SBOS463B December 2008 – February 2020 OPA2333-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.1 Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage
The OPA2333-Q1 input common-mode voltage range extends 0.1 V beyond the supply rails. The device is designed to cover the full range without the troublesome transition region found in some other rail-to-rail amplifiers.
Normally, input bias current is approximately 70 pA; however, input voltages exceeding the power supplies can cause excessive current to flow into or out of the input pins. Momentary voltages greater than the power supply can be tolerated if the input current is limited to 10 mA. This limitation is easily accomplished with an input resistor (see Figure 18).
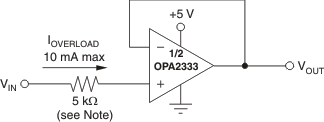
NOTE:
A current-limiting resistor required if the input voltage exceeds the supply rails by ≥ 0.5 V.