SNAS668E August 2015 – September 2024 LMK03328
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics - Power Supply
- 6.7 Pullable Crystal Characteristics (SECREF_P, SECREF_N)
- 6.8 Non-Pullable Crystal Characteristics (SECREF_P, SECREF_N)
- 6.9 Clock Input Characteristics (PRIREF_P/PRIREF_N, SECREF_P/SECREF_N)
- 6.10 VCO Characteristics
- 6.11 PLL Characteristics
- 6.12 1.8-V LVCMOS Output Characteristics (OUT[7:0])
- 6.13 LVCMOS Output Characteristics (STATUS[1:0]
- 6.14 Open-Drain Output Characteristics (STATUS[1:0])
- 6.15 AC-LVPECL Output Characteristics
- 6.16 AC-LVDS Output Characteristics
- 6.17 AC-CML Output Characteristics
- 6.18 HCSL Output Characteristics
- 6.19 Power-On/Reset Characteristics
- 6.20 2-Level Logic Input Characteristics (HW_SW_CTRL, PDN, GPIO[5:0])
- 6.21 3-Level Logic Input Characteristics (REFSEL, GPIO[3:1])
- 6.22 Analog Input Characteristics (GPIO[5])
- 6.23 I2C-Compatible Interface Characteristics (SDA, SCL)
- 6.24 Typical 156.25-MHz, Closed-Loop Output Phase Noise Characteristics
- 6.25 Typical 161.1328125-MHz, Closed-Loop Output Phase Noise Characteristics
- 6.26 Closed-Loop Output Jitter Characteristics
- 6.27 PCIe Clock Output Jitter
- 6.28 Typical Power Supply Noise Rejection Characteristics
- 6.29 Typical Power Supply Noise Rejection Characteristics
- 6.30 Typical Closed-Loop Output Spur Characteristics
- 6.31 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Smart Input MUX
- 8.4.2 Universal Input Buffer (PRI_REF, SEC_REF)
- 8.4.3 Crystal Input Interface (SEC_REF)
- 8.4.4 Reference Doubler
- 8.4.5 Reference (R) Divider
- 8.4.6 Input (M) Divider
- 8.4.7 Feedback (N) Divider
- 8.4.8 Phase Frequency Detector (PFD)
- 8.4.9 Charge Pump
- 8.4.10 Loop Filter
- 8.4.11 VCO Calibration
- 8.4.12 Fractional Circuitry
- 8.4.13 Post Divider
- 8.4.14 High-Speed Output MUX
- 8.4.15 High-Speed Output Divider
- 8.4.16 High-Speed Clock Outputs
- 8.4.17 Output Synchronization
- 8.4.18 Status Outputs
- 8.5 Programming
-
9 Register Maps
- 9.1
LMK03328
Registers
- 9.1.1 VNDRID_BY1 Register; R0
- 9.1.2 VNDRID_BY0 Register; R1
- 9.1.3 PRODID Register; R2
- 9.1.4 REVID Register; R3
- 9.1.5 PARTID Register; R4
- 9.1.6 PINMODE_SW Register; R8
- 9.1.7 PINMODE_HW Register; R9
- 9.1.8 TARGETADR Register; R10
- 9.1.9 EEREV Register; R11
- 9.1.10 DEV_CTL Register; R12
- 9.1.11 INT_LIVE Register; R13
- 9.1.12 INT_MASK Register; R14
- 9.1.13 INT_FLAG_POL Register; R15
- 9.1.14 INT_FLAG Register; R16
- 9.1.15 INTCTL Register; R17
- 9.1.16 OSCCTL2 Register; R18
- 9.1.17 STATCTL Register; R19
- 9.1.18 MUTELVL1 Register; R20
- 9.1.19 MUTELVL2 Register; R21
- 9.1.20 OUT_MUTE Register; R22
- 9.1.21 STATUS_MUTE Register; R23
- 9.1.22 DYN_DLY Register; R24
- 9.1.23 REFDETCTL Register; R25
- 9.1.24 STAT0_INT Register; R27
- 9.1.25 STAT1 Register; R28
- 9.1.26 OSCCTL1 Register; R29
- 9.1.27 PWDN Register; R30
- 9.1.28 OUTCTL_0 Register; R31
- 9.1.29 OUTCTL_1 Register; R32
- 9.1.30 OUTDIV_0_1 Register; R33
- 9.1.31 OUTCTL_2 Register; R34
- 9.1.32 OUTCTL_3 Register; R35
- 9.1.33 OUTDIV_2_3 Register; R36
- 9.1.34 OUTCTL_4 Register; R37
- 9.1.35 OUTDIV_4 Register; R38
- 9.1.36 OUTCTL_5 Register; R39
- 9.1.37 OUTDIV_5 Register; R40
- 9.1.38 OUTCTL_6 Register; R41
- 9.1.39 OUTDIV_6 Register; R42
- 9.1.40 OUTCTL_7 Register; R43
- 9.1.41 OUTDIV_7 Register; R44
- 9.1.42 CMOSDIVCTRL Register; R45
- 9.1.43 CMOSDIV0 Register; R46
- 9.1.44 CMOSDIV1 Register; R47
- 9.1.45 STATUS_SLEW Register; R49
- 9.1.46 IPCLKSEL Register; R50
- 9.1.47 IPCLKCTL Register; R51
- 9.1.48 PLL1_RDIV Register; R52
- 9.1.49 PLL1_MDIV Register; R53
- 9.1.50 PLL2_RDIV Register; R54
- 9.1.51 PLL2_MDIV Register; R55
- 9.1.52 PLL1_CTRL0 Register; R56
- 9.1.53 PLL1_CTRL1 Register; R57
- 9.1.54 PLL1_NDIV_BY1 Register; R58
- 9.1.55 PLL1_NDIV_BY0 Register; R59
- 9.1.56 PLL1_FRACNUM_BY2 Register; R60
- 9.1.57 PLL1_FRACNUM_BY1 Register; R61
- 9.1.58 PLL1_FRACNUM_BY0 Register; R62
- 9.1.59 PLL_FRACDEN_BY2 Register; R63
- 9.1.60 PLL1_FRACDEN_BY1 Register; R64
- 9.1.61 PLL1_FRACDEN_BY0 Register; R65
- 9.1.62 PLL1_MASHCTRL Register; R66
- 9.1.63 PLL1_LF_R2 Register; R67
- 9.1.64 PLL1_LF_C1 Register; R68
- 9.1.65 PLL1_LF_R3 Register; R69
- 9.1.66 PLL1_LF_C3 Register; R70
- 9.1.67 PLL2_CTRL0 Register; R71
- 9.1.68 PLL2_CTRL1 Register; R72
- 9.1.69 PLL2_NDIV_BY1 Register; R73
- 9.1.70 PLL2_NDIV_BY0 Register; R74
- 9.1.71 PLL2_FRACNUM_BY2 Register; R75
- 9.1.72 PLL2_FRACNUM_BY1 Register; R76
- 9.1.73 PLL2_FRACNUM_BY0 Register; R77
- 9.1.74 PLL2_FRACDEN_BY2 Register; R78
- 9.1.75 PLL2_FRACDEN_BY1 Register; R79
- 9.1.76 PLL2_FRACDEN_BY0 Register; R80
- 9.1.77 PLL2_MASHCTRL Register; R81
- 9.1.78 PLL2_LF_R2 Register; R82
- 9.1.79 PLL2_LF_C1 Register; R83
- 9.1.80 PLL2_LF_R3 Register; R84
- 9.1.81 PLL2_LF_C3 Register; R85
- 9.1.82 XO_MARGINING Register; R86
- 9.1.83 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_1_BY1 Register; R88
- 9.1.84 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_1_BY0 Register; R89
- 9.1.85 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_2_BY1 Register; R90
- 9.1.86 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_2_BY0 Register; R91
- 9.1.87 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_3_BY1 Register; R92
- 9.1.88 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_3_BY0 Register; R93
- 9.1.89 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_4_BY1 Register; R94
- 9.1.90 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_4_BY0 Register; R95
- 9.1.91 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_5_BY1 Register; R96
- 9.1.92 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_5_BY0 Register; R97
- 9.1.93 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_6_BY1 Register; R98
- 9.1.94 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_6_BY0 Register; R99
- 9.1.95 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_7_BY1 Register; R100
- 9.1.96 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_7_BY0 Register; R101
- 9.1.97 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_8_BY1 Register; R102
- 9.1.98 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_8_BY0 Register; R103
- 9.1.99 XO_OFFSET_SW_BY1 Register; R104
- 9.1.100 XO_OFFSET_SW_BY0 Register; R105
- 9.1.101 PLL1_CTRL2 Register; R117
- 9.1.102 PLL1_CTRL3 Register; R118
- 9.1.103 PLL1_CALCTRL0 Register; R119
- 9.1.104 PLL1_CALCTRL1 Register; R120
- 9.1.105 PLL2_CTRL2 Register; R131
- 9.1.106 PLL2_CTRL3 Register; R132
- 9.1.107 PLL2_CALCTRL0 Register; R133
- 9.1.108 PLL2_CALCTRL1 Register; R134
- 9.1.109 NVMSCRC Register; R135
- 9.1.110 NVMCNT Register; R136
- 9.1.111 NVMCTL Register; R137
- 9.1.112 NVMLCRC Register; R138
- 9.1.113 MEMADR_BY1 Register; R139
- 9.1.114 MEMADR_BY0 Register; R140
- 9.1.115 NVMDAT Register; R141
- 9.1.116 RAMDAT Register; R142
- 9.1.117 ROMDAT Register; R143
- 9.1.118 NVMUNLK Register; R144
- 9.1.119 REGCOMMIT_PAGE Register; R145
- 9.1.120 POR_CTRL Register; R173
- 9.1.121 XOCAPCTRL_BY1 Register; R199
- 9.1.122 XOCAPCTRL_BY0 Register; R200
- 9.2 EEPROM Map
- 9.1
LMK03328
Registers
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2 Typical Applications
- 10.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10.4 Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHS|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHS|48
Orderable Information
8.3.2 Device Configuration Control
Figure 8-1 shows the relationships between device states, the configuration pins, device initialization and configuration, and device operational modes.
In hard pin configuration mode, the state of the configuration pins determines the configuration of the device as selected from all device states programmed in the on-chip EEPROM. In soft pin configuration mode, the state of the configuration pins determines the initialized state of the device as programmed in the on-chip EEPROM.
In either mode, the host can update any device configuration after the device enables the host interface to write a sequence that updates the device registers. When the device configuration is set, the host can also write to the on-chip EEPROM for a new set of power-up defaults based on the configuration pin settings in the soft pin configuration mode. The engineer can change the state of the HW_SW_CTRL pin and trigger a device power cycle through the PDN pin to transition the device from hard pin mode to soft pin mode. In reset mode, the device disables the outputs so that unwanted sporadic activity associated with device initialization does not appear on the device outputs. Table 8-1 lists the functionality of the GPIO[5:0] pins during hard pin and soft pin modes.
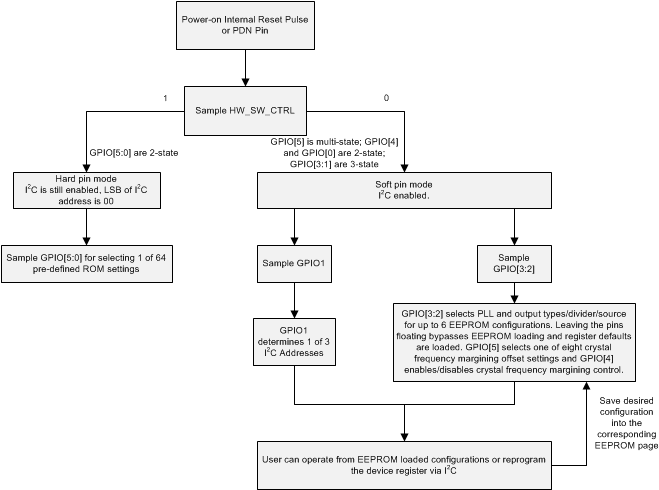 Figure 8-1 LMK03328 Simplified Programming
Flow
Figure 8-1 LMK03328 Simplified Programming
Flow| PIN NAME | HARD PIN MODE | SOFT PIN MODE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FUNCTION | STATE | FUNCTION | STATE | |
| GPIO0 | ROM page select for hard pin mode | 2 | Output synchronization (active low) | 2 |
| GPIO1 | 2 | I2C target address LSB select | 3 | |
| GPIO2 | 2 | EEPROM page select for soft pin mode or register default mode | 3 | |
| GPIO3 | 2 | 3 | ||
| GPIO4 | 2 | Frequency margining enable | 2 | |
| GPIO5 | 2 | Frequency margining offset select | 8 | |