SNVS731B September 2011 – June 2019 LMR12010
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDC|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1.3 Input Capacitor
An input capacitor is necessary to ensure that VIN does not drop excessively during switching transients. The primary specifications of the input capacitor are capacitance, voltage, RMS current rating, and equivalent series inductance (ESL). The recommended input capacitance is 10 µF, although 4.7 µF works well for input voltages below 6 V. The input voltage rating is specifically stated by the capacitor manufacturer. Make sure to check any recommended deratings and also verify if there is any significant change in capacitance at the operating input voltage and the operating temperature. The input capacitor maximum RMS input current rating (IRMS-IN) must be greater than:
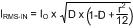
It can be shown from Equation 19 that maximum RMS capacitor current occurs when D = 0.5. Always calculate the RMS at the point where the duty cycle, D, is closest to 0.5. The ESL of an input capacitor is usually determined by the effective cross sectional area of the current path. A large leaded capacitor will have high ESL and a 0805 ceramic chip capacitor will have very low ESL. At the operating frequencies of the LMR12010, certain capacitors may have an ESL so large that the resulting impedance (2πfL) will be higher than that required to provide stable operation. As a result, surface mount capacitors are strongly recommended. Sanyo POSCAP, Tantalum or Niobium, Panasonic SP or Cornell Dubilier ESR, and multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCC) are all good choices for both input and output capacitors and have very low ESL. For MLCCs TI recommends using X7R or X5R dielectrics. Consult capacitor manufacturer datasheet to see how rated capacitance varies over operating conditions.