SNVSC42A September 2023 – July 2024 LMQ64480-Q1 , LMQ644A0-Q1 , LMQ644A2-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Input Voltage Range (VIN)
- 7.3.2 Enable EN Pin and Use as VIN UVLO
- 7.3.3 Output Voltage Selection and Soft Start
- 7.3.4 SYNC Allows Clock Synchronization and Mode Selection
- 7.3.5 Clock Locking
- 7.3.6 Adjustable Switching Frequency
- 7.3.7 Power-Good Output Voltage Monitoring
- 7.3.8 Internal LDO, VCC UVLO, and BIAS Input
- 7.3.9 Bootstrap Voltage and VCBOOT-UVLO (CB1 and CB2 Pin)
- 7.3.10 CONFIG Device Configuration Pin
- 7.3.11 Spread Spectrum
- 7.3.12 Soft Start and Recovery From Dropout
- 7.3.13 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
- 7.3.14 Hiccup
- 7.3.15 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Choosing the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2 Setting the Output Voltage
- 8.2.2.3 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 BOOT Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 VCC
- 8.2.2.8 CFF and RFF Selection
- 8.2.2.9 SYNCHRONIZATION AND MODE
- 8.2.2.10 External UVLO
- 8.2.2.11 Typical Thermal Performance
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RXA|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
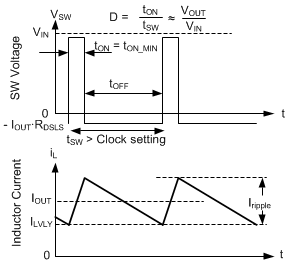
7.4.3.4 Minimum On-time (High Input Voltage) Operation
The LMQ644xx continues to regulate output voltage. This is true even if the input-to-output voltage ratio requires an on-time less than the minimum on-time of the chip with a given clock setting. This is accomplished using valley current control. At all times, the compensation circuit dictates both a maximum peak inductor current and a maximum valley inductor current. If, for any reason, valley current is exceeded, the clock cycle is extended until valley current falls below that determined by the compensation circuit. If it is not operating in current limit, the maximum valley current is set above the peak inductor current. This prevents valley control from being used unless there is a failure to regulate using peak current only. If the input-voltage to output-voltage ratio is too high, even though current exceeds the peak value dictated by compensation, the high-side device cannot be turned off quickly enough to regulate output voltage. See tON_MIN in the Electrical Characteristics. As a result, the compensation circuit reduces both peak and valley current. After a low enough current is selected by the compensation circuit, valley current matches that being commanded by the compensation circuit. Under these conditions, the low-side device is kept on and the next clock cycle is prevented from starting until inductor current drops below the desired valley current. Because on-time is fixed at its minimum value, this type of operation resembles that of a device using a COT control scheme. See Figure 7-21.