SBOS557E August 2011 – April 2018 OPA170 , OPA2170 , OPA4170
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.8 Typical Characteristics
VS = ±18 V, VCM = VS / 2, RLOAD = 10 kΩ connected to VS / 2, and CL = 100 pF, (unless otherwise noted)Table 1. Characteristic Performance Measurements
| DESCRIPTION | FIGURE |
|---|---|
| Offset Voltage Production Distribution | Figure 1 |
| Offset Voltage Drift Distribution | Figure 2 |
| Offset Voltage vs Temperature | Figure 3 |
| Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Voltage | Figure 4 |
| Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Voltage (Upper Stage) | Figure 5 |
| Offset Voltage vs Power Supply | Figure 6 |
| IB and IOS vs Common-Mode Voltage | Figure 7 |
| Input Bias Current vs Temperature | Figure 8 |
| Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current (Maximum Supply) | Figure 9 |
| CMRR and PSRR vs Frequency (Referred-to-Input) | Figure 10 |
| CMRR vs Temperature | Figure 11 |
| PSRR vs Temperature | Figure 12 |
| 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Noise | Figure 13 |
| Input Voltage Noise Spectral Density vs Frequency | Figure 14 |
| THD+N Ratio vs Frequency | Figure 15 |
| THD+N vs Output Amplitude | Figure 16 |
| Quiescent Current vs Temperature | Figure 17 |
| Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage | Figure 18 |
| Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs Frequency | Figure 19 |
| Closed-Loop Gain vs Frequency | Figure 20 |
| Open-Loop Gain vs Temperature | Figure 21 |
| Open-Loop Output Impedance vs Frequency | Figure 22 |
| Small-Signal Overshoot vs Capacitive Load (100-mV Output Step) | Figure 23, Figure 24 |
| No Phase Reversal | Figure 25 |
| Positive Overload Recovery | Figure 26 |
| Negative Overload Recovery | Figure 27 |
| Small-Signal Step Response (100 mV) | Figure 28, Figure 29 |
| Large-Signal Step Response | Figure 30, Figure 31 |
| Large-Signal Settling Time (10-V Positive Step) | Figure 32 |
| Large-Signal Settling Time (10-V Negative Step) | Figure 33 |
| Short-Circuit Current vs Temperature | Figure 34 |
| Maximum Output Voltage vs Frequency | Figure 35 |
| EMIRR IN+ vs Frequency | Figure 36 |
 Figure 1. Offset Voltage Production Distribution
Figure 1. Offset Voltage Production Distribution
 Figure 3. Offset Voltage vs Temperature
Figure 3. Offset Voltage vs Temperature
 Figure 5. Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 5. Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Voltage
(Upper Stage)
 Figure 7. IB and IOS vs Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 7. IB and IOS vs Common-Mode Voltage
 Figure 9. Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current (Maximum Supply)
Figure 9. Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current (Maximum Supply)
 Figure 11. CMRR vs Temperature
Figure 11. CMRR vs Temperature
 Figure 13. 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Noise
Figure 13. 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Noise
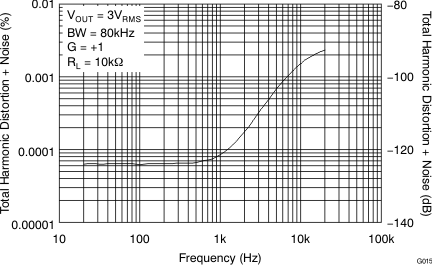 Figure 15. THD+N Ratio vs Frequency
Figure 15. THD+N Ratio vs Frequency
 Figure 17. Quiescent Current vs Temperature
Figure 17. Quiescent Current vs Temperature
 Figure 19. Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs Frequency
Figure 19. Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs Frequency
 Figure 21. Open-Loop Gain vs Temperature
Figure 21. Open-Loop Gain vs Temperature

| 100-mV output step |
 Figure 25. No Phase Reversal
Figure 25. No Phase Reversal
 Figure 27. Negative Overload Recovery
Figure 27. Negative Overload Recovery
 Figure 29. Small-Signal Step Response (100 mV)
Figure 29. Small-Signal Step Response (100 mV)


A.
Figure 33. Large-Signal Settling Time
| 10-V negative step |
 Figure 35. Maximum Output Voltage vs Frequency
Figure 35. Maximum Output Voltage vs Frequency
 Figure 2. Offset Voltage Drift Distribution
Figure 2. Offset Voltage Drift Distribution
 Figure 4. Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 4. Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Voltage
 Figure 6. Offset Voltage vs Power Supply
Figure 6. Offset Voltage vs Power Supply
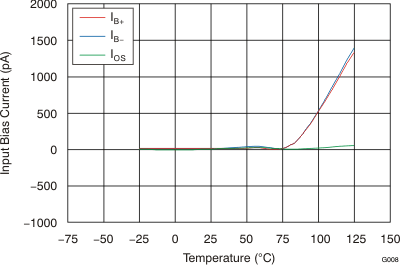 Figure 8. Input Bias Current vs Temperature
Figure 8. Input Bias Current vs Temperature
 Figure 10. CMRR and PSRR vs Frequency
Figure 10. CMRR and PSRR vs Frequency
(Referred-to Input)
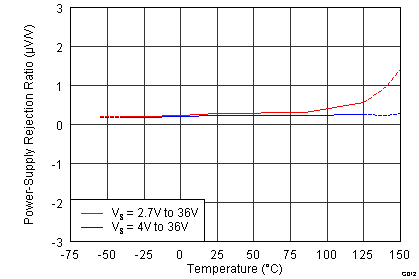 Figure 12. PSRR vs Temperature
Figure 12. PSRR vs Temperature
 Figure 14. Input Voltage Noise Spectral Density vs Frequency
Figure 14. Input Voltage Noise Spectral Density vs Frequency
 Figure 16. THD+N vs Output Amplitude
Figure 16. THD+N vs Output Amplitude
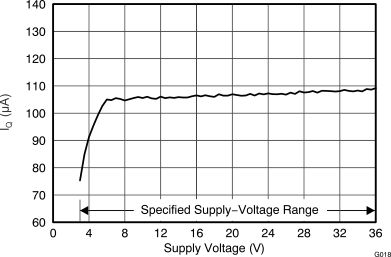 Figure 18. Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 18. Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage
 Figure 20. Closed-Loop Gain vs Frequency
Figure 20. Closed-Loop Gain vs Frequency
 Figure 22. Open-Loop Output Impedance vs Frequency
Figure 22. Open-Loop Output Impedance vs Frequency

| 100-mV output step |
 Figure 26. Positive Overload Recovery
Figure 26. Positive Overload Recovery
 Figure 28. Small-Signal Step Response (100 mV)
Figure 28. Small-Signal Step Response (100 mV)
 Figure 30. Large-Signal Step Response
Figure 30. Large-Signal Step Response

| 10-V positive step |
 Figure 36. EMIRR IN+ vs Frequency
Figure 36. EMIRR IN+ vs Frequency