SNVSB91C July 2019 – June 2020 LMR36506-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Enable, Start-up and Shutdown
- 8.3.2 External CLK SYNC (with MODE/SYNC)
- 8.3.3 Adjustable Switching Frequency (with RT)
- 8.3.4 Power-Good Output Operation
- 8.3.5 Internal LDO, VCC UVLO, and VOUT/BIAS Input
- 8.3.6 Bootstrap Voltage and VCBOOT-UVLO (CBOOT Terminal)
- 8.3.7 Output Voltage Selection
- 8.3.8 Spread Spectrum
- 8.3.9 Soft Start and Recovery from Dropout
- 8.3.10 Current Limit and Short Circuit
- 8.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.12 Input Supply Current
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 9.3 What to Do and What Not to Do
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RPE|9
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RPE|9
Orderable Information
8.4.3.2.1 Diode Emulation
Diode emulation prevents reverse current through the inductor which requires a lower frequency needed to regulate given a fixed peak inductor current. Diode emulation also limits ripple current as frequency is reduced. With a fixed peak current, as output current is reduced to zero, frequency must be reduced to near zero to maintain regulation.
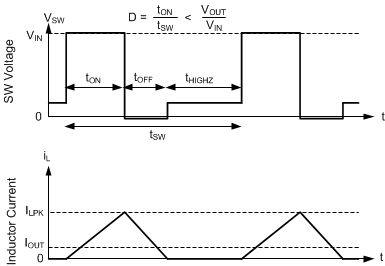
The LMR36506-Q1 has a minimum peak inductor current setting (ILPK (see IPEAK-MIN in the Electrical Characteristics) while in auto mode. Once current is reduced to a low value with fixed input voltage, on-time is constant. Regulation is then achieved by adjusting frequency. This mode of operation is called PFM mode regulation.