SNVSAQ4C December 2017 – March 2023 LMZM23601
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- SIL|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.5.1.1 Thermal Design
Thermal design is an important aspect of any power regulator design. Every supply dissipates some power, and providing sufficient copper area for proper heat dissipation is important. The package thermal resistance curves vs PCB copper area along with the power dissipation curves in GUID-CE8EB451-1634-4063-9734-9C45FBC8CE23.html#GUID-CE8EB451-1634-4063-9734-9C45FBC8CE23 can be used to estimate the necessary copper area for the design. Consider #X2806 and #X6004.

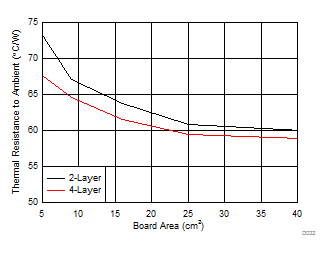 Figure 8-48 Package Thermal Resistance vs Board Copper Area
Figure 8-48 Package Thermal Resistance vs Board Copper AreaAs an example, consider a typical application of 24-V input 5-V output with 0.8 A of output current and estimate the required heat-sinking area. For this example consider a maximum ambient temperature TA_MAX of 75°C and no air flow or additional heat sinking besides the PCB layers. Calculate the maximum allowed package thermal resistance for this design specification.
From GUID-CE8EB451-1634-4063-9734-9C45FBC8CE23.html#GUID-CE8EB451-1634-4063-9734-9C45FBC8CE23, it can be seen that the power dissipation for 24-V input, 5-V output, and 0.8A load is 0.75 W. Based on #X2806, for this power dissipation level and 75°C maximum ambient temperature, the maximum package thermal resistance must be less than 66.7°C/W. To achieve this thermal resistance with a 2-layer board, the approximate area of the board copper must be at least 9 cm2.