SBOSAC7A february 2023 – july 2023 OPA1633
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DGN|8
Orderable Information
8.4.1.1 PowerPAD™ Integrated Circuit Package Design Considerations
The OPA1633 is available in a thermally-enhanced PowerPAD integrated circuit package. This package is constructed using a downset leadframe upon which the die is mounted (see Figure 8-5(a) and Figure 8-5(b)). This arrangement results in the lead frame being exposed as a thermal pad on the underside of the package (see Figure 8-5(c)). Because this thermal pad has direct thermal contact with the die, excellent thermal performance can be achieved by providing a good thermal path away from the thermal pad.
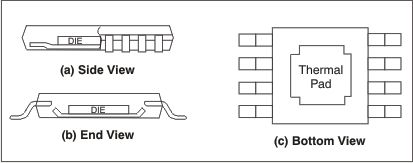 Figure 8-5 Views of
the Thermally-Enhanced Package
Figure 8-5 Views of
the Thermally-Enhanced PackageThe PowerPAD integrated circuit package allows for both assembly and thermal management in one manufacturing operation. During the surface-mount solder operation (when the leads are being soldered), the thermal pad must be soldered to a copper area underneath the package. Through the use of thermal paths within this copper area, heat can be conducted away from the package into either a ground plane or other heat-dissipating device. Soldering the thermal pad to the PCB is always required, even with applications that have low power dissipation. The PowerPAD integrated circuit package provides the necessary thermal and mechanical connection between the lead frame die pad and the PCB.