SBOS936E November 2019 – August 2022 OPA182 , OPA2182 , OPA4182
PRODMIX
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
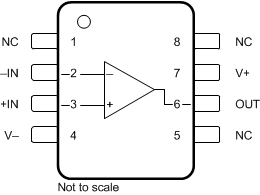 Figure 6-1 OPA182 D (8-Pin SOIC)
Package, Top View
Figure 6-1 OPA182 D (8-Pin SOIC)
Package, Top View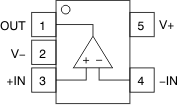 Figure 6-2 OPA182 DBV (5-Pin SOT-23)
Package, Top View
Figure 6-2 OPA182 DBV (5-Pin SOT-23)
Package, Top ViewTable 6-1 Pin Functions: OPA182
| PIN | TYPE | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | D (SOIC) | DBV (SOT-23) | ||
| –IN | 2 | 4 | Input | Inverting input |
| +IN | 3 | 3 | Input | Noninverting input |
| NC | 1, 5, 8 | — | — | No internal connection; can be left floating. |
| OUT | 6 | 1 | Output | Output channel |
| V– | 4 | 2 | Power | Negative supply |
| V+ | 7 | 5 | Power | Positive supply |
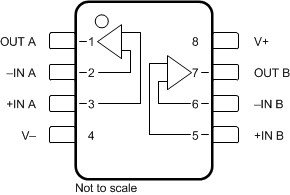 Figure 6-3 D (8-Pin SOIC) and DGK
(8-Pin VSSOP) Packages, Top View
Figure 6-3 D (8-Pin SOIC) and DGK
(8-Pin VSSOP) Packages, Top ViewTable 6-2 Pin Functions: OPA2182
| PIN | TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| –IN A | 2 | Input | Inverting input channel A |
| +IN A | 3 | Input | Noninverting input channel A |
| –IN B | 6 | Input | Inverting input channel B |
| +IN B | 5 | Input | Noninverting input channel B |
| OUT A | 1 | Output | Output channel A |
| OUT B | 7 | Output | Output channel B |
| V– | 4 | Power | Negative supply |
| V+ | 8 | Power | Positive supply |
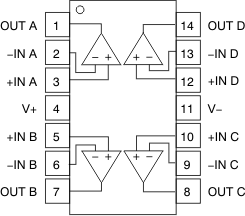 Figure 6-4 D (14-Pin SOIC) and PW
(14-Pin TSSOP, Preview) Packages, Top View
Figure 6-4 D (14-Pin SOIC) and PW
(14-Pin TSSOP, Preview) Packages, Top ViewTable 6-3 Pin Functions: OPA4182
| PIN | TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| –IN A | 2 | Input | Inverting input channel A |
| +IN A | 3 | Input | Noninverting input channel A |
| –IN B | 6 | Input | Inverting input channel B |
| +IN B | 5 | Input | Noninverting input channel B |
| –IN C | 9 | Input | Inverting input channel C |
| +IN C | 10 | Input | Noninverting input channel C |
| –IN D | 13 | Input | Inverting input channel D |
| +IN D | 12 | Input | Noninverting input channel D |
| OUT A | 1 | Output | Output channel A |
| OUT B | 7 | Output | Output channel B |
| OUT C | 8 | Output | Output channel C |
| OUT D | 14 | Output | Output channel D |
| V– | 11 | Power | Negative supply |
| V+ | 4 | Power | Positive supply |