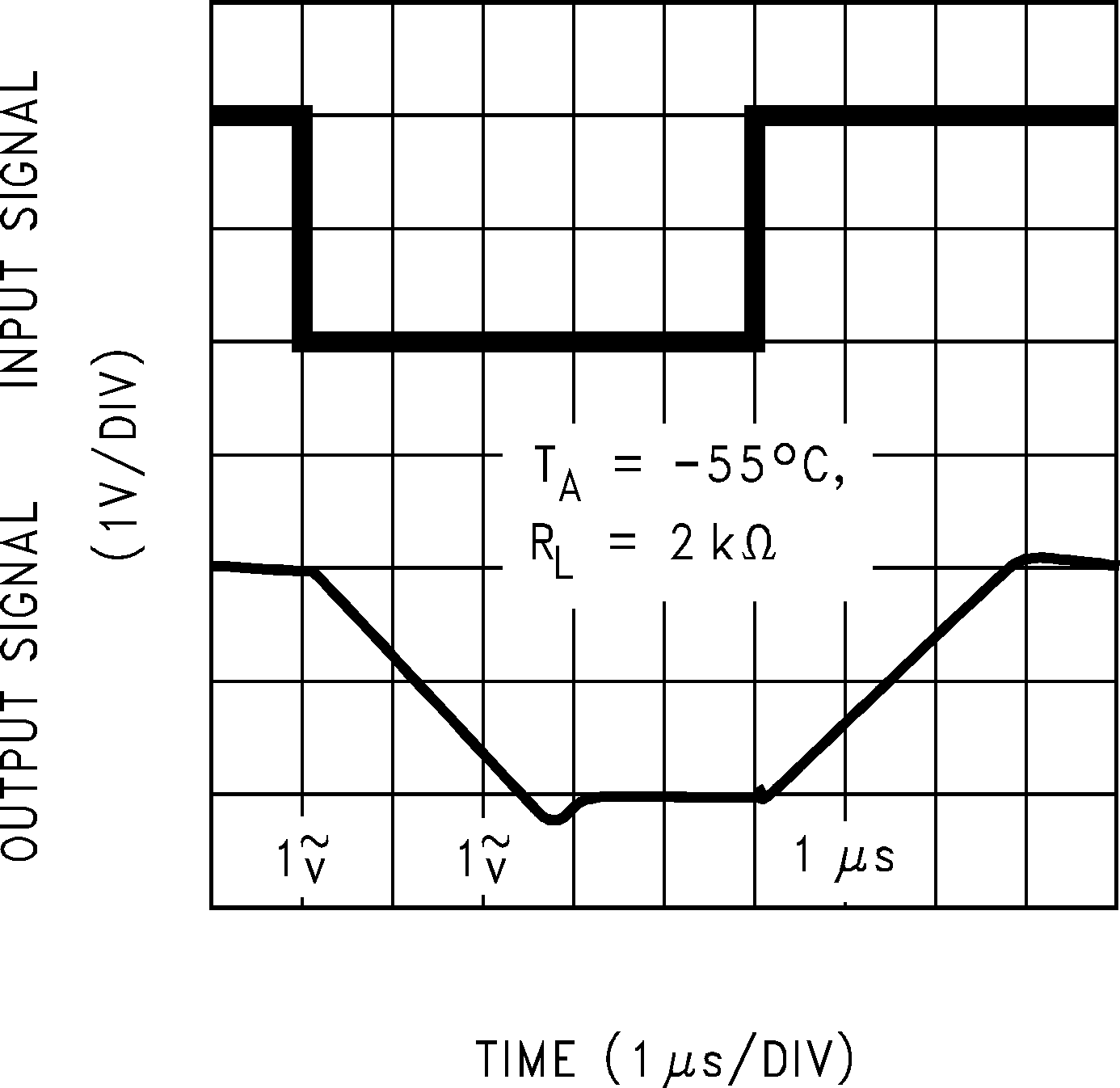 Figure 5-27 Non-Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response
Figure 5-27 Non-Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response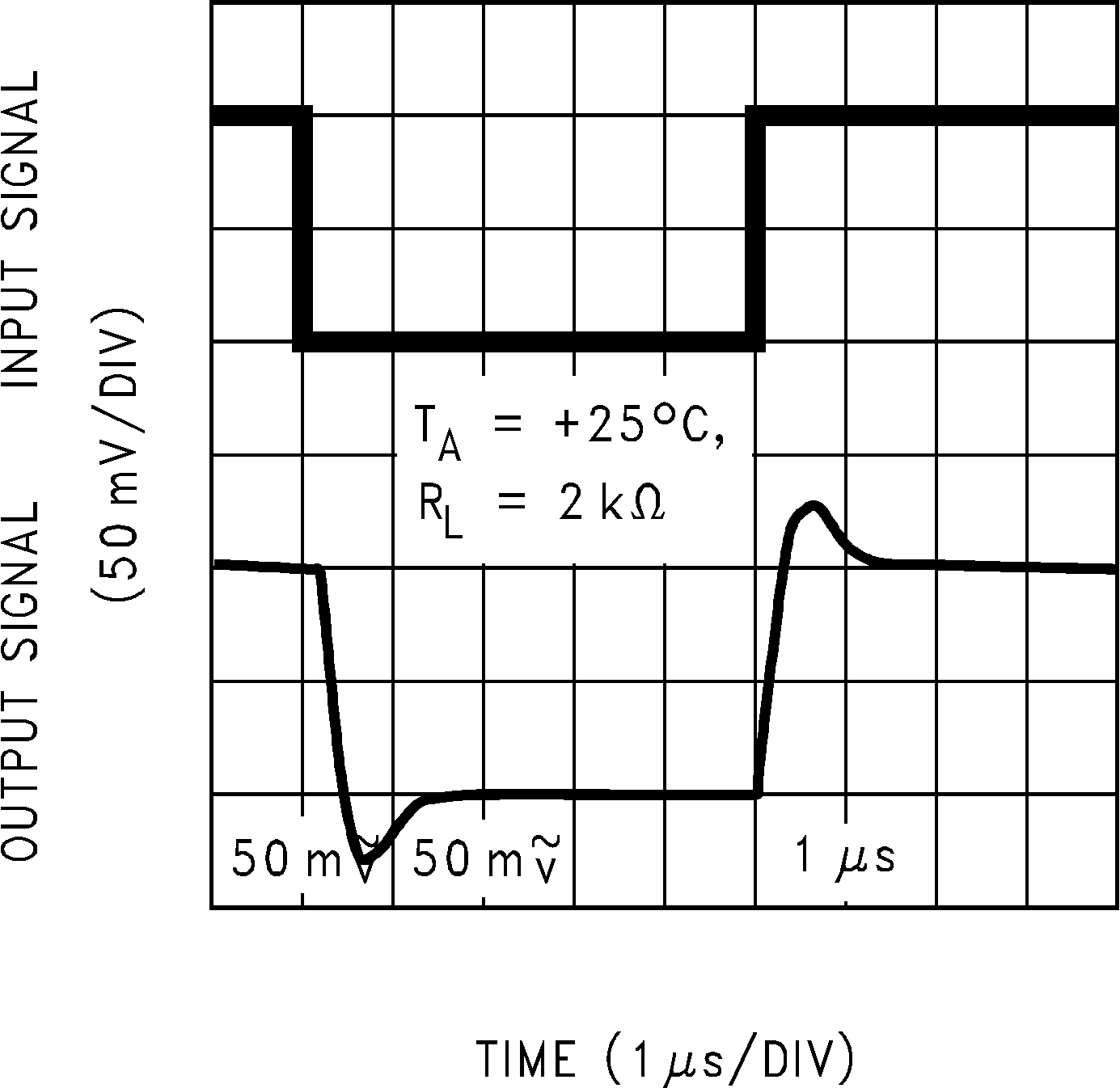 Figure 5-29 Non-Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response
Figure 5-29 Non-Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response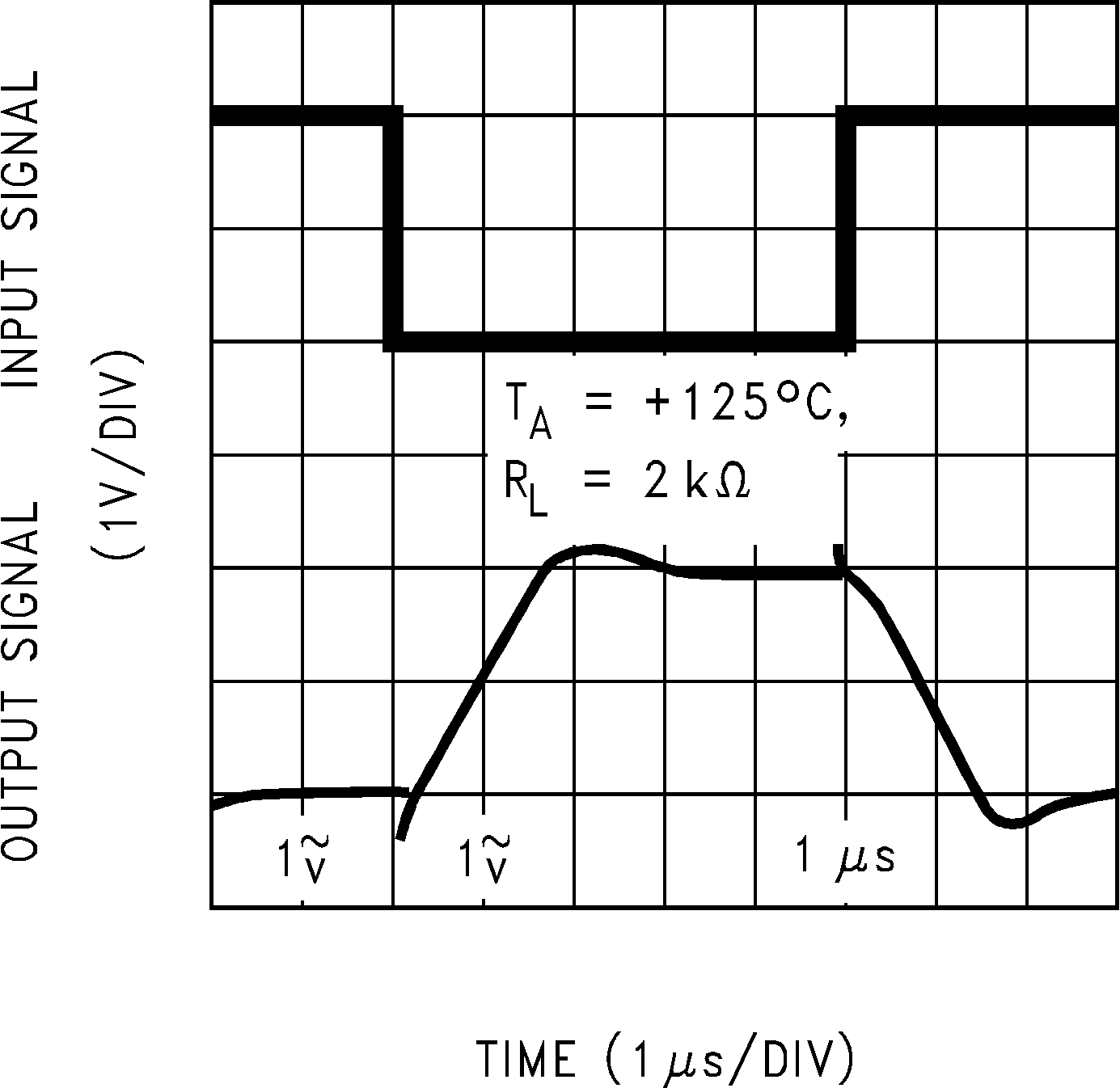 Figure 5-31 Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response
Figure 5-31 Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response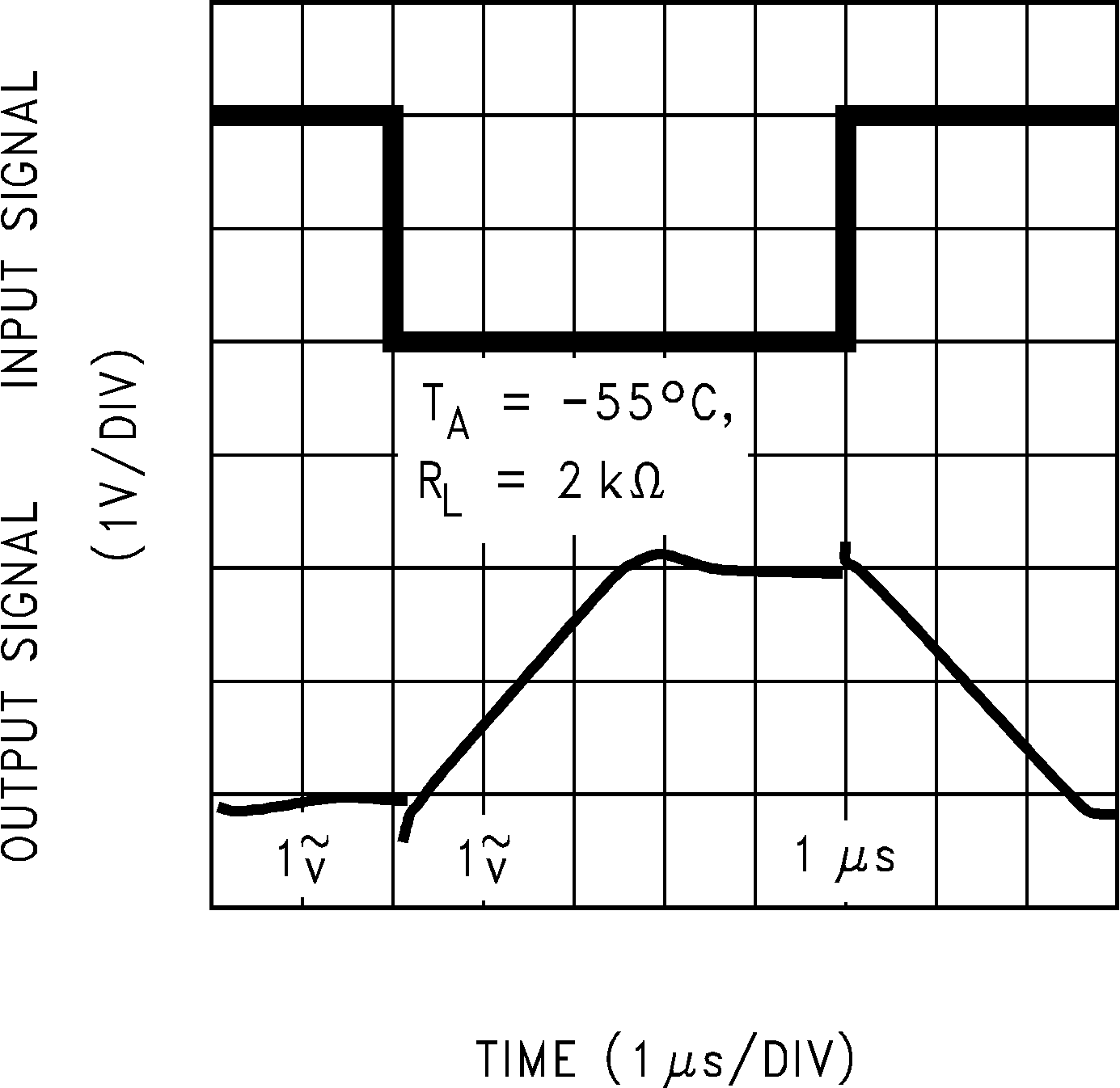 Figure 5-33 Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response
Figure 5-33 Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response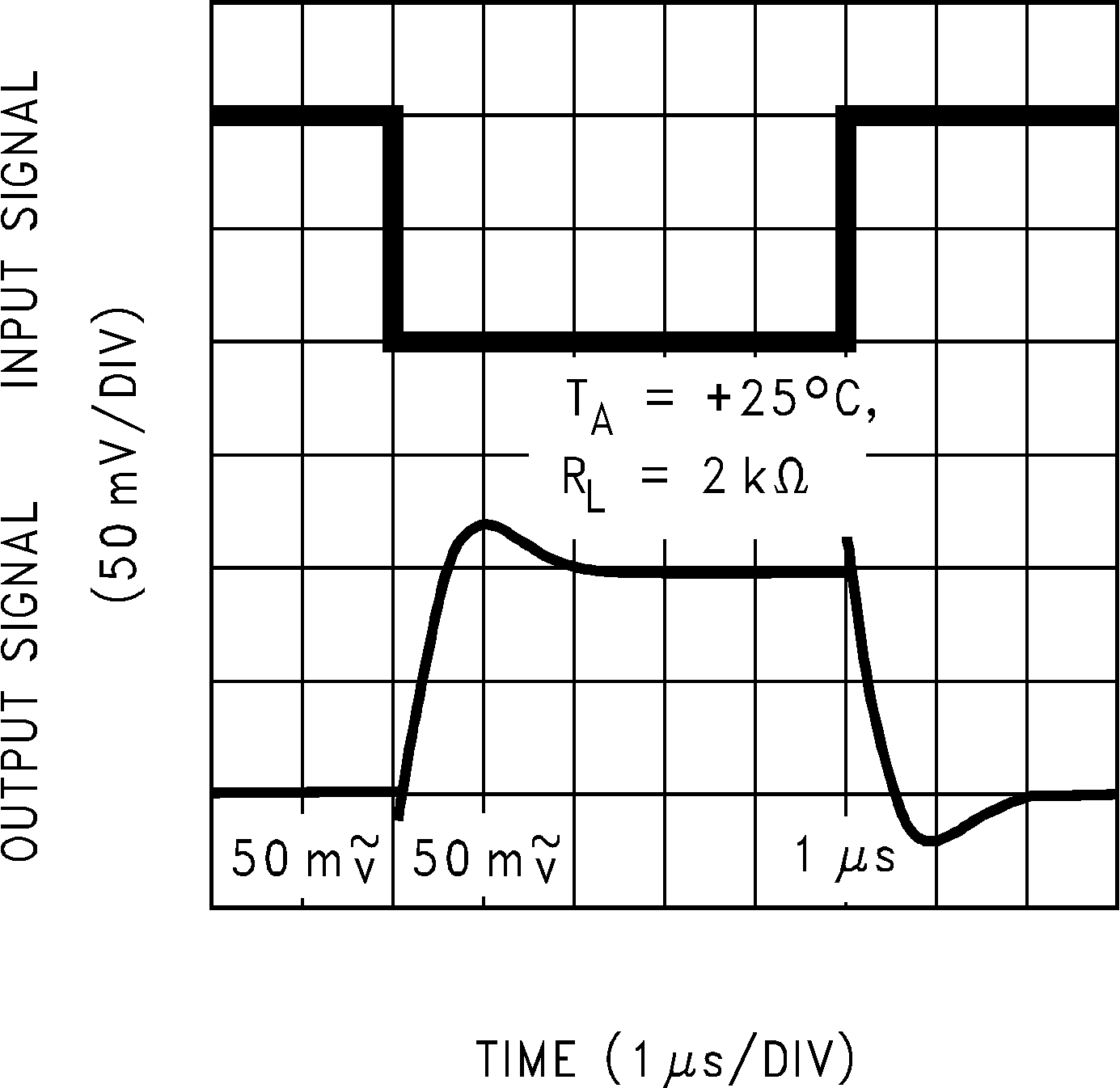 Figure 5-35 Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response
Figure 5-35 Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response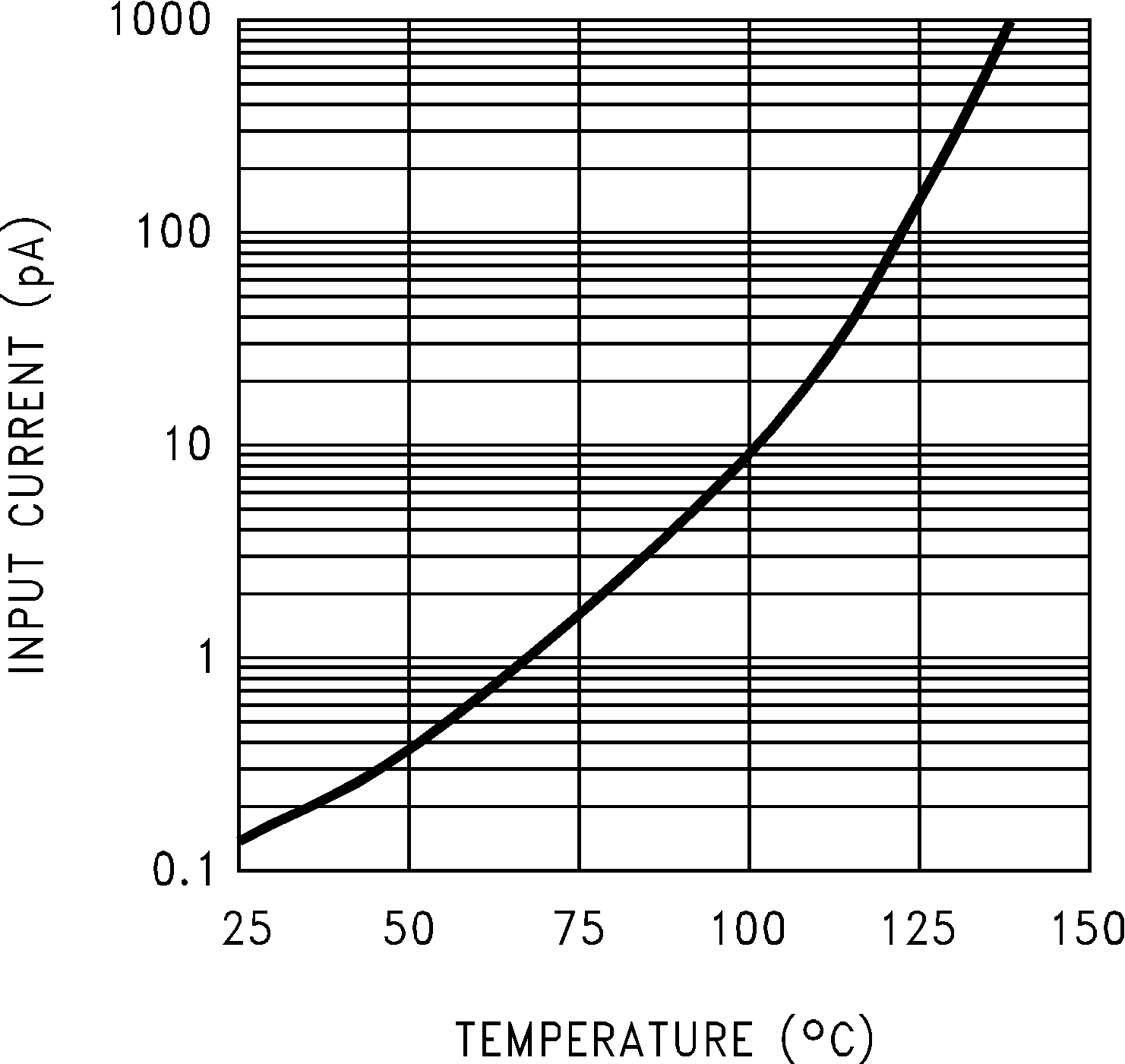 Figure 5-2 Input Current vs Temperature
Figure 5-2 Input Current vs Temperature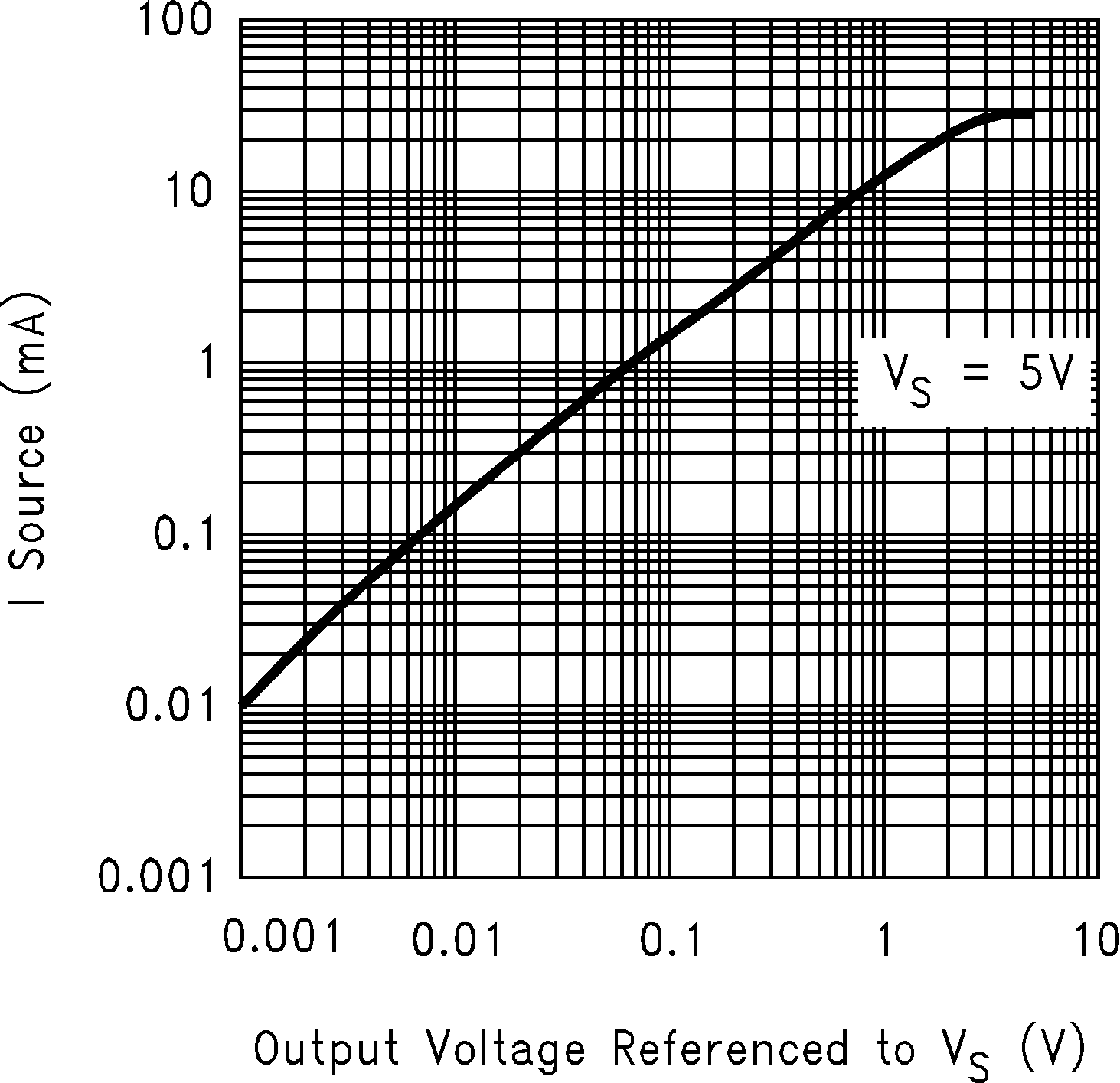 Figure 5-4 Sourcing Current vs Output Voltage
Figure 5-4 Sourcing Current vs Output Voltage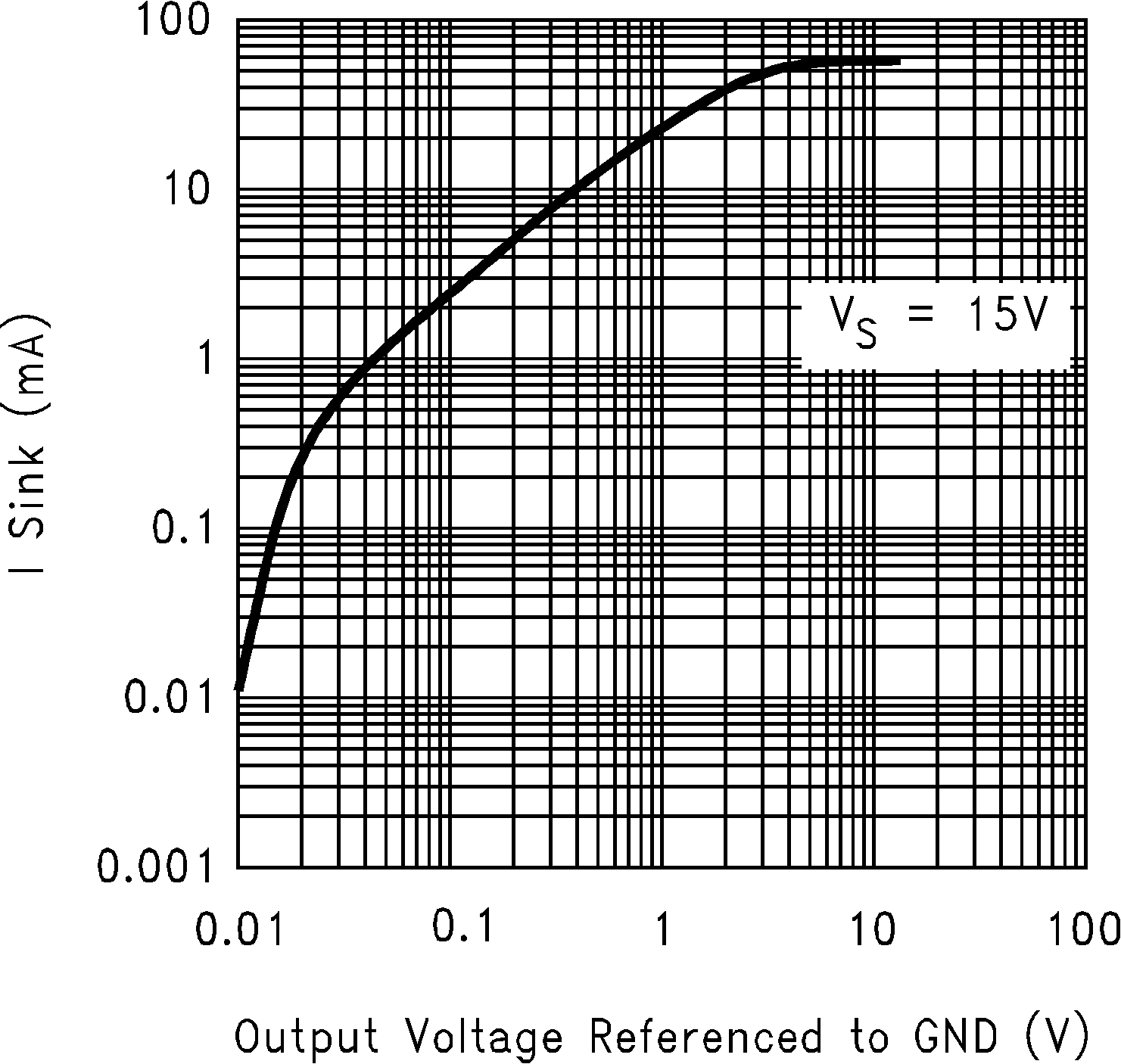 Figure 5-6 Sinking Current vs Output Voltage
Figure 5-6 Sinking Current vs Output Voltage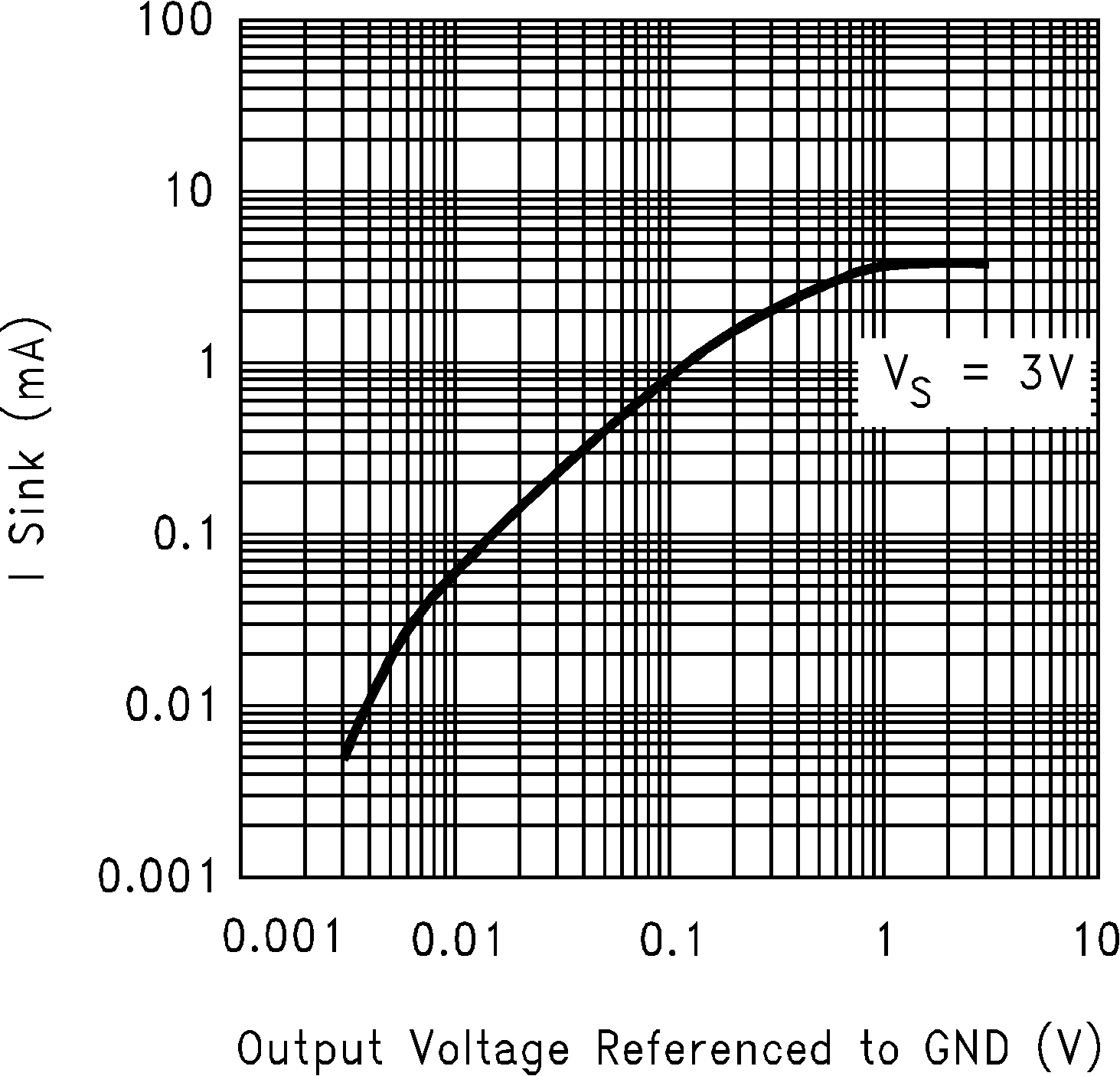 Figure 5-8 Sinking Current vs Output Voltage
Figure 5-8 Sinking Current vs Output Voltage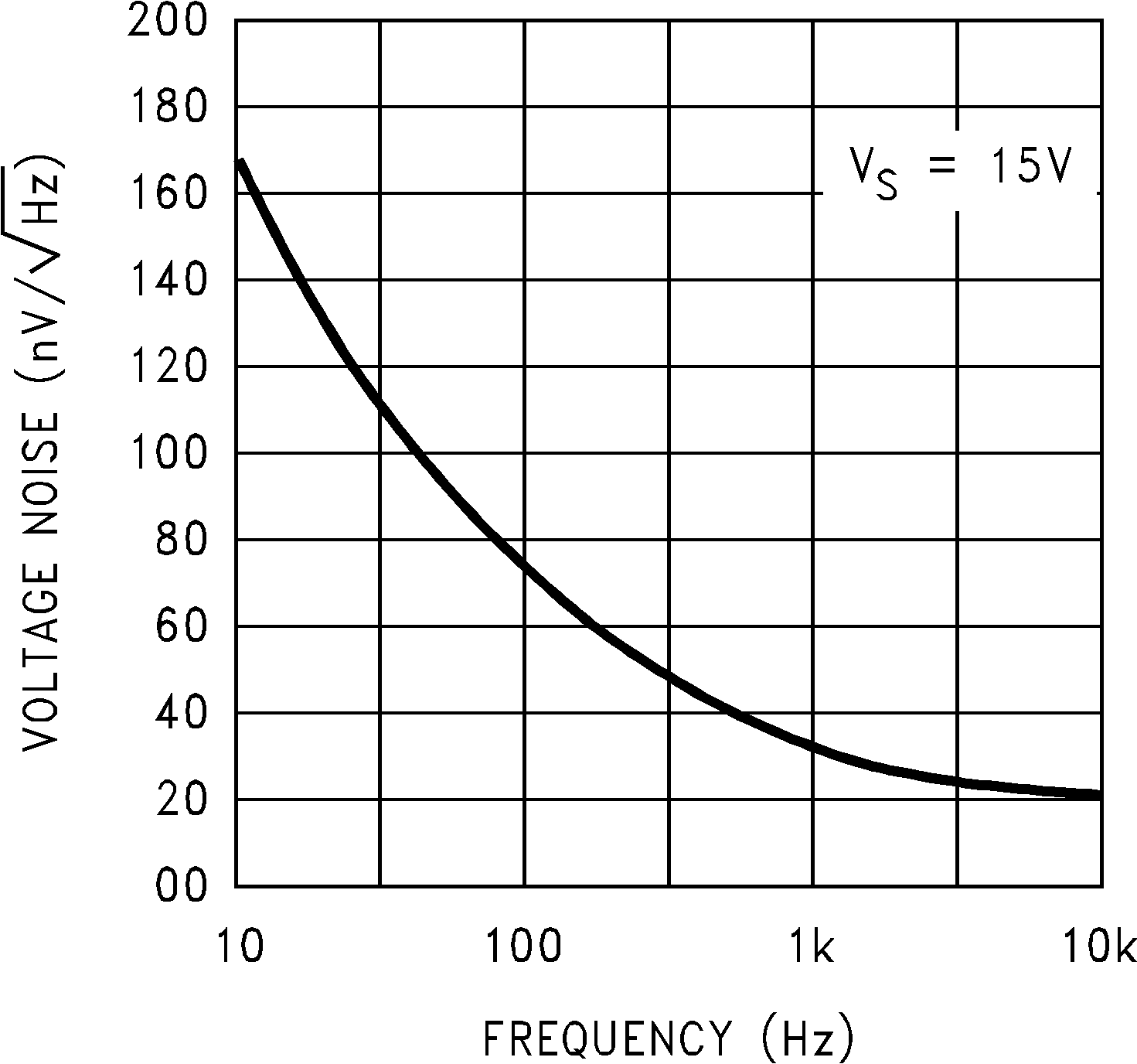 Figure 5-10 Input Voltage Noise vs Frequency
Figure 5-10 Input Voltage Noise vs Frequency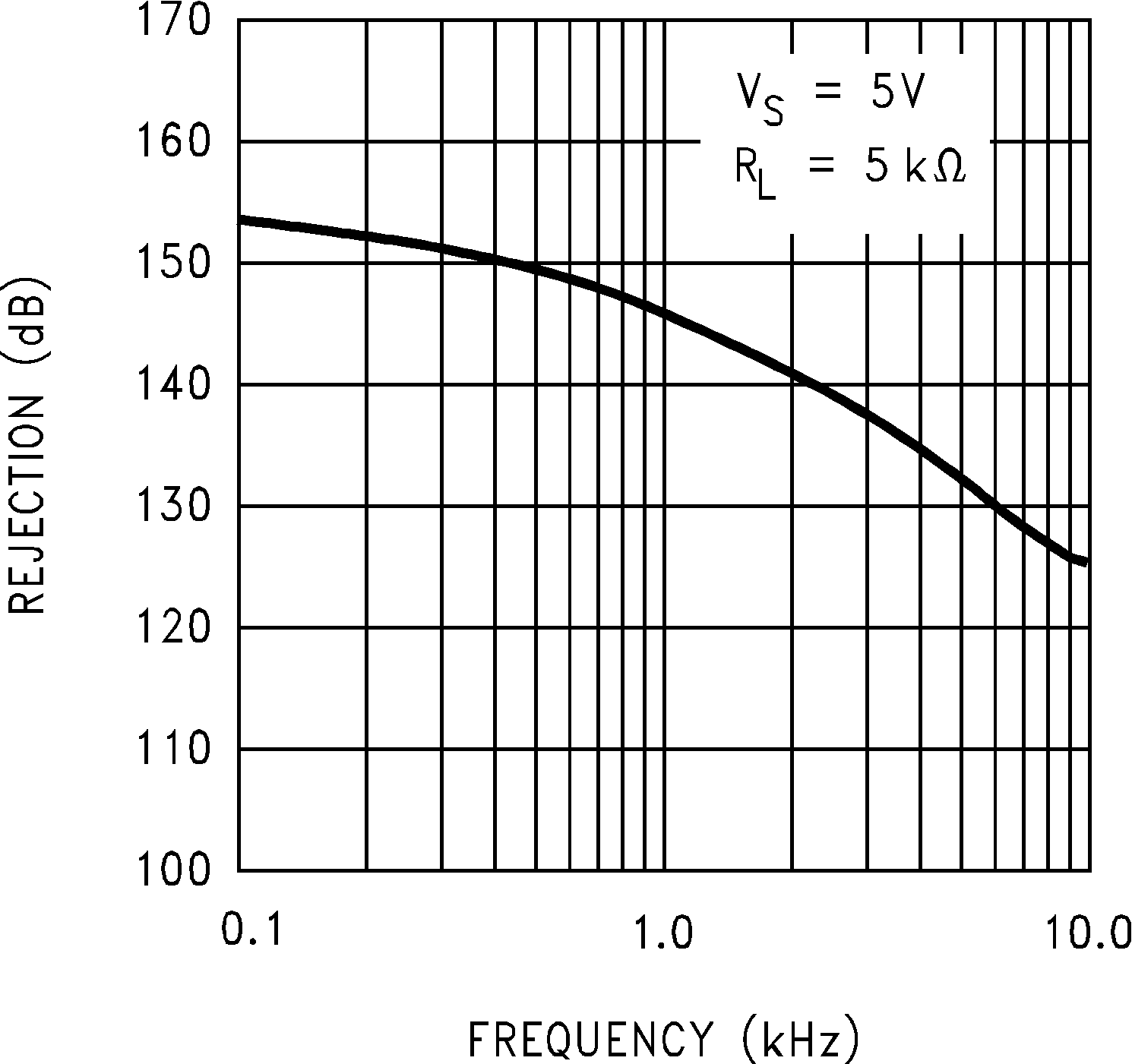 Figure 5-12 Crosstalk Rejection vs Frequency
Figure 5-12 Crosstalk Rejection vs Frequency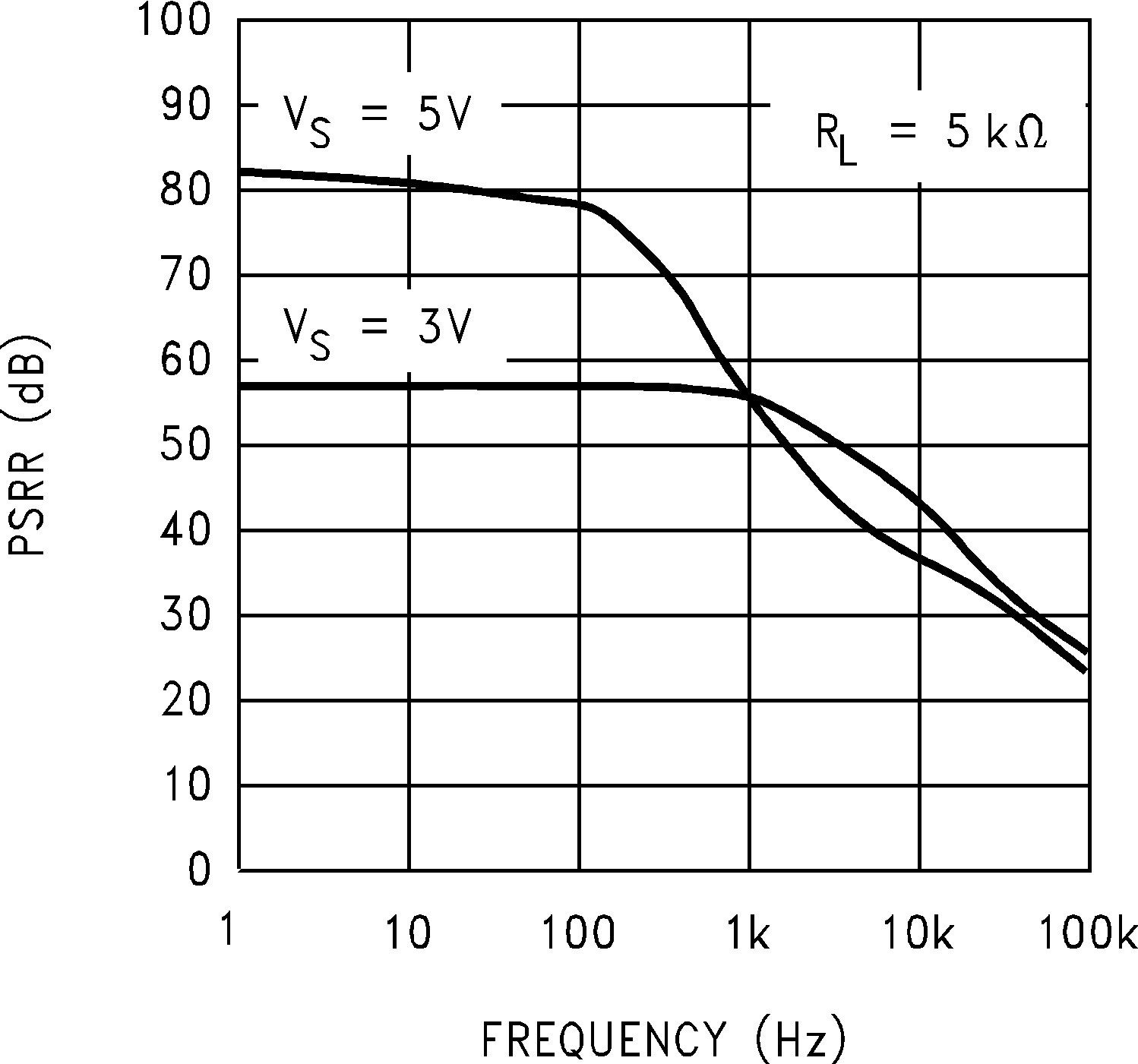 Figure 5-14 Negative PSRR vs Frequency
Figure 5-14 Negative PSRR vs Frequency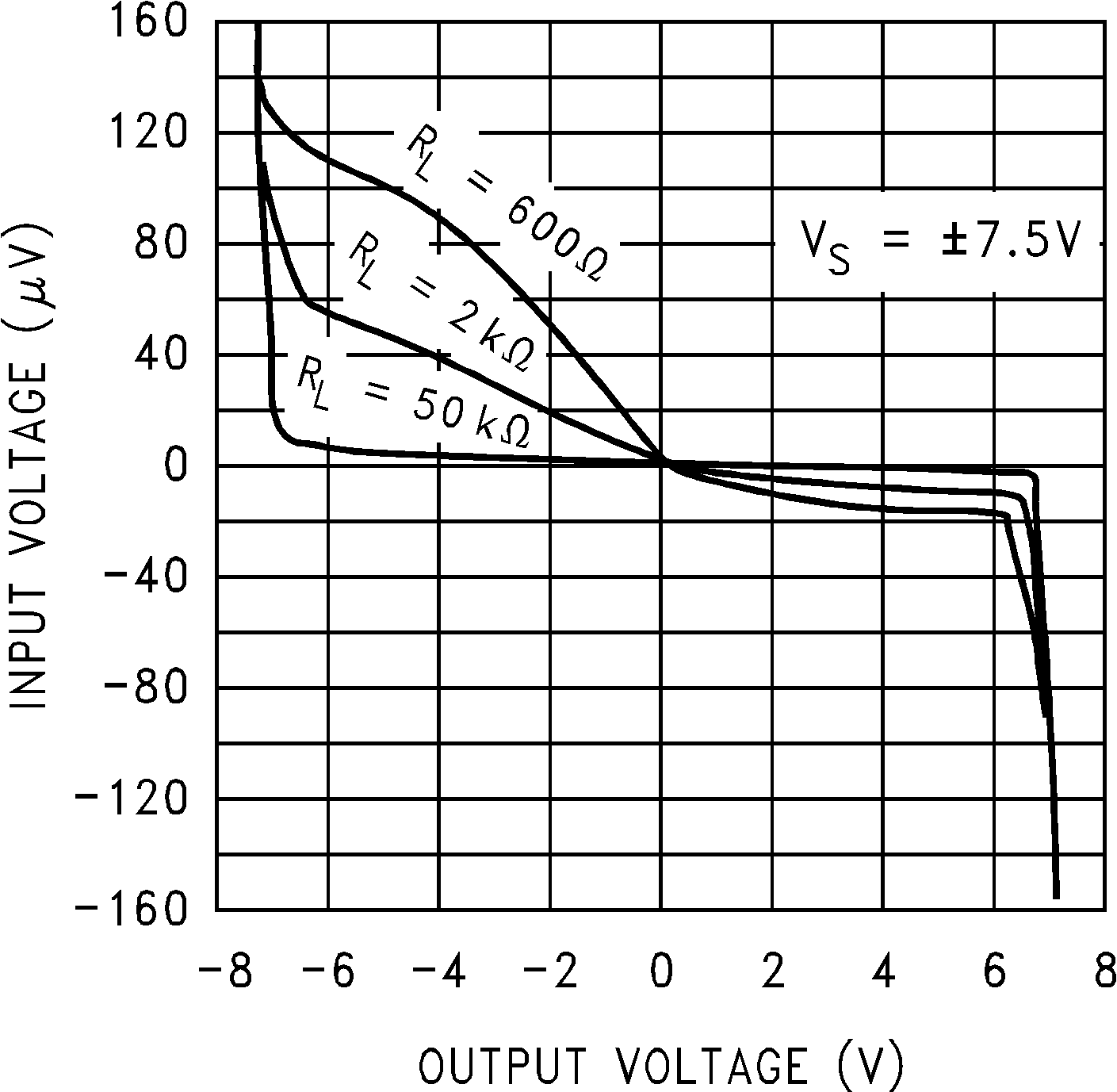 Figure 5-16 Input Voltage vs Output Voltage
Figure 5-16 Input Voltage vs Output Voltage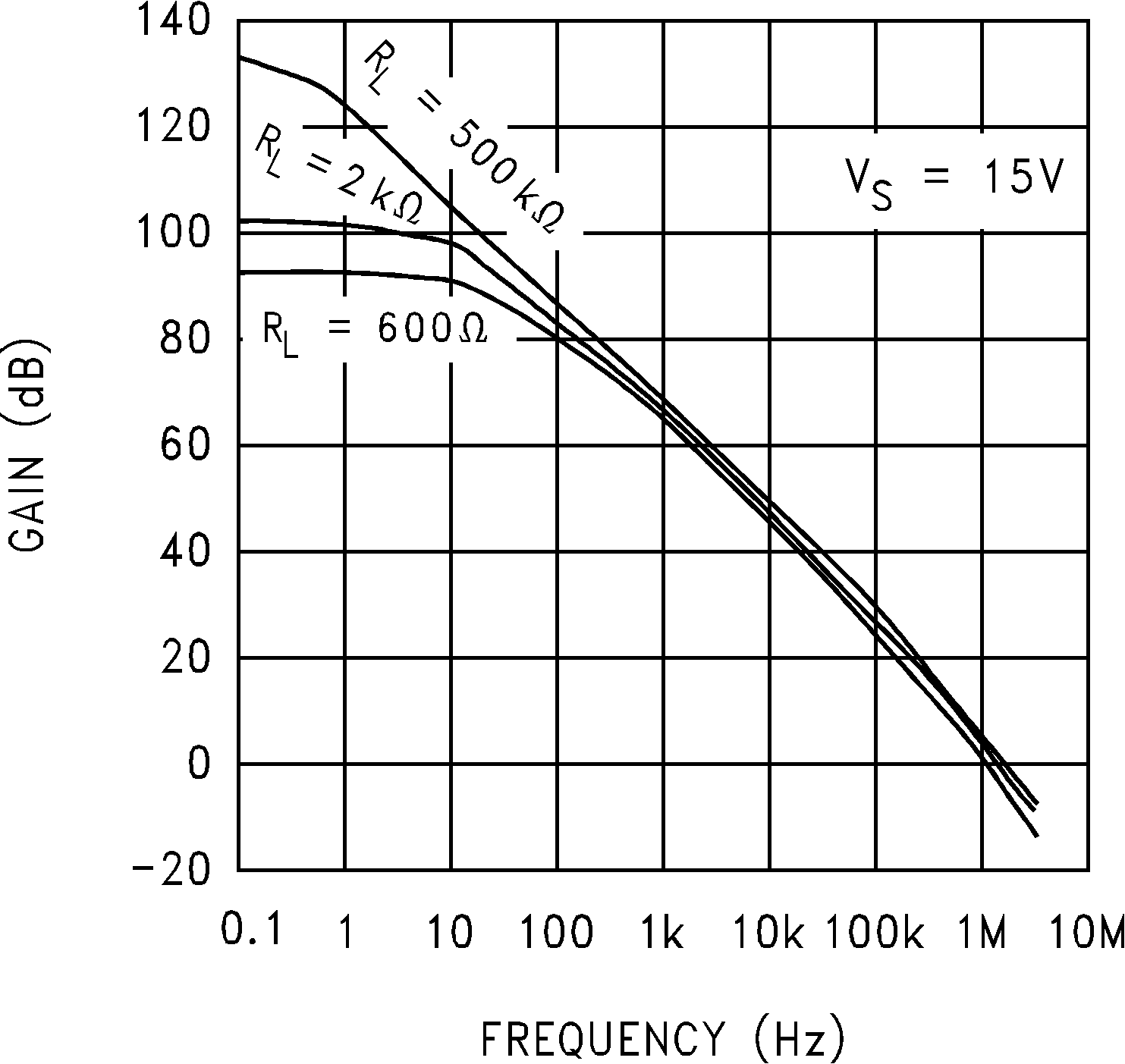 Figure 5-18 Open Loop Frequency Response
Figure 5-18 Open Loop Frequency Response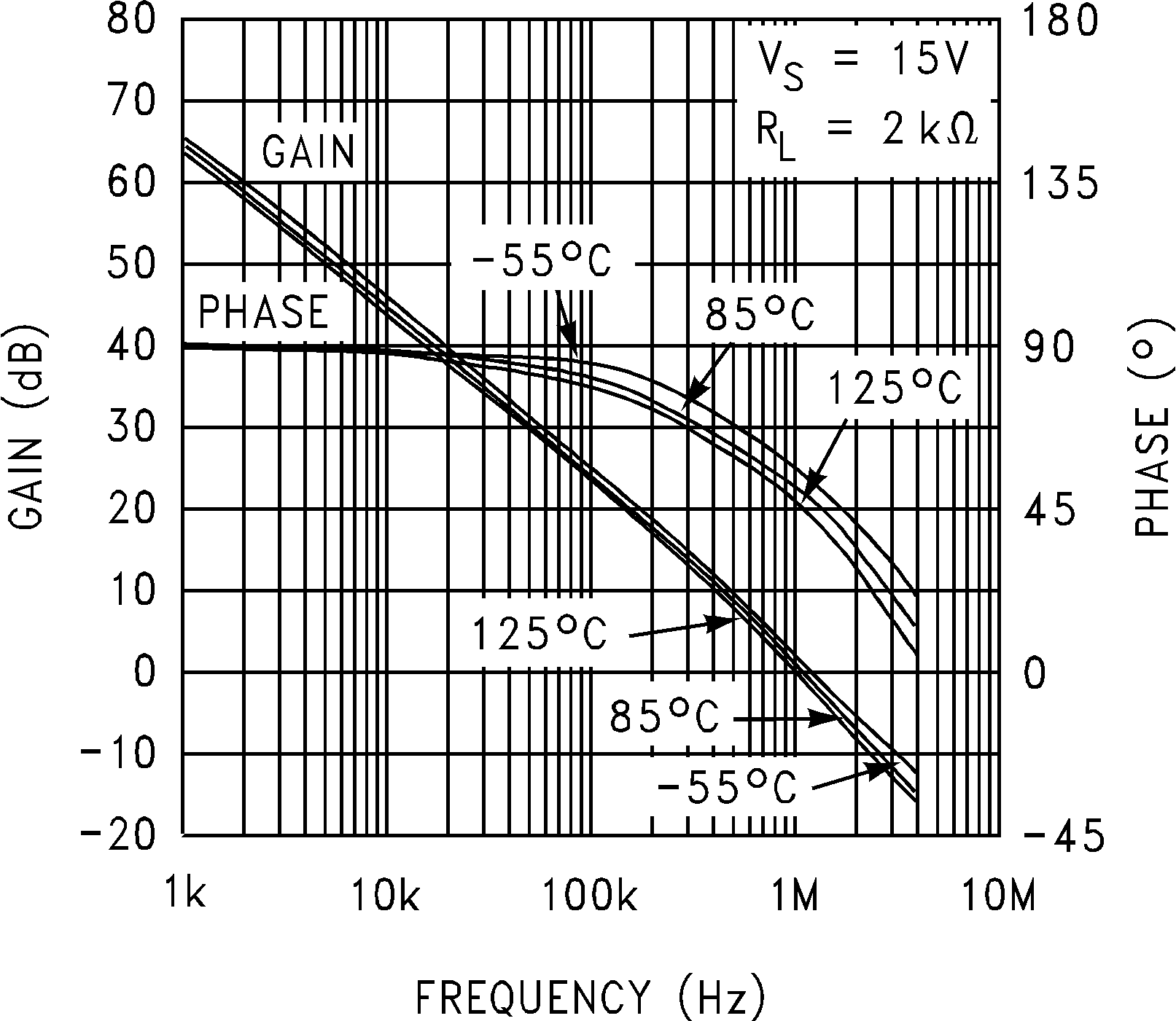 Figure 5-20 Open Loop Frequency Response vs Temperature
Figure 5-20 Open Loop Frequency Response vs Temperature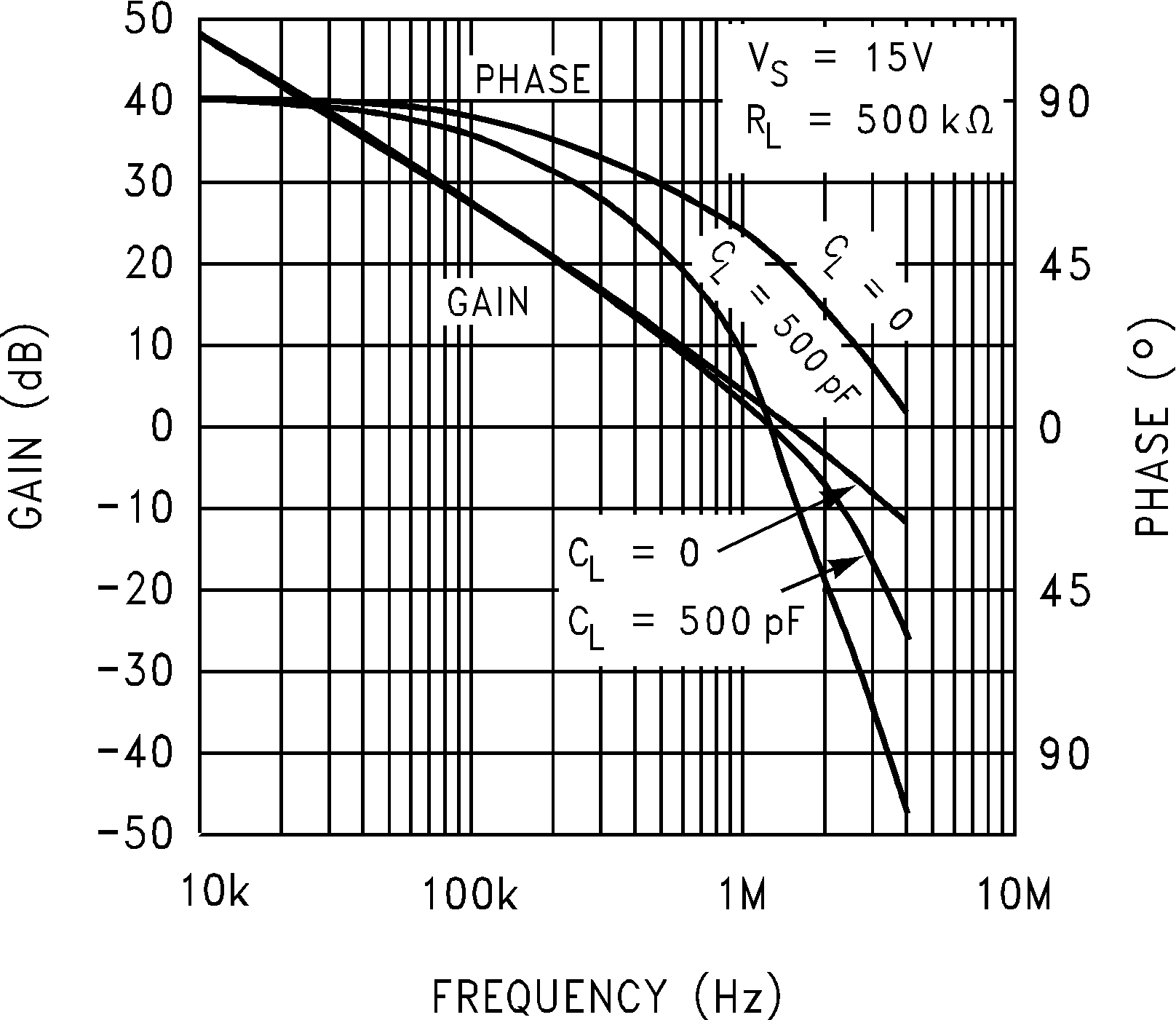 Figure 5-22 Gain and Phase vs Capacitive Load
Figure 5-22 Gain and Phase vs Capacitive Load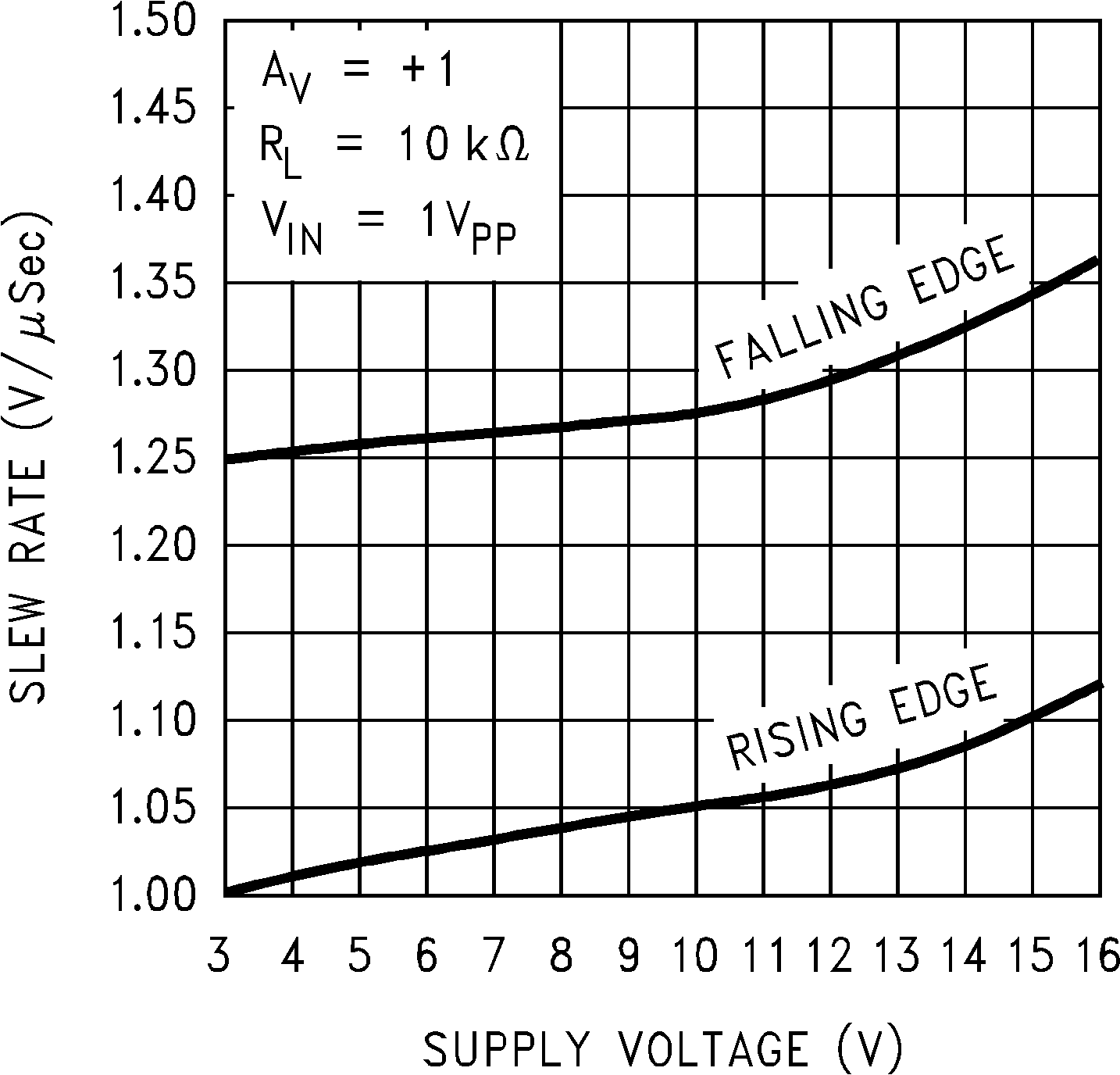 Figure 5-24 Slew Rate vs Supply Voltage
Figure 5-24 Slew Rate vs Supply Voltage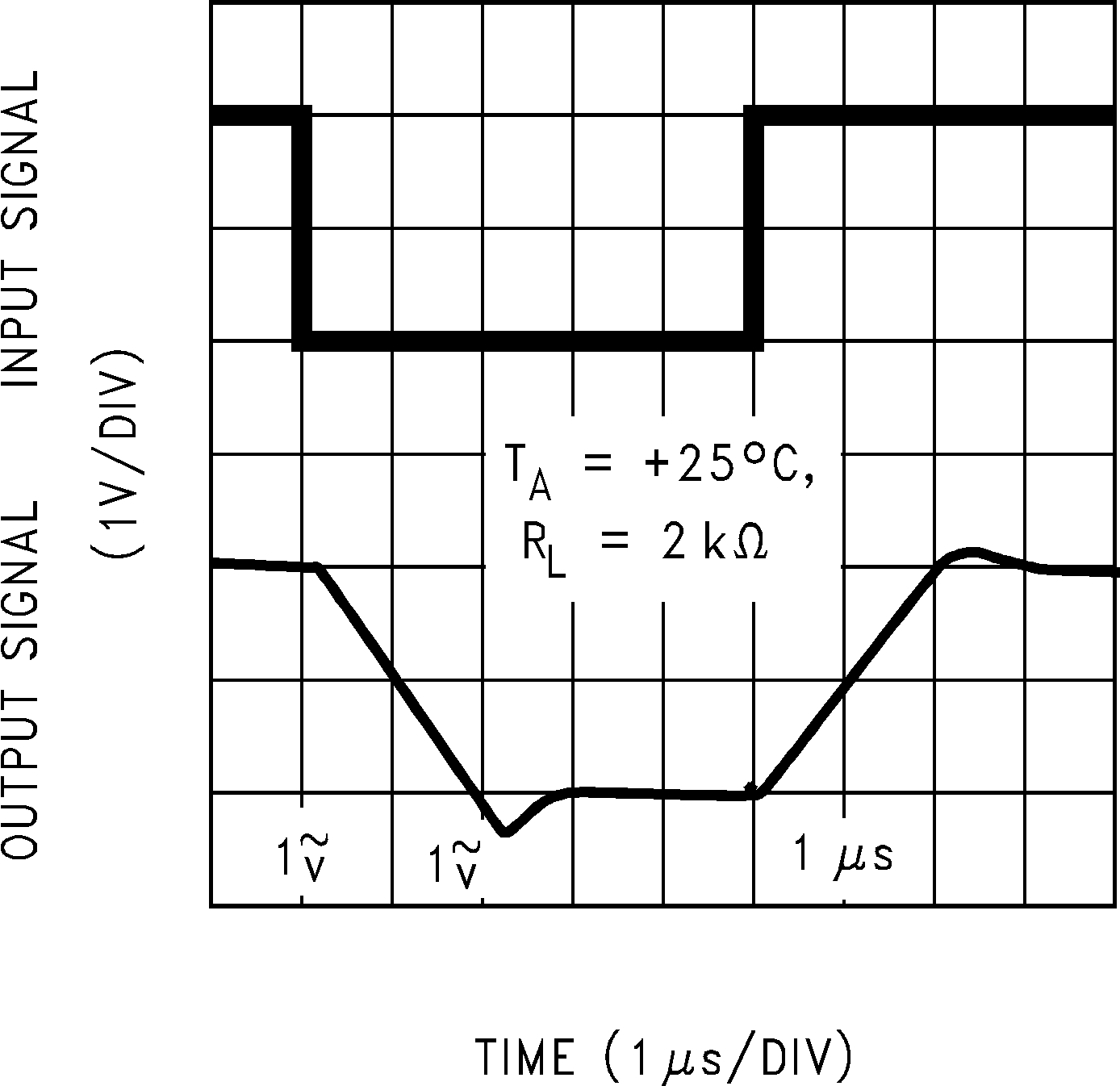 Figure 5-26 Non-Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response
Figure 5-26 Non-Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response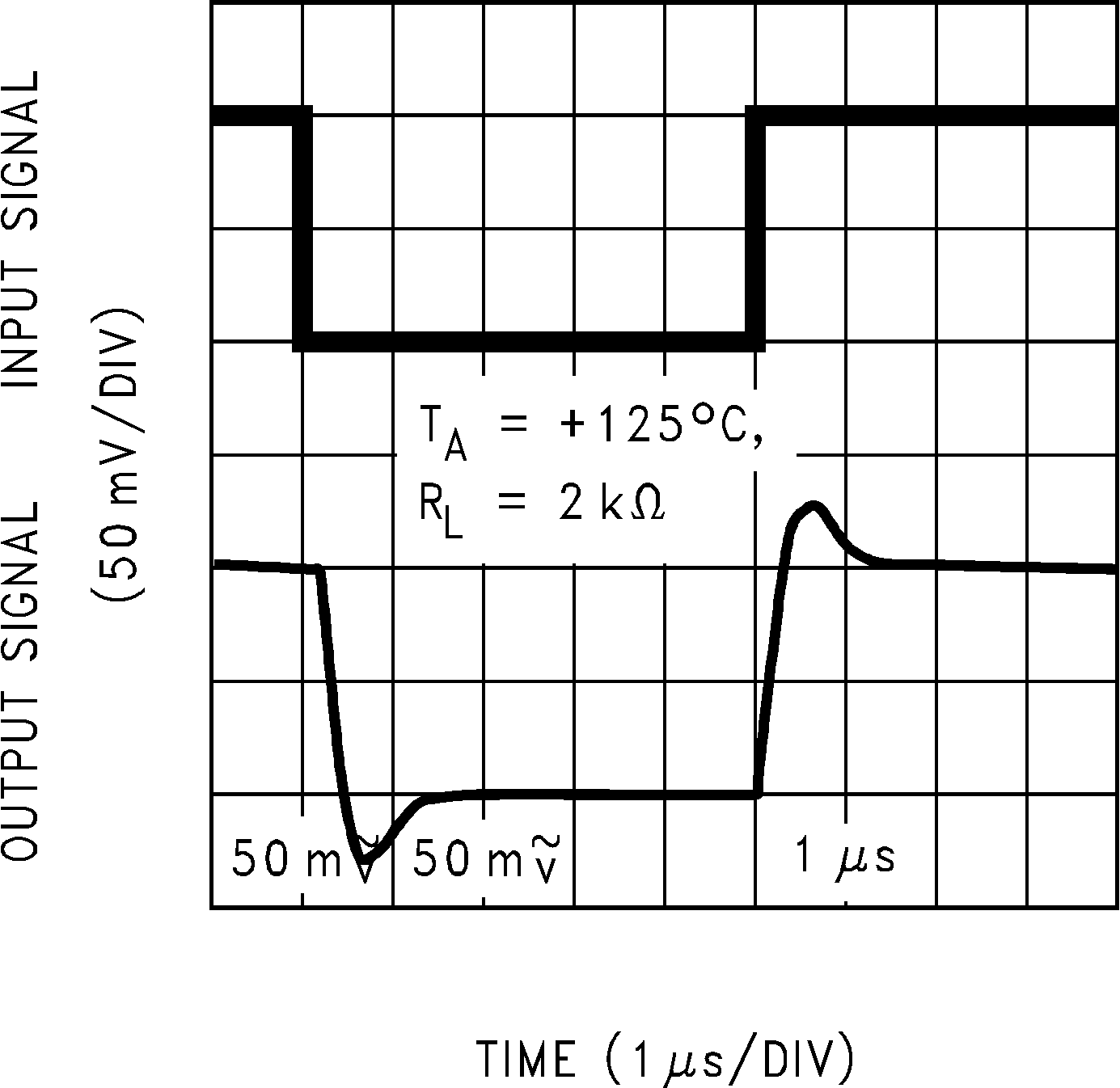 Figure 5-28 Non-Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response
Figure 5-28 Non-Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response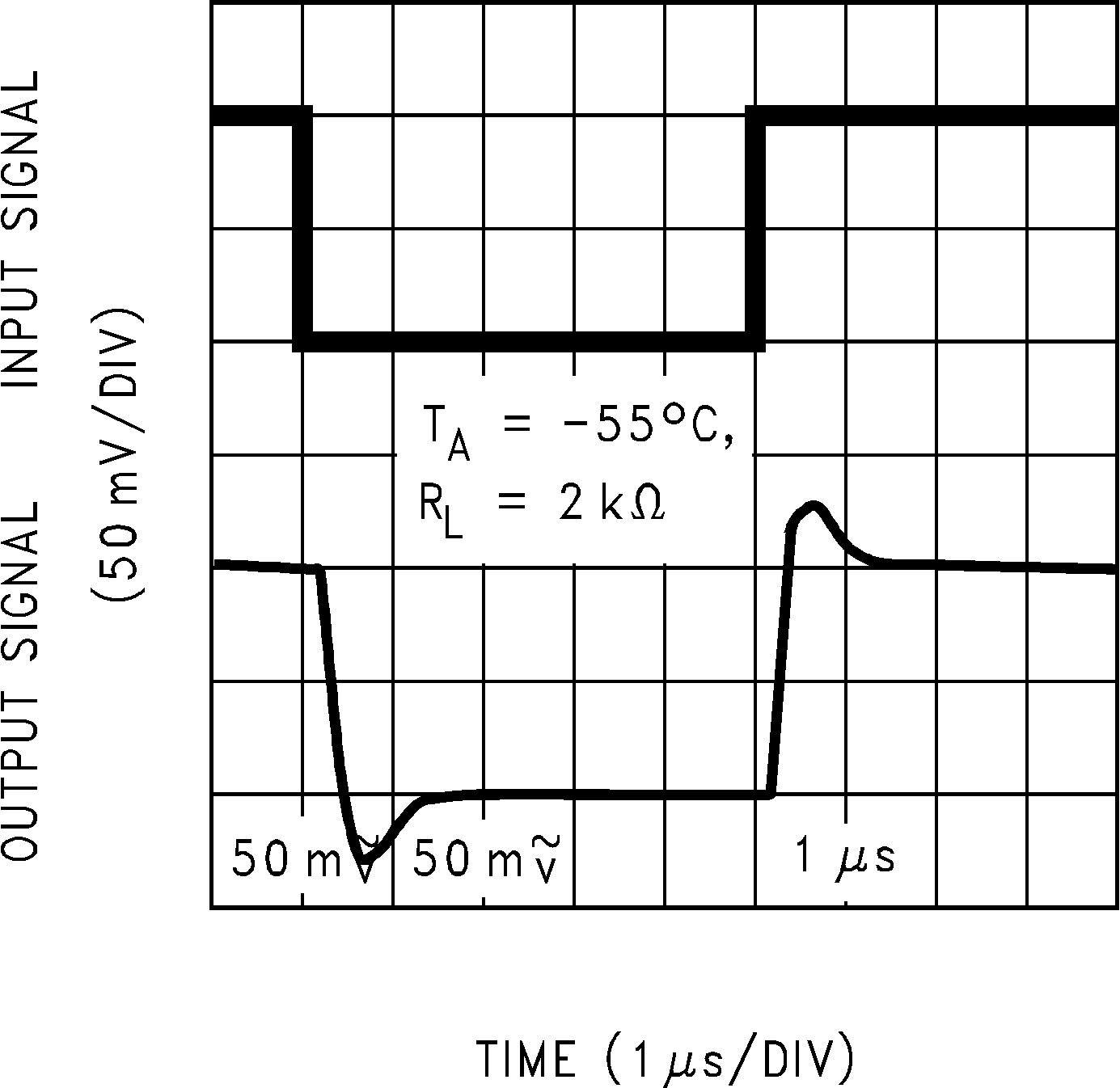 Figure 5-30 Non-Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response
Figure 5-30 Non-Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response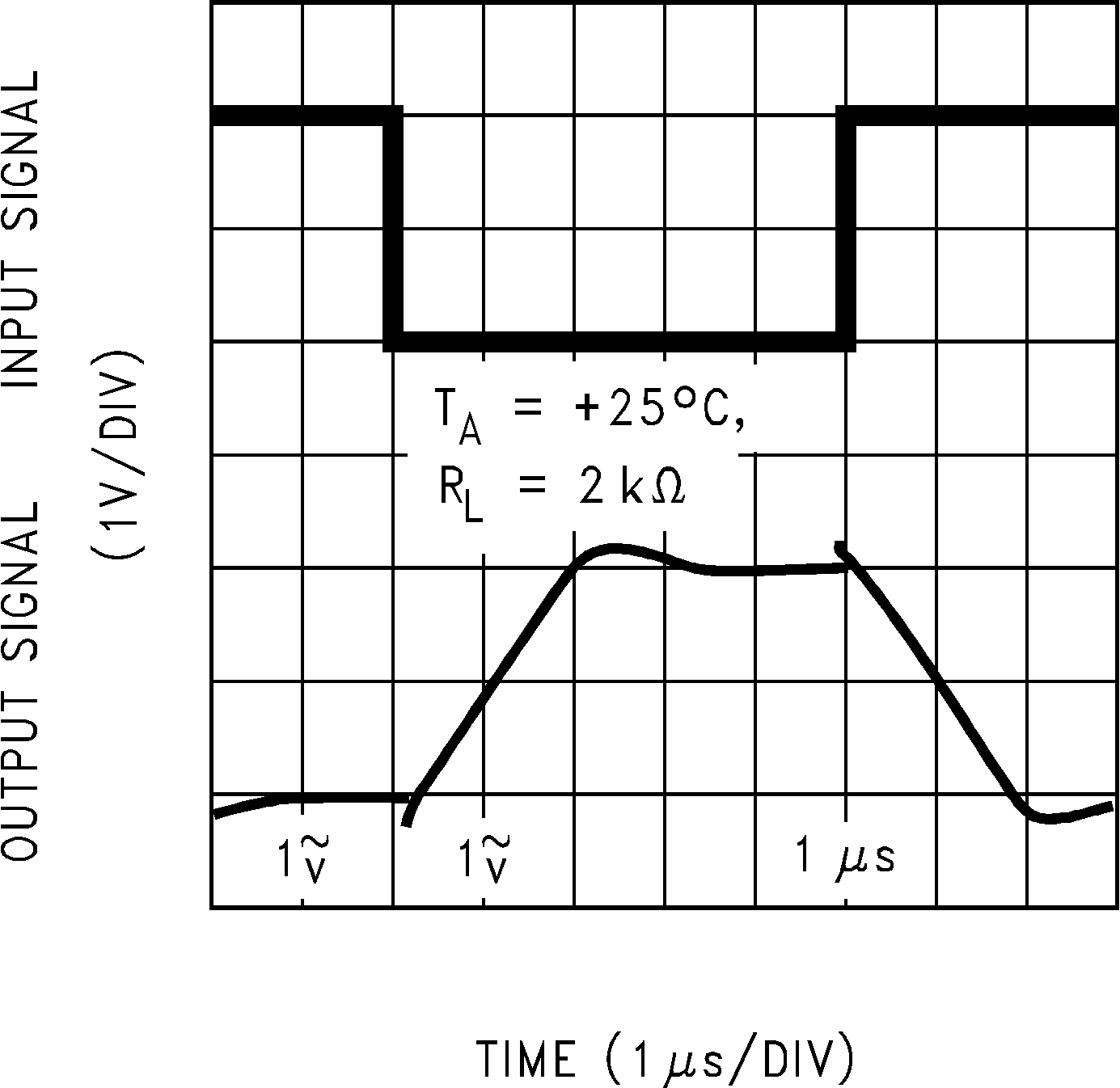 Figure 5-32 Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response
Figure 5-32 Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response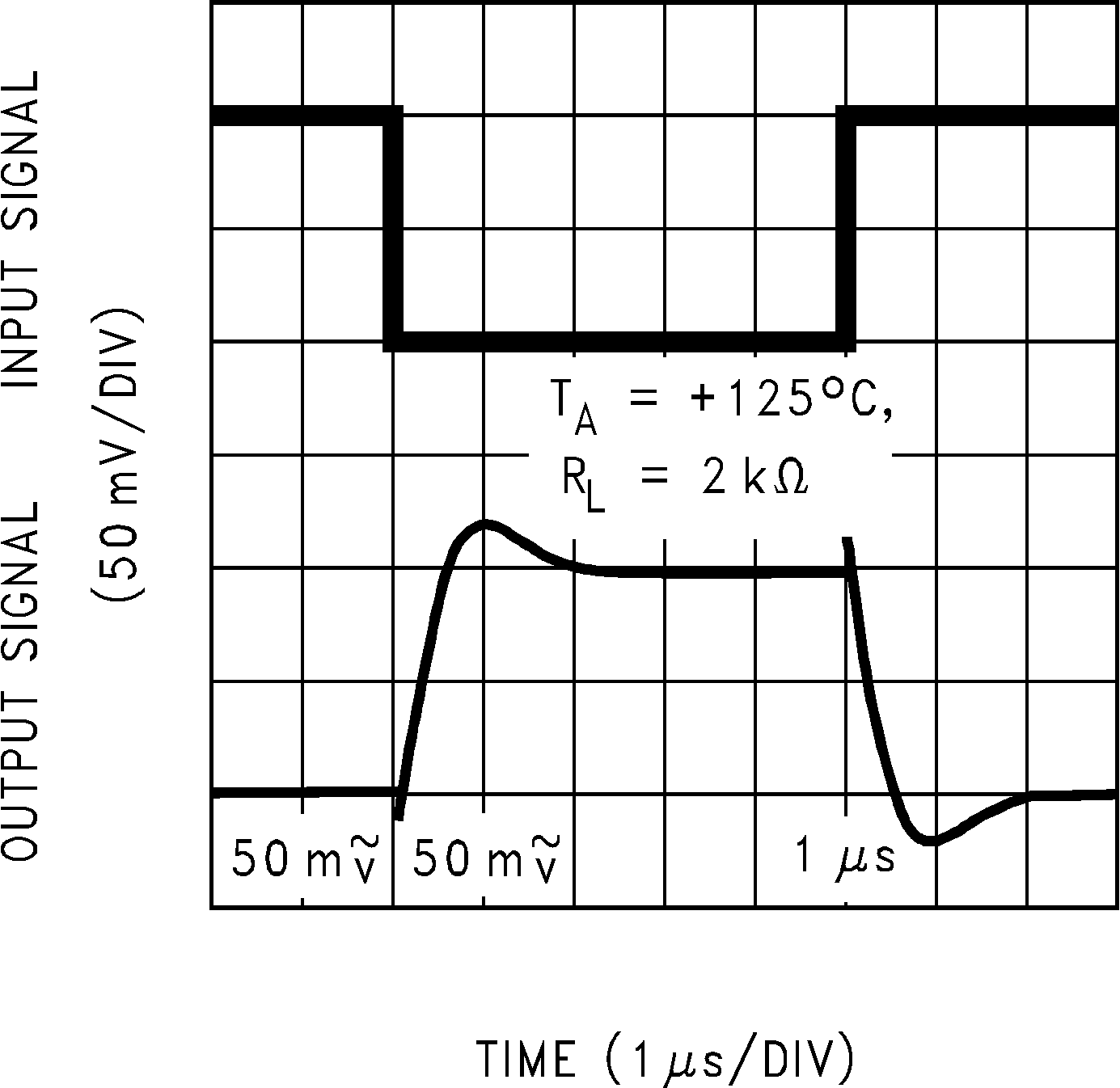 Figure 5-34 Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response
Figure 5-34 Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response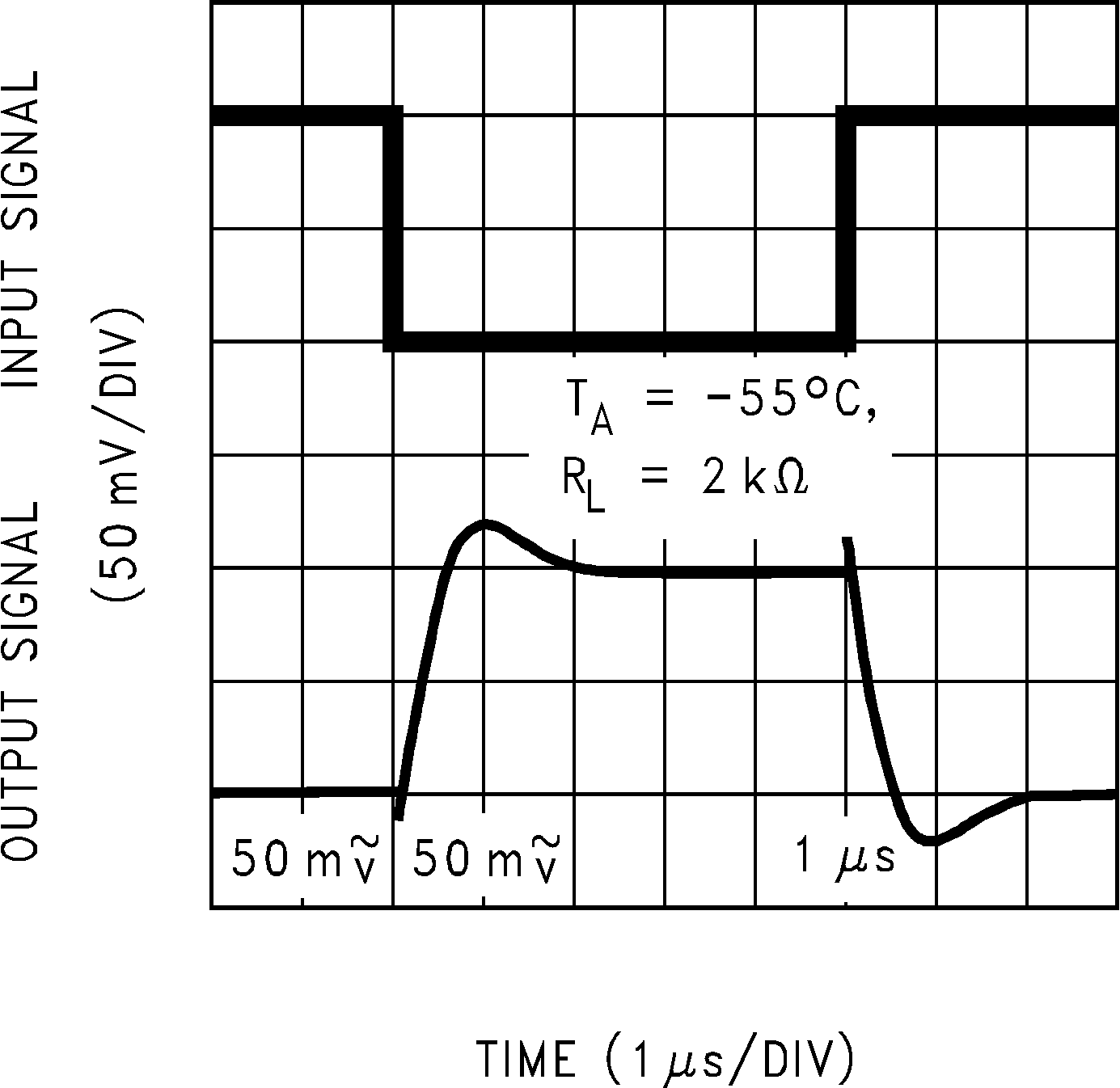 Figure 5-36 Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response
Figure 5-36 Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response