SNVS481M November 2006 – December 2015 LP3910
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Tables
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: I2C Interface
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics: Li-Ion Battery Charger
- 7.8 Detection and Timing
- 7.9 Output Electrical Characteristics: CHG, STAT
- 7.10 Output Electrical Characteristics: NRST, IRQB, ONSTAT
- 7.11 Input Electrical Characteristics: USBSUSP, USBISEL
- 7.12 Input Electrical Characteristics: POWERACK, ONOFF, LDO2EN, BUCK1EN
- 7.13 Electrical Characteristics: LDO1 Low Dropout Linear Regulators
- 7.14 Electrical Characteristics: LDO2 Low Dropout Linear Regulator
- 7.15 Electrical Characteristics: Buck1 Converter
- 7.16 Electrical Characteristics: Buck2 Converter
- 7.17 Electrical Characteristics: Buck-Boost
- 7.18 Electrical Characteristics: ADC
- 7.19 I2C Timing Requirements
- 7.20 USB Timing Requirements
- 7.21 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Buck1, Buck2: Synchronous Step-Down Magnetic DC-DC Converters
- 8.3.2 Buck-Boost: Synchronous Buck-Boost Magnetic DC-DC Converter
- 8.3.3 Linear Low Dropout Regulators (LDOs)
- 8.3.4 Li-Ion Linear Charger
- 8.3.5 ADC
- 8.3.6 Interrupt Request Output
- 8.3.7 Power-On-Reset
- 8.3.8 Thermal Shutdown and Thermal Alarm
- 8.3.9 NRST Pin
- 8.3.10 Operation Without I2C Interface
- 8.3.11 I2C Master Power Concern
- 8.3.12 System Operation When the Load Current Exceeds the USB or Adapter Current Limit
- 8.3.13 Power Routing
- 8.3.14 Battery Monitor
- 8.3.15 External Power and Battery Detection
- 8.3.16 USB Suspend Mode
- 8.3.17 Setting the USB Current Limit
- 8.3.18 Control Registers
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 LDO1 Control Register
- 8.6.2 BATTLOW Register (04)H Battery Low Alarm Register
- 8.6.3 PON Register (00)H Power-On Event Register
- 8.6.4 CHCTL Register (01)H Charger Control Register
- 8.6.5 CHSPV Register (02)H Charger Supervisor Register
- 8.6.6 ILIMIT Register (03)H Current Limit Register
- 8.6.7 ADCC Register (0a)H ADC Control Register
- 8.6.8 ADCD Register (0b)H ADC Output Data Register
- 8.6.9 IMR Register (0c)H Interrupt Mask Register
- 8.6.10 IRQ Register (0d)H Interrupt Request Register
- 8.6.11 LDO1 Control Register (08)H
- 8.6.12 LDO2 Control Register
- 8.6.13 Buck1, Buck2 Control Registers and BUCK1EN Pin
- 8.6.14 Buck-Boost Control Register
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- NJV|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
For good performance of the circuit, it is essential to place the input and output capacitors very close to the circuit, using wide routing for the traces to allow high currents. Sensitive components must be placed far from those components with high pulsating current, and decoupling capacitors must be placed close to circuit VIN pins. Digital and analog grounds must be routed separately and connected together in a star connection. It is good practice to minimize high current and switching current paths.
11.1.1 LDO Regulators
Place the filter capacitors very close to the input and output pins. Use large trace width for high current-carrying traces and the returns to ground.
11.1.2 Buck and Buck-Boost Regulators
Place the supply bypass, filter capacitor, and inductor close together, keeping the traces short. The traces between these components carry relatively high switching current and act as antennas. Following these rules reduces radiated noise. Arrange the components so that the switching current loops curl in the same direction.
Connect the buck ground and the ground of the capacitors together using generous component-side copper fill as a pseudo-ground plane. Connect the grounds to the general board system ground plane at a single point. Place the pseudo-ground plane below these components and then have it tied to system ground of the output capacitor outside of the current loops. This prevents the switched current from injecting noise into the system ground. These components, along with the inductor and output, must be placed on the same side of the circuit board, and their connections must be made on the same layer.
Route the noise sensitive traces such as the voltage feedback path away from the inductor. This is done by routing it on the bottom layer or by adding a grounded copper area between switching node and feedback path. Noisy traces between the power components and keep any digital lines away from this section. Keep the feedback node as small as possible so that the ground pin and ground traces shield the feedback node from the SW or buck output.
Use wide traces between the power components and for power connections to the DC-DC converter circuit. This reduces voltage errors caused by resistive losses.
11.2 Layout Example
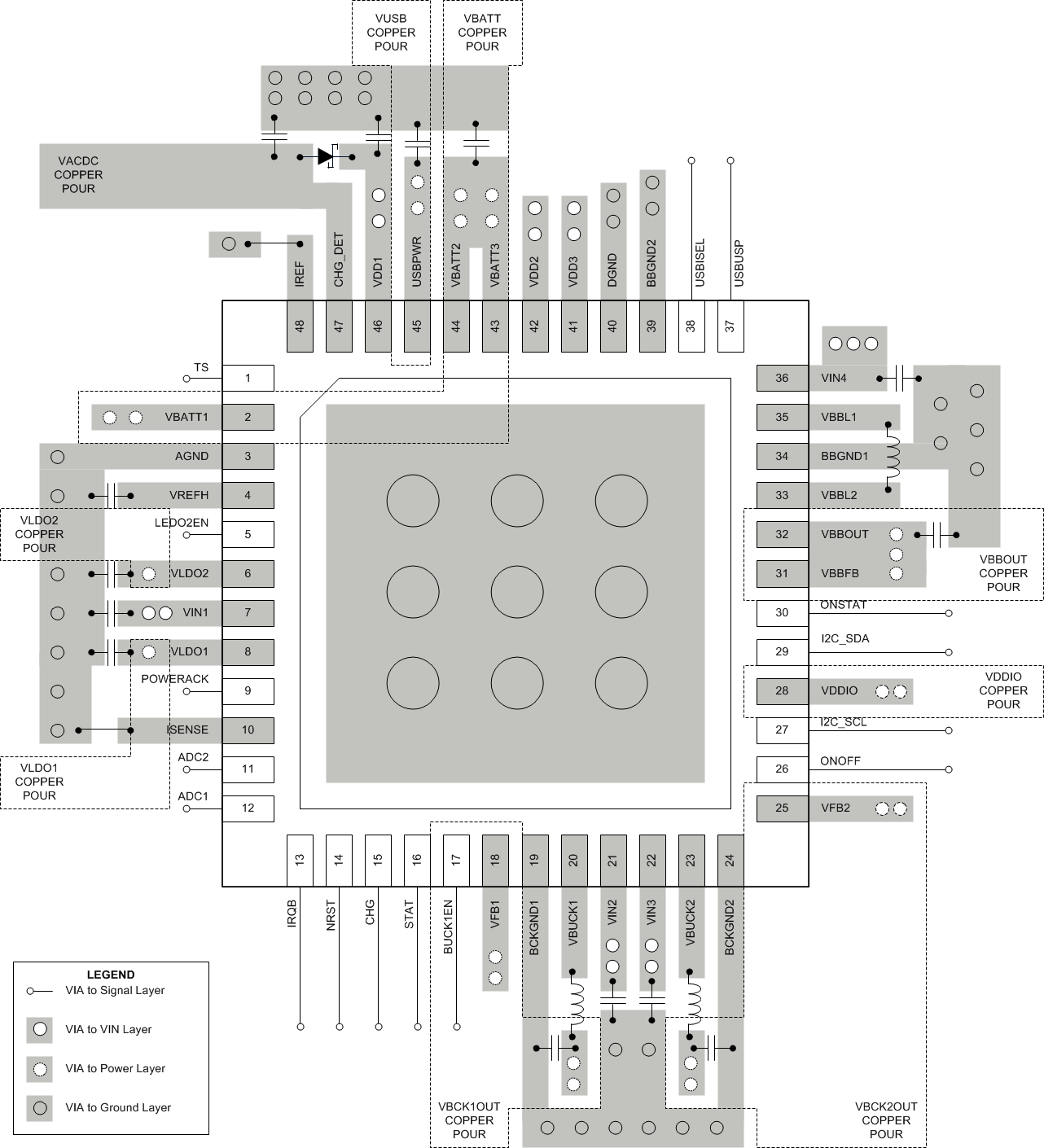 Figure 84. LP3910 Layout Example
Figure 84. LP3910 Layout Example
11.3 Thermal Performance of the WQFN Package
The LP3910 is a monolithic device with integrated power FETs. For that reason, it is important to pay special attention to the thermal impedance of the WQFN package and to the PCB layout rules in order to maximize power dissipation of the WQFN package.
The WQFN package is designed for enhanced thermal performance and features an exposed die attach pad at the bottom center of the package that creates a direct path to the PCB for maximum power dissipation. Compared to the traditional leaded packages where the die attach pad is embedded inside the molding compound, the WQFN reduces one layer in the thermal path.
The thermal advantage of the WQFN package is fully realized only when the exposed die-attach pad is soldered down to a thermal land on the PCB board with thermal vias planted underneath the thermal land. Based on thermal analysis of the WQFN package, the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance (RθJA) can be improved by a factor of two when the die attach pad of the WQFN package is soldered directly onto the PCB with thermal land and thermal vias, as opposed to an alternative with no direct soldering to a thermal land. Typical pitch and outer diameter for thermal vias are 1.27 mm and 0.33 mm, respectively. Typical copper via barrel plating is 1 oz., although thicker copper may be used to further improve thermal performance. The LP3910 die attach pad is connected to the substrate of the device and therefore, the thermal land and vias on the PCB board need to be connected to ground (GND pin).
For more information on board layout techniques, refer to AN-1187 Leadless Leadframe Package (LLP) (SNOA401). This application note also discusses package handling, solder stencil, and the assembly process.