SNAS633A March 2014 – September 2014 LMP93601
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Simplified Thermopile Array System Diagram
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Data Format
- 8.3.2 Transfer Function
- 8.3.3 Input Routing Mux
- 8.3.4 Programmable Gain Amplifier
- 8.3.5 PGA Bypass Mode
- 8.3.6 Over-Range Detection
- 8.3.7 Analog-To-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 8.3.8 Programmable Digital Filters
- 8.3.9 Common Mode Voltage Generator
- 8.3.10 Low Drop-Out Regulator (LDO)
- 8.3.11 External Clock
- 8.3.12 Operating Modes
- 8.3.13 Data Ready Function (DRDYB)
- 8.3.14 Synchronous Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 8.3.15 Power Management Mode; Standby, Conversion and Shutdown
- 8.3.16 Power-On Sequence and Reset (POR) Function
- 8.3.17 Brown-Out Detection Function
- 8.3.18 Reset Function
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Maps
- 8.7 Multi Byte Access (Auto Increment) Mode
- 8.8 Multi-Channel Data Read
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- NHZ|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
To achieve high noise performance of the LMP93601, particular attention must be paid to the layout of the input signals, inputs INPx and INNx. To avoid introduction of differential noise into the pins, the input traces must lay out symmetrically.
Proper power-supply decoupling is required on both AVDD and IOVDD. The Supply pins should be decoupled with at least a 0.1 μF bypass capacitor each. The bypass capacitors should be placed as close to the power-supply pins as possible with a low impedance connection. For very sensitive systems, or for systems in harsh noise environments, avoiding the use of vias for connecting the bypass capacitor may offer superior bypass and noise immunity.
It is recommended that in the layout, analog components [such as ADCs, amplifiers, references, digital-to-analog converters (DACs), and analog MUXs] be separated from digital components [such as microcontrollers, complex programmable logic devices (CPLDs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), radio frequency (RF) transceivers, universal serial bus (USB) transceivers, and switching regulators]. The best placement for each application is unique to the geometries, components, and PCB fabrication capabilities employed. That is, there is no single layout that is perfect for every design and careful consideration must always be used when designing with any analog component.
TI recommends placing 47 Ω resistors in series with all digital input and output pins (CS, SCLK, DIN, DOUT/DRDY, and DRDY). This resistance smooths sharp transitions, suppresses overshoot, and offers some overvoltage protection. Care must be taken to still meet all SPI timing requirements because the additional resistors interact with the bus capacitances present on the digital signal lines.
TI also strongly recommends that digital components, especially RF portions, be kept as far as practically possible from analog circuitry in a given system. Additionally, one should minimize the distance that digital control traces run through analog areas and avoid placing these traces near sensitive analog components. Digital return currents usually flow through a ground path that is as close as possible to the digital path. If a solid ground connection to a plane is not available, these currents may find paths back to the source that interfere with analog performance. The implications that layout has on the temperature-sensing functions are much more significant than for ADC functions.
The internal ADC reference supply of the LMP93601 requires a 1 µF high performance (low ESR & ESL) cap on the XCAP1. This cap must be placed in the immediate proximity of the pin. For best performance it is recommended that the DAP be connected to AGND. All three "GND" connections (AGND, DGND, and IOGND) must be connected to system ground and cannot be left floating.
11.2 Layout Example
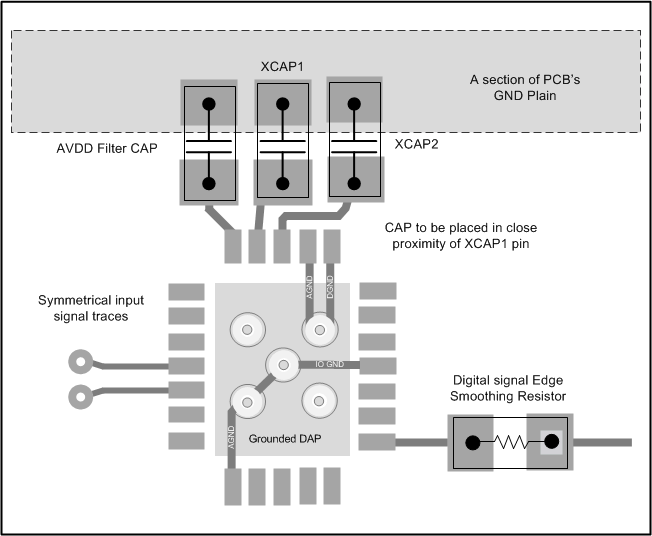 Figure 32. LMP93601 Layout Example
Figure 32. LMP93601 Layout Example