SNAS828A february 2022 – june 2023 LMK1D1208I
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|40
Orderable Information
9.5 Programming
The LMK1D1208I uses I2C to program the states of its eight output drivers. See I2C for more information on the I2C features and address assignment, and Register Maps for the list of programmable registers.
Table 9-9 Command Code Definition
| BIT | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| 7 | 0 = Block Read or Block Write operation 1 = Byte Read or Byte Write operation |
| (6:0) | Register address for Byte operations, or starting register address for Block, operations |
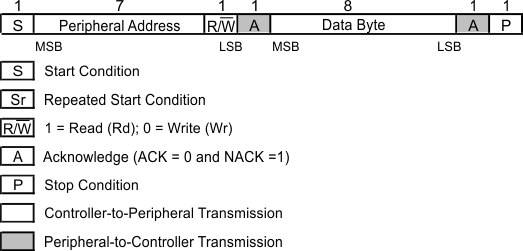 Figure 9-7 Generic Programming Sequence
Figure 9-7 Generic Programming Sequence Figure 9-8 Byte Write Protocol
Figure 9-8 Byte Write Protocol Figure 9-9 Byte Read Protocol
Figure 9-9 Byte Read Protocol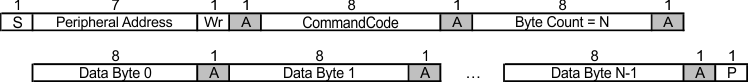 Figure 9-10 Block Write Protocol
Figure 9-10 Block Write Protocol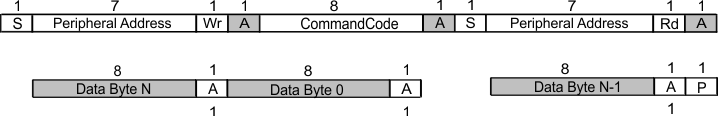 Figure 9-11 Block Read Protocol
Figure 9-11 Block Read Protocol