SNAS597C July 2012 – January 2016 LMK04816
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1
Overview
- 8.1.1 System Architecture
- 8.1.2 PLL1 Redundant Reference Inputs (CLKin0/CLKin0*, CLKin1/CLKin1*, and CLKin2/CLKin2*)
- 8.1.3 PLL1 Tunable Crystal Support
- 8.1.4 VCXO and CRYSTAL-Buffered Outputs
- 8.1.5 Frequency Holdover
- 8.1.6 Integrated Loop Filter Poles
- 8.1.7 Internal VCO
- 8.1.8 External VCO Mode
- 8.1.9 Clock Distribution
- 8.1.10 0-Delay
- 8.1.11 Default Start-Up Clocks
- 8.1.12 Status Pins
- 8.1.13 Register Readback
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Serial MICROWIRE Timing Diagram
- 8.3.2 Advanced MICROWIRE Timing Diagrams
- 8.3.3 Inputs and Outputs
- 8.3.4 Input Clock Switching
- 8.3.5 Holdover Mode
- 8.3.6 PLLs
- 8.3.7 Status Pins
- 8.3.8 VCO
- 8.3.9
Clock Distribution
- 8.3.9.1 Fixed Digital Delay
- 8.3.9.2
Clock Output Synchronization (SYNC)
- 8.3.9.2.1 Effect of SYNC
- 8.3.9.2.2 Methods of Generating SYNC
- 8.3.9.2.3 Avoiding Clock Output Interruption due to SYNC
- 8.3.9.2.4 SYNC Timing
- 8.3.9.2.5
Dynamically Programming Digital Delay
- 8.3.9.2.5.1 Absolute versus Relative Dynamic Digital Delay
- 8.3.9.2.5.2 Dynamic Digital Delay and 0-Delay Mode
- 8.3.9.2.5.3 SYNC and Minimum Step Size
- 8.3.9.2.5.4 Programming Overview
- 8.3.9.2.5.5 Internal Dynamic Digital Delay Timing
- 8.3.9.2.5.6 Other Timing Requirements
- 8.3.9.2.5.7 Absolute Dynamic Digital Delay
- 8.3.9.2.5.8 Relative Dynamic Digital Delay
- 8.3.10 0-Delay Mode
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 Register Map and Readback Register Map
- 8.6.2 Default Device Register Settings After Power On Reset
- 8.6.3
Register Descriptions
- 8.6.3.1
Registers R0 to R5
- 8.6.3.1.1 CLKoutX_Y_PD, Powerdown CLKoutX_Y Output Path
- 8.6.3.1.2 CLKoutX_Y_OSCin_Sel, Clock group source
- 8.6.3.1.3 CLKoutY_ADLY_SEL[29], CLKoutX_ADLY_SEL[28], Select Analog Delay
- 8.6.3.1.4 CLKoutX_Y_DDLY, Clock Channel Digital Delay
- 8.6.3.1.5 RESET
- 8.6.3.1.6 POWERDOWN
- 8.6.3.1.7 CLKoutX_Y_HS, Digital Delay Half Shift
- 8.6.3.1.8 CLKoutX_Y_DIV, Clock Output Divide
- 8.6.3.2 Registers R6 TO R8
- 8.6.3.3 Register R10
- 8.6.3.4 Register R11
- 8.6.3.5 Register R12
- 8.6.3.6 Register R13
- 8.6.3.7 Register 14
- 8.6.3.8 Register 15
- 8.6.3.9 Register 16
- 8.6.3.10 Register 23
- 8.6.3.11
REGISTER 24
- 8.6.3.11.1 PLL2_C4_LF, PLL2 Integrated Loop Filter Component
- 8.6.3.11.2 PLL2_C3_LF, PLL2 Integrated Loop Filter Component
- 8.6.3.11.3 PLL2_R4_LF, PLL2 Integrated Loop Filter Component
- 8.6.3.11.4 PLL2_R3_LF, PLL2 Integrated Loop Filter Component
- 8.6.3.11.5 PLL1_N_DLY
- 8.6.3.11.6 PLL1_R_DLY
- 8.6.3.11.7 PLL1_WND_SIZE
- 8.6.3.12 Register 25
- 8.6.3.13 Register 26
- 8.6.3.14 Register 27
- 8.6.3.15 Register 28
- 8.6.3.16 Register 29
- 8.6.3.17 Register 30
- 8.6.3.18 Register 31
- 8.6.3.1
Registers R0 to R5
- 8.1
Overview
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1
Application Information
- 9.1.1 Loop Filter
- 9.1.2 Driving CLKin and OSCin Inputs
- 9.1.3 Termination and Use of Clock Output (Drivers)
- 9.1.4 Frequency Planning With the LMK04816
- 9.1.5 PLL Programming
- 9.1.6 Digital Lock Detect Frequency Accuracy
- 9.1.7 Calculating Dynamic Digital Delay Values for Any Divide
- 9.1.8 Optional Crystal Oscillator Implementation (OSCin and OSCin*)
- 9.2 Typical Application
- 9.3 System Examples
- 9.1
Application Information
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- NKD|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- NKD|64
Orderable Information
1 Features
- Ultralow RMS Jitter Performance
- 100-fs RMS Jitter (12 kHz to 20 MHz)
- 123-fs RMS Jitter (100 Hz to 20 MHz)
- Dual-Loop PLLATINUM™ PLL Architecture
- PLL1
- Integrated Low-Noise Crystal Oscillator Circuit
- Holdover Mode When Input Clocks are Lost
- Automatic or Manual Triggering and Recovery
- PLL2
- Normalized 1-Hz PLL Noise Floor of
–227 dBc/Hz - Phase Detector Rate Up to 155 MHz
- OSCin Frequency-Doubler
- Integrated Low-Noise VCO
- VCO Frequency Ranges From 2370 MHz to 2600 MHz
- Normalized 1-Hz PLL Noise Floor of
- PLL1
- Three Redundant Input Clocks With LOS
- Automatic and Manual Switch-Over Modes
- 50% Duty Cycle Output Divides, 1 to 1045 (Even and Odd)
- LVPECL, LVDS, or LVCMOS Programmable Outputs
- Precision Digital Delay, Fixed or Dynamically-Adjustable
- 25-ps Step Analog Delay Control, Up to 575 ps
- 1/2 Clock Distribution Period Step Digital Delay, up to 522 Steps
- 13 Differential Outputs; up to 26 Single-Ended
- Up to 5 VCXO and Crystal-Buffered Outputs
- Clock Rates of Up to 2600 MHz
- 0-Delay Mode
- Three Default Clock Outputs at Power Up
- Multi-Mode: Dual PLL, Single PLL, and Clock Distribution
- Industrial Temperature Range: –40°C to +85°C
- 3.15-V to 3.45-V Operation
- Package: 64-Pin WQFN (9.0 × 9.0 × 0.8 mm)
2 Applications
- Data Converter Clocking and Wireless Infrastructure
- Networking, SONET or SDH, DSLAM
- Medical, Video, Military, and Aerospace
- Test and Measurement
3 Description
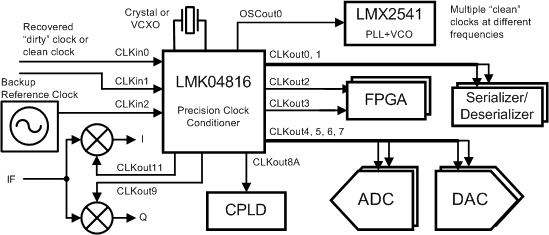
The LMK04816 device is the industry's highest performance clock conditioner with superior clock jitter cleaning, generation, and distribution with advanced features to meet next generation system requirements. The dual-loop PLLATINUM architecture enables 111-fs RMS jitter (12 kHz to
20 MHz) using a low-noise VCXO module or sub-200-fs RMS jitter (12 kHz to 20 MHz) using a low-cost external crystal and varactor diode.
The dual-loop architecture consists of two high-performance phase-locked loops (PLL), a low-noise crystal oscillator circuit, and a high-performance voltage controlled oscillator (VCO). The first PLL (PLL1) provides a low-noise jitter cleaner function while the second PLL (PLL2) performs the clock generation. PLL1 can be configured to either work with an external VCXO module or the integrated crystal oscillator with an external tunable crystal and varactor diode. When used with a very narrow loop bandwidth, PLL1 uses the superior close-in phase noise (offsets below 50 kHz) of the VCXO module or the tunable crystal to clean the input clock. The output of PLL1 is used as the clean input reference to PLL2 where it locks the integrated VCO. The loop bandwidth of PLL2 can be optimized to clean the far-out phase noise (offsets above 50 kHz) where the integrated VCO outperforms the VCXO module or tunable crystal used in PLL1.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| LMK04816 | WQFN (64) | 9.00 mm × 9.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
Simplified Schematic
4 Revision History
Changes from B Revision (April 2013) to C Revision
- Added Pin Configuration and Functions section, ESD Ratings table, Thermal Information table, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation section, Power Supply Recommendations section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information section Go
- Changed organization of Detailed Description section for improved readability. Go
- Added Typical Application section for expanded example of device use.Go
Changes from A Revision (April 2013) to B Revision
- Changed layout of National Data Sheet to TI format Go