SNOSAT7G August 2007 – October 2015 LMP7300
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN differential | ±VS | V | ||
| Supply voltage (VS = V+ – V−) | 13.6 | V | ||
| Voltage at input/output pins | V+ + 0.3 | V− − 0.3 | V | |
| Soldering information | Infrared or convection (20 s) | 235 | °C | |
| Wave soldering lead temperature (10 s) | 260 | °C | ||
| Junction temperature, TJ(2) | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±250 | |||
| Machine model | ±200 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature(2) | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
| Supply Voltage (VS = V+ – V−) | 2.7 | 12 | V | ||
(1) Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is intended to be functional, but specific performance is not ensured. For ensured specifications and the test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics Tables.
(2) The maximum power dissipation is a function of TJ(MAX), θJA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is PD = (TJ(MAX) – TA)/θJA. All numbers apply for packages soldered directly onto a PC Board.
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LMP7300 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGK (VSSOP) | D (SOIC) | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance(2) | 175.5 | 121.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 66.1 | 67.5 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 95.6 | 61.5 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 10 | 18.3 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 94.2 | 61 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953..
(2) The maximum power dissipation is a function of TJ(MAX), θJA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is PD = (TJ(MAX) – TA)/ θJA. All numbers apply for packages soldered directly onto a PC Board.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics: 2.7-V
Unless otherwise specified, all limits are ensured for TA = 25°C, V+ = 2.7 V, V− = 0 V, and VCM = V+/2, RPULLUP = 100 kΩ, CLOAD = 10 pF.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | Supply Current | RPULLUP = Open | TA = 25°C | 9 | 12 | μA | |
| TJ = TA | 17 | ||||||
| COMPARATOR | |||||||
| VOS | Input Offset Voltage | VCM = V+/2 SOIC | TA = 25°C | ±0.07 | ±0.75 | mV | |
| TJ = TA | ±2 | ||||||
| VCM = V+/2 VSSOP | TA = 25°C | ±0.07 | ±1 | mV | |||
| TJ = TA | ±2.2 | ||||||
| TCVOS | Input Offset Average Drift | See(6) | 1.8 | μV/°C | |||
| IB | Input Bias Current(5) | |VID| < 2.5 V | TA = 25°C | 1.2 | 3 | nA | |
| TJ = TA | 4 | ||||||
| IOS | Input Offset Current | 0.15 | 0.5 | nA | |||
| CMRR | Common Mode Rejection Ratio | 1 V < VCM < 2.7 V | 80 | 100 | dB | ||
| PSRR | Power Supply Rejection Ratio | V+ = 2.7 V to 12 V | 80 | 100 | dB | ||
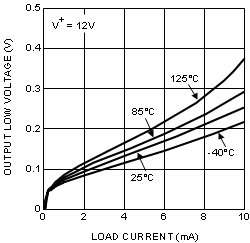
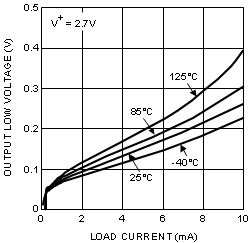
| VOL | Output Low Voltage | ILOAD = 10 mA | TA = 25°C | 0.25 | 0.4 | V | |
| TJ = TA | 0.5 | ||||||
| ILEAK | Output Leakage Current | Comparator Output in High State | 1 | pA | |||
| HCLIN | Hysteresis Control Voltage Linearity | 0 < Ref-HYSTP,N < 25 mV | 1 | mV/V | |||
| 25 mV < Ref-HYSTP,N < 100 mV | 0.950 | ||||||
| IHYS | Hysteresis Leakage Current | TA = 25°C | 1.2 | 3 | nA | ||
| TJ = TA | 4 | ||||||
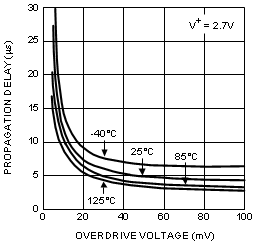
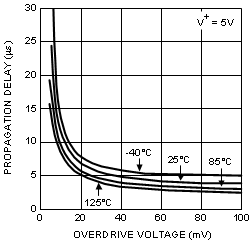
| TPD | Propagation Delay (High to Low) |
Overdrive = 10 mV, CL = 10 pF | 12 | 17 | μs | ||
| Overdrive = 100 mV, CL = 10 pF | 4.5 | 7.6 | |||||
| REFERENCE | |||||||
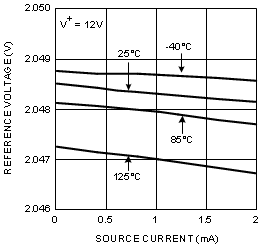
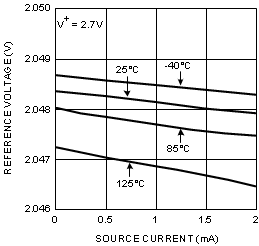
| VO | Reference Voltage | SOIC | 2.043 | 2.048 | 2.053 | V | |
| VSSOP | 2.043 | 2.048 | 2.056 | V | |||
| Line Regulation | VCC = 2.7 V to 12 V | 14 | 80 | μV/V | |||
| Load Regulation | IOUT = 0 to 1 mA | 0.2 | 0.5 | mV/mA | |||
| TCVREF/°C | Temperature Coefficient | −40°C to 125°C | 55 | ppm/°C | |||
| VN | Output Noise Voltage | 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz | 80 | μVPP | |||
| 10 Hz to 10 kHz | 100 | μVRMS | |||||
6.6 Electrical Characteristics: 5-V
Unless otherwise specified, all limits are ensured for TA = 25°C, V+ = 5 V, V− = 0 V, and VCM = V+/2, RPULLUP = 100 kΩ,CLOAD = 10 pF. (2)
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN(4) | TYP(3) | MAX(4) | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | Supply Current | RPULLUP = Open | TA = 25°C | 10 | 13 | μA | |
| TJ = TA | 18 | ||||||
| COMPARATOR | |||||||
| VOS | Input Offset Voltage | VCM = V+/2 SOIC | TA = 25°C | ±0.07 | ±0.75 | mV | |
| TJ = TA | ±2 | ||||||
| VCM = V+/2 VSSOP | TA = 25°C | ±0.07 | ±1 | mV | |||
| TJ = TA | ±2.2 | ||||||
| TCVOS | Input Offset Average Drift | See(6) | 1.8 | μV/°C | |||
| IB | Input Bias Current(5) | |VID| < 2.5 V | TA = 25°C | 1.2 | 3 | nA | |
| TJ = TA | 4 | ||||||
| IOS | Input Offset Current | 0.15 | 0.5 | nA | |||
| CMRR | Common Mode Rejection Ratio | 1 ≤ VCM ≤ 5 V | 80 | 100 | dB | ||
| PSRR | Power Supply Rejection Ratio | V+ = 2.7 V to 12 V | 80 | 100 | dB | ||
| VOL | Output Voltage Low | ILOAD = 10 mA | 0.25 | 0.4 | V | ||
| ILEAK | Output Leakage Current | Comparator Output in High State | 1 | pA | |||
| HCLIN | Hysteresis Control Voltage Linearity | 0 < Ref-VHYSTP,N < 25 mV | 1 | mV/V | |||
| 25 mV < Ref-VHYSTP,N < 100 mV | 0.950 | ||||||
| IHYS | Hysteresis Leakage Current | TA = 25°C | 1.2 | 3 | nA | ||
| TJ = TA | 4 | ||||||
| TPD | Propagation Delay (High to Low) |
Overdrive = 10 mV, CL = 10 pF | 12 | 15 | μs | ||
| Overdrive = 100 mV, CL = 10 pF | 4 | 7 | |||||
| REFERENCE | |||||||
| VO | Reference Voltage | SOIC | 2.043 | 2.048 | 2.053 | V | |
| VSSOP | 2.043 | 2.048 | 2.056 | V | |||
| Line Regulation | VCC = 2.7 V to 12 V | 14 | 80 | μV/V | |||
| Load Regulation | IOUT = 0 to 1 mA | 0.2 | 0.5 | mV/mA | |||
| TCVREF/°C | Temperature Coefficient | −40°C to 125°C | 55 | ppm/°C | |||
| VN | Output Noise Voltage | 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz | 80 | μVPP | |||
| 10 Hz to 10 kHz | 100 | μVRMS | |||||
6.7 Electrical Characteristics: 12-V
Unless otherwise specified, all limits are ensured for TA = 25°C, V+ = 12 V, V− = 0 V, and VCM = V+/2, RPULLUP = 100 kΩ,CLOAD = 10 pF. (2)
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | Supply Current | RPULLUP = Open | TA = 25°C | 11 | 14 | µA | |
| TJ = TA | 20 | ||||||
| COMPARATOR | |||||||
| VOS | Input Offset Voltage | VCM = V+/2 SOIC | TA = 25°C | ±0.08 | ±0.75 | mV | |
| TJ = TA | ±2 | ||||||
| VCM = V+/2 VSSOP | TA = 25°C | ±0.08 | ±1 | mV | |||
| TJ = TA | ±2.2 | ||||||
| TCVOS | Input Offset Average Drift | See(6) | 1.8 | μV/°C | |||
| IB | Input Bias Current(5) | |VID| > 2.5 V | TA = 25°C | 1.2 | 3 | nA | |
| TJ = TA | 4 | ||||||
| IOS | Input Offset Current | 0.15 | 0.5 | nA | |||
| CMRR | Common Mode Rejection Ratio | 1 V ≤ VCM ≤ 12 V | 80 | 100 | dB | ||
| PSRR | Power Supply Rejection Ratio | V+ = 2.7 V to 12 V | 80 | 100 | dB | ||
| VOL | Output Voltage Low | ILOAD = 10 mA | 0.25 | 0.4 | V | ||
| ILEAK | Output Leakage Current | Comparator Output in High State | 1 | pA | |||
| HCLIN | Hysteresis Control Voltage Linearity | 0 < Ref-V+HYSTP, N < 25 mV | 1 | mV/V | |||
| 25 mV < Ref-V+HYSTP, N < 100 mV | 0.95 | ||||||
| IHYS | Hysteresis Leakage Current | TA = 25°C | 1.2 | 3 | nA | ||
| TJ = TA | 4 | ||||||
| TPD | Propagation Delay (High to Low) |
Overdrive = 10 mV, CL = 10 pF | 11 | 15 | μs | ||
| Overdrive = 100 mV, CL = 10 pF | 3.5 | 6.8 | |||||
| REFERENCE | |||||||
| VO | Reference Voltage | TJ = 25°C SOIC | 2.043 | 2.048 | 2.053 | V | |
| TJ = 25°C VSSOP | 2.043 | 2.048 | 2.056 | V | |||
| Line Regulation | VCC = 2.7 V to 12 V | 14 | 80 | μV/V | |||
| Load Regulation | IOUT = 0 to 1 mA | 0.2 | 0.5 | mV/mA | |||
| TCVREF/°C | Temperature Coefficient | −40°C to 125°C | 55 | ppm/°C | |||
| VN | Output Noise Voltage | 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz | 80 | μVPP | |||
| 10 Hz to 10 kHz | 100 | μVRMS | |||||
(1) If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, contact the Texas Instruments Sales Office/ Distributors for availability and specifications.
(2) Electrical Table values apply only for factory testing conditions at the temperature indicated. Factory testing conditions result in very limited self-heating of the device such that TJ = TA. No ensured specification of parametric performance is indicated in the electrical tables under conditions of internal self-heating where TJ > TA.
(3) Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm as determined at the time of characterization. Actual typical values may vary over time and will also depend on the application and configuration. The typical values are not tested and are not ensured on shipped production material.
(4) Limits are 100% production tested at 25°C. Limits over the operating temperature range are specified through correlations using statistical quality control (SQC) method.
(5) Positive current corresponds to current flowing into the device.
(6) Offset voltage average drift determined by dividing the change in VOS at temperature extremes, by the total temperature change.
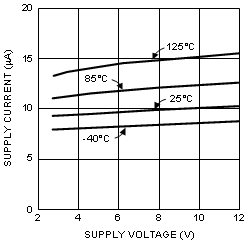
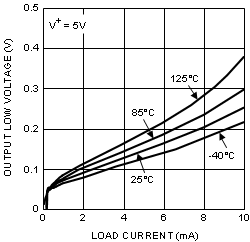
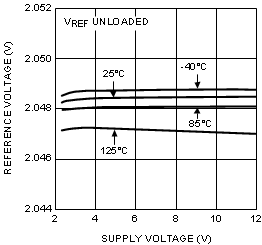
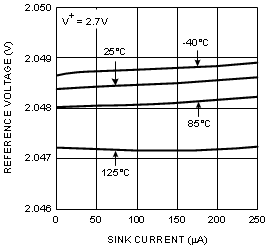
6.8 Typical Characteristics