SLUSEP7 December 2022 LMR51440 , LMR51450
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Fixed Frequency Peak Current Mode Control
- 8.3.2 Adjustable Output Voltage
- 8.3.3 Enable
- 8.3.4 Switching Frequency
- 8.3.5 Power-Good Flag Output
- 8.3.6 Minimum ON-Time, Minimum OFF-Time, and Frequency Foldback
- 8.3.7 Bootstrap Voltage
- 8.3.8 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
- 8.3.9 Soft Start
- 8.3.10 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRR|12
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRR|12
Orderable Information
8.3.2 Adjustable Output Voltage
A precision 0.8-V reference voltage (VREF) is used to maintain a tightly regulated output voltage over the entire operating temperature range. The output voltage is set by a resistor divider from VOUT to the FB pin. TI recommends to use 1% tolerance resistors with a low temperature coefficient for the FB divider. Select the bottom-side resistor RFBB for the desired divider current and use Equation 1 to calculate top-side resistor RFBT. The recommend range for RFBT is 10 kΩ to 100 kΩ. A lower RFBT value can be used if pre-loading is desired to reduce VOUT offset in PFM operation. Lower RFBT reduces efficiency at very light load. Less static current goes through a larger RFBT and can be more desirable when light-load efficiency is critical. However, TI does not recommend RFBT larger than 1 MΩ because it makes the feedback path more susceptible to noise. Larger RFBT values require more carefully designed feedback path trace from the feedback resistors to the feedback pin of the device. The tolerance and temperature variation of the resistor divider network affect the output voltage regulation.
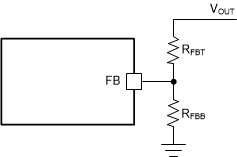 Figure 8-2 Output Voltage Setting
Figure 8-2 Output Voltage Setting