SBOS771B December 2016 – November 2024 OPA4277-SP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- JDJ|28
- HFR|14
- KGD|0
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
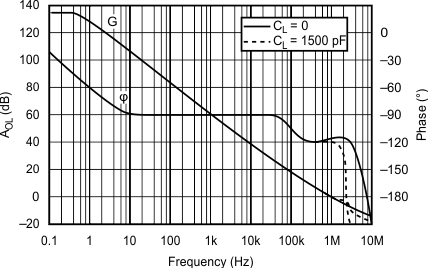
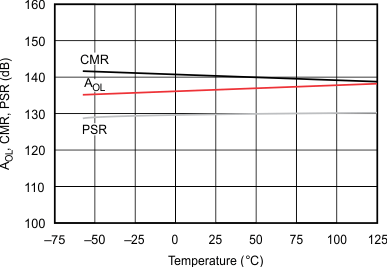
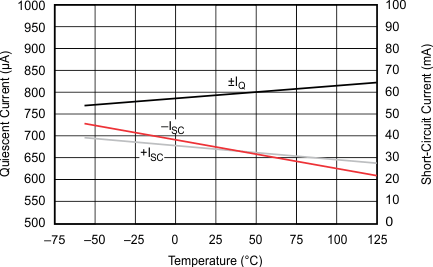
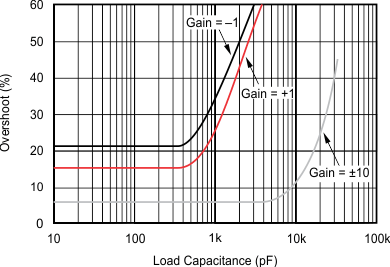
5.6 Typical Characteristics
at TJ = 25°C, VS = ±15 V, RL = 2 kΩ, and pre-irradiated (unless otherwise noted)

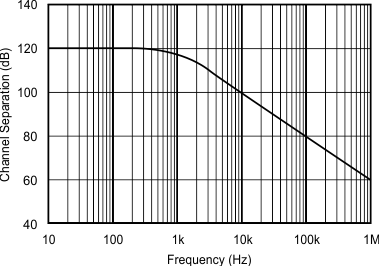
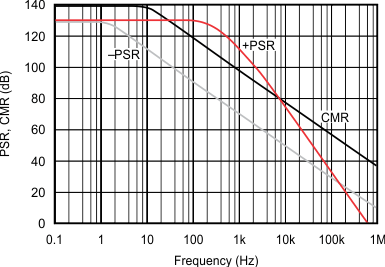
| G = 1, measured channel A to D or B to C. | ||
| Other combinations yield similar or improved rejection. |
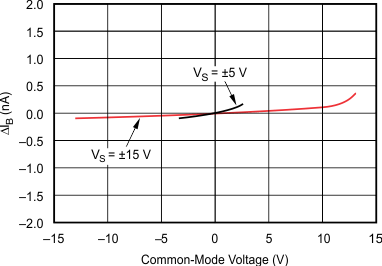
| Curve shows normalized change in bias current with respect to VCM = 0 V. Typical IB can range from –0.5 nA to 0.5 nA at VCM = 0 V. |
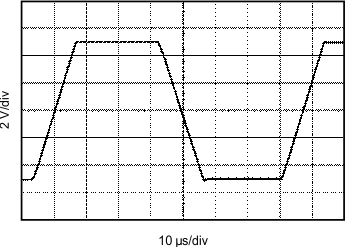
| 10-V step | CL = 1500 pF |
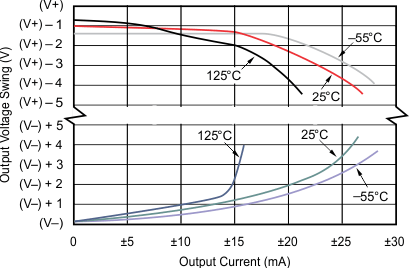
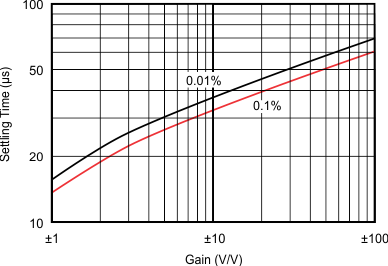
| G = 1 | CL = 1500 pF | VS = ±15 V |
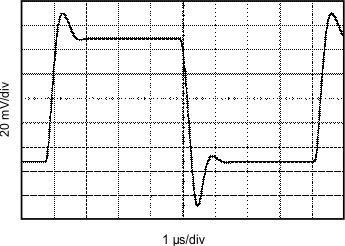
| G = 1 | CL = 1500 pF | VS = ±15 V |
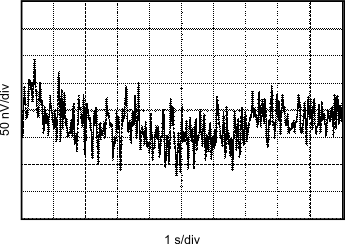
| Noise signal is bandwidth limited to lie between 0.1 Hz and 10 Hz |
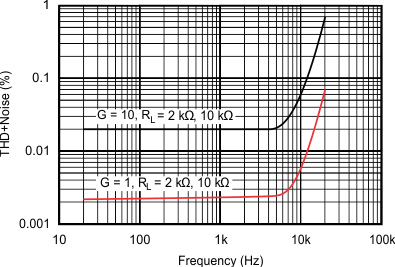
| VOUT = 3.5 Vrms | ||
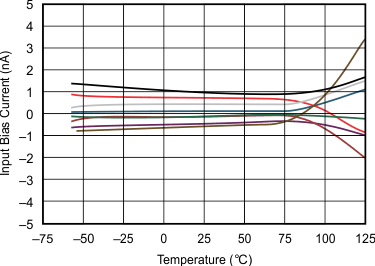
| Curves represent typical production units. |
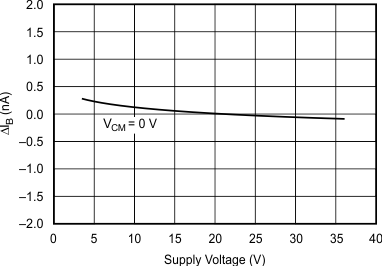
| Curve shows normalized change in bias current with respect to VS = ±10 V (+20 V). Typical IB can range from –0.5 nA to 0.5 nA at VS = ±10 V. |
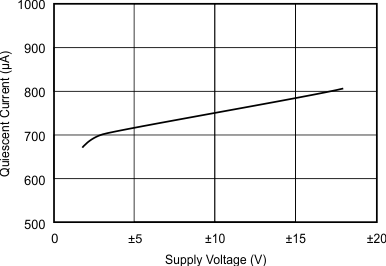
| Per amplifier | ||
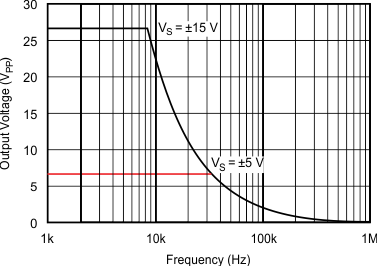
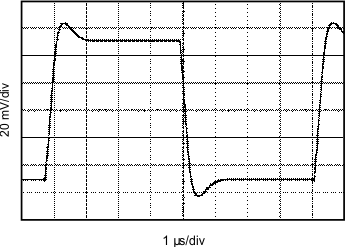
| G = 1 | CL = 0 pF | VS = ±15 V |