SLUSFS7 September 2024 LMR51603-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Output Voltage Setpoint
- 8.2.2.3 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.2.9 Replacing Non Sync Buck Converter
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.1 Fixed Frequency Peak Current Mode Control
The following operating description of the LMR51603-Q1 refers to the Functional Block Diagram and to the waveforms in Figure 7-1. The LMR51603-Q1 is a step-down synchronous buck converter with integrated high-side (HS) and low-side (LS) switches (synchronous rectifier). The LMR51603-Q1 supplies a regulated output voltage by turning on the high-side and low-side NMOS switches with controlled duty cycle. During high-side switch ON time, the SW pin voltage swings up to approximately VIN, and the inductor current, iL, increases with a linear slope of (VIN – VOUT) / L. When the high-side switch is turned off by the control logic, the low-side switch is turned on after an anti-shoot-through dead time. Inductor current discharges through the low-side switch with a slope of –VOUT / L. The control parameter of a buck converter is defined as Duty Cycle D = tON / TSW, where tON is the high-side switch ON time and TSW is the switching period. The converter control loop maintains a constant output voltage by adjusting the duty cycle D. In an ideal buck converter, where losses are ignored, D is proportional to the output voltage and inversely proportional to the input voltage: D = VOUT / VIN.
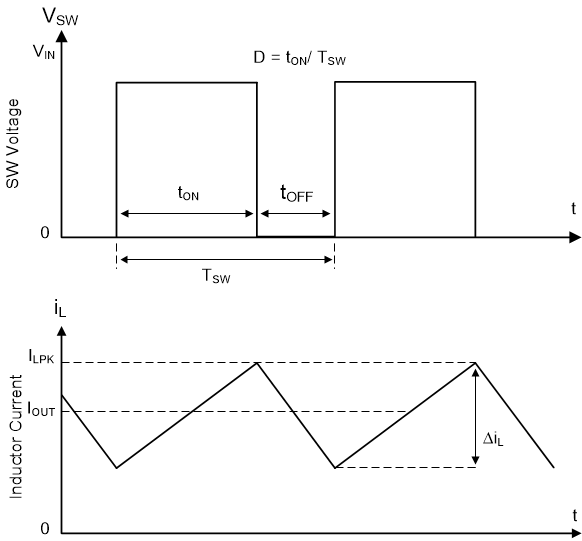 Figure 7-1 SW Node and Inductor Current Waveforms in Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM)
Figure 7-1 SW Node and Inductor Current Waveforms in Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM)The LMR51603-Q1 employs fixed-frequency peak-current mode control. A voltage feedback loop is used to get accurate DC voltage regulation by adjusting the peak-current command based on voltage offset. The peak inductor current is sensed from the high-side switch and compared to the peak current threshold to control the ON time of the high-side switch. The voltage feedback loop is internally compensated, which allows for fewer external components, making designing easy and providing stable operation when using a variety of output capacitors. The converter operates with fixed switching frequency at normal load conditions. During light-load condition, the LMR51603-Q1 operates in PFM mode to maintain high efficiency (PFM version) or in FPWM mode for low output voltage ripple, tight output voltage regulation, and constant switching frequency (FPWM version).