SNLS531B April 2016 – June 2018 LMH0324
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 LMH0324 Register Map
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Orderable Information
7.4.1.1 SMBus Read and Write Transactions
SMBus is a two-wire serial interface through which various system component chips can communicate with the master. Slave devices are identified by having a unique device address. The two-wire serial interface consists of SCL and SDA signals. SCL is a clock output from the master to all of the slave devices on the bus. SDA is a bidirectional data signal between the master and slave devices. The LMH0324 SMBus SCL and SDA signals are open drain and require external pull-up resistors.
Start and Stop:
The master generates start and stop patterns at the beginning and end of each transaction.
- Start: High to low transition (falling edge) of SDA while SCL is high.
- Stop: Low to high transition (rising edge) of SDA while SCL is high.
 Figure 9. Start and Stop Conditions
Figure 9. Start and Stop Conditions
The master generates nine clock pulses for each byte transfer. The 9th clock pulse constitutes the ACK cycle. The transmitter releases SDA to allow the receiver to send the ACK signal. An ACK is recorded when the device pulls SDA low, while a NACK is recorded if the line remains high.
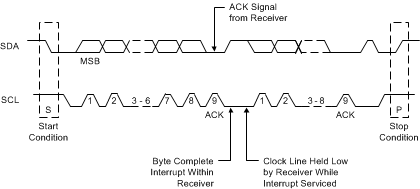 Figure 10. Acknowledge (ACK)
Figure 10. Acknowledge (ACK)