SNVS633K January 2010 – April 2019 LMZ10505
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- NDW|7
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10.3 Estimate Power Dissipation and Thermal Considerations
Use the current derating curves in the Typical Characteristics section to obtain an estimate of power loss (PIC_LOSS). For the design case of VIN = 5 V, VOUT = 2.5 V, IOUT = 5 A, TA(MAX) = 85°C , and TJ(MAX) = 125°C, the device must see a thermal resistance from case to ambient (θCA) of less than:
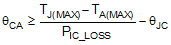
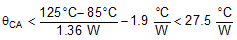
Given the typical thermal resistance from junction to case (θJC) to be 1.9°C/W (typ.). Continuously operating at a TJ greater than 125°C will have a shorten life span.
To reach θCA = 27.5°C/W, the PCB is required to dissipate heat effectively. With no airflow and no external heat, a good estimate of the required board area covered by 1-oz. copper on both the top and bottom metal layers is:
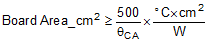
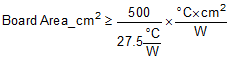
As a result, approximately 18 square cm of 1-oz. copper on top and bottom layers is required for the PCB design.
The PCB copper heat sink must be connected to the exposed pad (EP). Approximately thirty six, 8 mils thermal vias spaced 59 mils (1.5 mm) apart must connect the top copper to the bottom copper. For an extended discussion and formulations of thermal rules of thumb, refer to AN-2020 Thermal Design By Insight, Not Hindsight (SNVA419). For an example of a high thermal performance PCB layout with θJA of 20°C/W, refer to the evaluation board application note AN-2022 LMZ1050x Evaluation Board (SNVA421) and for results of a study of the effects of the PCB designs, refer to AN-2026 Effect of PCB Design on Thermal Performance of SIMPLE SWITCHER Power Modules (SNVA424).