SNVSCJ3 December 2023 LMR66410 , LMR66420 , LMR66430
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Enable, Start-Up, and Shutdown
- 7.3.2 External CLK SYNC (With MODE/SYNC)
- 7.3.3 Adjustable Switching Frequency (with RT)
- 7.3.4 Power-Good Output Operation
- 7.3.5 Internal LDO, VCC, and VOUT/FB Input
- 7.3.6 Bootstrap Voltage and VBOOT-UVLO (BOOT Terminal)
- 7.3.7 Output Voltage Selection
- 7.3.8 Spread Spectrum
- 7.3.9 Soft Start and Recovery from Dropout
- 7.3.10 Current Limit and Short Circuit
- 7.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.12 Input Supply Current
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Synchronous Buck Regulator at 400 kHz
- 8.2.2 Design Requirements
- 8.2.3 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.4 Application Curves
- 8.3 Best Design Practices
- 8.4 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.5 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RXB|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.7 Output Voltage Selection
In the device family, an adjustable output or fixed output voltage option is configurable for every device variant (see Section 4). For an adjustable output, the user needs an external resistor divider connection between the output voltage node, the device FB pin, and the system GND, as shown in Figure 7-9. The adjustable output voltage operation uses a 1-V internal reference voltage. Refer to Section 8.2.3.2.1 for more details on how to adjust the output voltage.
When using the fixed-output configuration from the device family, simply connect the FB pin (identified as VOUT/FB pin for fixed-output variants in the rest of the data sheet) to the system output voltage node. See Section 4 for more details.
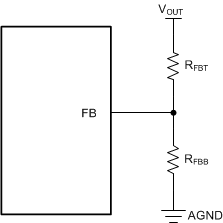 Figure 7-9 Setting
Output Voltage for Adjustable Output Variant
Figure 7-9 Setting
Output Voltage for Adjustable Output VariantIn adjustable output voltage variants, an additional feedforward capacitor, CFF, in parallel with the RFBT, can be used to optimize the phase margin and transient response. See Section 8.2.3.8 for more details. No additional resistor divider or feedforward capacitor is needed in fixed-output variants.