SBOS309E August 2004 – December 2024 OPA2830
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configurations and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics VS = ±5V
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics VS = 5V
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics VS = 3V
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5V
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5V, Differential Configuration
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics: VS = 5V
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics: VS = 5V, Differential Configuration
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics: VS = 3V
- 6.13 Typical Characteristics: VS = 3V, Differential Configuration
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Wideband Voltage-Feedback Operation
- 8.1.2 Single-Supply ADC Interface
- 8.1.3 DC Level-Shifting
- 8.1.4 AC-Coupled Output Video Line Driver
- 8.1.5 Noninverting Amplifier With Reduced Peaking
- 8.1.6 Single-Supply Active Filter
- 8.1.7 Differential Low-Pass Active Filters
- 8.1.8 High-Pass Filters
- 8.1.9 High-Performance DAC Transimpedance Amplifier
- 8.1.10 Operating Suggestions Optimizing Resistor Values
- 8.1.11 Bandwidth vs Gain: Noninverting Operation
- 8.1.12 Inverting Amplifier Operation
- 8.1.13 Output Current and Voltages
- 8.1.14 Driving Capacitive Loads
- 8.1.15 Distortion Performance
- 8.1.16 Noise Performance
- 8.1.17 DC Accuracy and Offset Control
- 8.2 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.3 Layout
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
- DGK|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.1.9 High-Performance DAC Transimpedance Amplifier
High-frequency video digital-to-analog converters (DACs) sometimes benefit from a low distortion output amplifier to retain the SFDR performance into real-world loads. Figure 8-14 shows a differential output drive implementation. The diagram shows one or more of the signal output currents connected into one or more of the virtual ground summing junctions of the OPA2830, which is set up as a transimpedance stage or I-V converter. If the DAC outputs require to terminate to a compliance voltage other than ground for operation, the appropriate voltage level can be applied to the noninverting input of the OPA2830. The dc gain for this circuit is equal to RF. At high frequencies, the DAC output capacitance (CD in Figure 8-14) produces a zero in the noise gain for the OPA2830 that can cause peaking in the closed-loop frequency response. CF is added across RF to compensate for this noise gain peaking. To achieve a flat transimpedance frequency response, the pole in each feedback network can be set to:
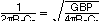
which gives a cutoff frequency f–3dB of approximately:
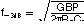
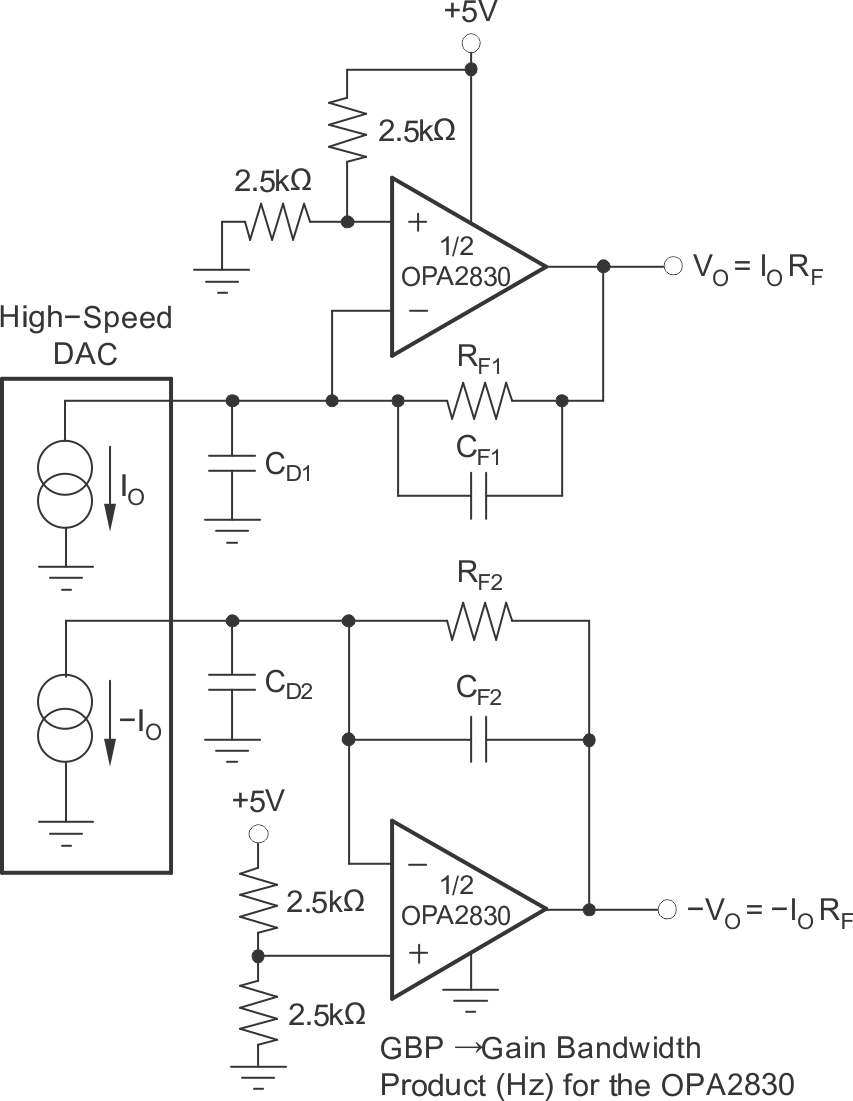 Figure 8-14 High-Speed DAC—Differential Transimpedance Amplifier
Figure 8-14 High-Speed DAC—Differential Transimpedance Amplifier