SLVSH53 December 2023 MCT8315Z
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Output Stage
- 8.3.2 PWM Control Mode (1x PWM Mode)
- 8.3.3 Device Interface Modes
- 8.3.4 Step-Down Mixed-Mode Buck Regulator
- 8.3.5 AVDD Linear Voltage Regulator
- 8.3.6 Charge Pump
- 8.3.7 Slew Rate Control
- 8.3.8 Cross Conduction (Dead Time)
- 8.3.9 Propagation Delay
- 8.3.10 Pin Diagrams
- 8.3.11 Active Demagnetization
- 8.3.12 Cycle-by-Cycle Current Limit
- 8.3.13 Hall Comparators (Analog Hall Inputs)
- 8.3.14 Advance Angle
- 8.3.15 FGOUT Signal
- 8.3.16
Protections
- 8.3.16.1 VM Supply Undervoltage Lockout (NPOR)
- 8.3.16.2 AVDD Undervoltage Lockout (AVDD_UV)
- 8.3.16.3 Buck Undervoltage Lockout (BUCK_UV)
- 8.3.16.4 VCP Charge Pump Undervoltage Lockout (CPUV)
- 8.3.16.5 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 8.3.16.6 Overcurrent Protection (OCP)
- 8.3.16.7 Buck Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.16.8 Motor Lock (MTR_LOCK)
- 8.3.16.9 Thermal Warning (OTW)
- 8.3.16.10 Thermal Shutdown (OTSD)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 SPI Communication
- 8.6 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RRY|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RRY|32
Orderable Information
8.3.11 Active Demagnetization
MCT8315Z family of devices has smart rectification features (active demagnetization) which decreases power losses in the device by reducing diode conduction losses. When this feature is enabled, the device automatically turns ON the corresponding MOSFET whenever it detects diode conduction. This feature can be configured with the MODE pins in hardware variants. In SPI device variants this can be configured through EN_ASR and EN_AAR bits. The smart rectification is classified into two categories of automatic synchronous rectification (ASR) mode and automatic asynchronous rectification (AAR) mode which are described in sections below.
The MCT8315Z device includes a high-side (AD_HS) and low-side (AD_LS) comparator which detects the negative flow of current in the device on each half-bridge. The AD_HS comparator compares the sense-FET output with the supply voltage (VM) threshold, whereas the AD_LS comparator compares with the ground (0-V) threshold. Depending upon the flow of current from OUTx to VM or PGND to OUTx, the AD_HS or the AD_LS comparator trips. This comparator provides a reference point for the operation of active demagnetization feature.
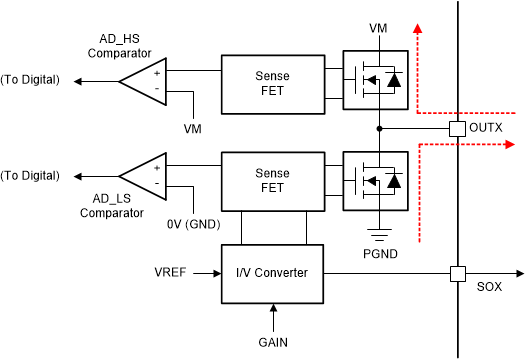 Figure 8-30 Active Demagnetization Operation
Figure 8-30 Active Demagnetization OperationTable 8-7 shows the configuration of ASR and AAR mode in theMCT8315Z device.
| MODE Type | MODE Pin (Hardware Variant) | ASR and AAR configuration | Hall Configuration | Modulation | ASR and AAR Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode 1 | Connected to AGND | EN_ASR = 0, EN_AAR = 0 | Analog Hall Input | Asynchronous | ASR and AAR Disabled |
| Mode 2 | Connected to AGND with RMODE1 | EN_ASR = 0, EN_AAR = 0 | Digital Hall Input | Asynchronous | ASR and AAR Disabled |
| Mode 3 | Connected to AGND with RMODE2 | EN_ASR = 0, EN_AAR = 0 | Analog Hall Input | Synchronous | ASR and AAR Disabled |
| Mode 4 | Hi-Z | EN_ASR = 0, EN_AAR = 0 | Digital Hall Input | Synchronous | ASR and AAR Disabled |
| Mode 5 | Connected to AVDD with RMODE2 | EN_ASR = 1, EN_AAR = 1 | Analog Hall Input | Synchronous | ASR and AAR Enabled |
| Mode 6 | Connected to AVDD with RMODE1 | EN_ASR = 1, EN_AAR = 1 | Digital Hall Input | Synchronous | ASR and AAR Enabled |
| Mode 7 | Connected to AVDD |