SNVSBR8D March 2020 – June 2022 LMQ61460
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 EN/SYNC Uses for Enable and VIN UVLO
- 8.3.2 EN/SYNC Pin Uses for Synchronization
- 8.3.3 Adjustable Switching Frequency
- 8.3.4 Clock Locking
- 8.3.5 PGOOD Output Operation
- 8.3.6 Internal LDO, VCC UVLO, and BIAS Input
- 8.3.7 Bootstrap Voltage and VCBOOT-UVLO (CBOOT Pin)
- 8.3.8 Adjustable SW Node Slew Rate
- 8.3.9 Spread Spectrum
- 8.3.10 Soft Start and Recovery From Dropout
- 8.3.11 Output Voltage Setting
- 8.3.12 Overcurrent and Short Circuit Protection
- 8.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.14 Input Supply Current
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RJR|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
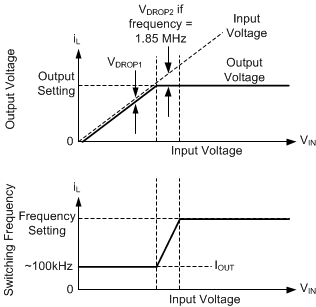
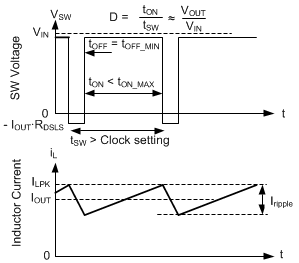
8.4.3.5 Dropout
Dropout operation is defined as any input-to-output voltage ratio that requires frequency to drop to achieve the required duty cycle. At a given clock frequency, duty cycle is limited by minimum off time. Once this limit is reached, if clock frequency were maintained, output voltage falls. Instead of allowing the output voltage to drop, the device extends on time past the end of the clock cycle until needed peak inductor current is achieved. The clock is allowed to start a new cycle once peak inductor current is achieved or once a pre-determined maximum on time, tON_MAX, of approximately 9 µs passes. As a result, once the needed duty cycle cannot be achieved at the selected clock frequency due to the existence of a minimum off time, frequency drops to maintain regulation. If input voltage is low enough so that output voltage cannot be regulated even with an on time of tON_MAX, output voltage drops to slightly below input voltage, VDROP1. For additional information on recovery from dropout, reference Figure 8-9.