SBOS641D June 2012 – September 2016 OPA4188
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Zero-Drift Amplifier Portfolio
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: High-Voltage Operation, VS = ±4 V to ±18 V (VS = 8 V to 36 V)
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: Low-Voltage Operation, VS = ±2 V to < ±4 V (VS = +4 V to < +8 V)
- 7.7 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Applications and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
For best operational performance of the device, use good PCB layout practices, including:
- Noise can propagate into analog circuitry through the power pins of the circuit as a whole and operational amplifier itself. Bypass capacitors are used to reduce the coupled noise by providing low-impedance power sources local to the analog circuitry.
- Connect low-ESR, 0.1-µF ceramic bypass capacitors between each supply pin and ground, placed as close to the device as possible. A single bypass capacitor from V+ to ground is applicable for single-supply applications.
- The OPA6x7 is capable of high-output current (in excess of 45 mA). Applications with low impedance loads or capacitive loads with fast transient signals demand large currents from the power supplies. Larger bypass capacitors such as 1-µF solid tantalum capacitors may improve dynamic performance in these applications.
- Separate grounding for analog and digital portions of circuitry is one of the simplest and most-effective methods of noise suppression. One or more layers on multilayer PCBs are usually devoted to ground planes. A ground plane helps distribute heat and reduces EMI noise pickup. Make sure to physically separate digital and analog grounds paying attention to the flow of the ground current. For more detailed information, see Circuit Board Layout Techniques.
- To reduce parasitic coupling, run the input traces as far away from the supply or output traces as possible. If these traces cannot be kept separate, crossing the sensitive trace perpendicular is much better as opposed to in parallel with the noisy trace.
- Place the external components as close to the device as possible. As shown in Figure 48, keeping RF and RG close to the inverting input minimizes parasitic capacitance.
- Keep the length of input traces as short as possible. Always remember that the input traces are the most sensitive part of the circuit.
- Consider a driven, low-impedance guard ring around the critical traces. A guard ring can significantly reduce leakage currents from nearby traces that are at different potentials.
- The case (TO-99 metal package only) is internally connected to the negative power supply, as with most common operational amplifiers.
- Pin 8 of the plastic PDIP, SOIC, and TO-99 packages has no internal connection.
- Cleaning the PCB following board assembly is recommended for best performance.
- Any precision integrated circuit may experience performance shifts due to moisture ingress into the plastic package. Following any aqueous PCB cleaning process, baking the PCB assembly is recommended to remove moisture introduced into the device packaging during the cleaning process. A low temperature, post cleaning bake at 85°C for 30 minutes is sufficient for most circumstances.
11.2 Layout Example
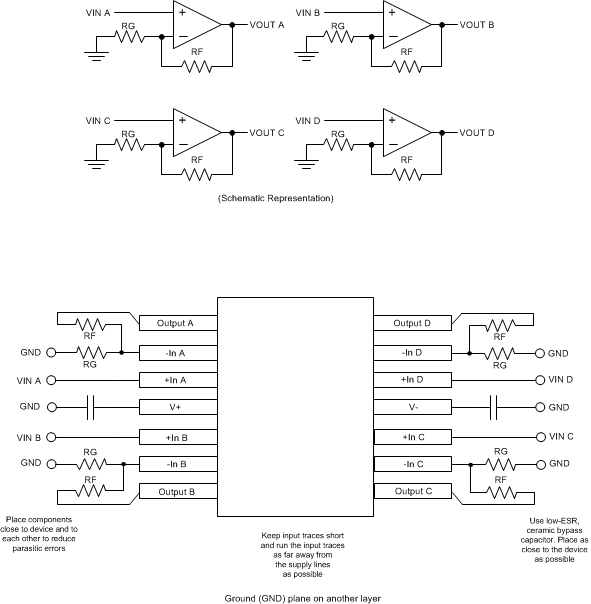 Figure 48. OPA4188 Layout Example
Figure 48. OPA4188 Layout Example