SBOS259F September 2002 – June 2018 OPA2363 , OPA2364 , OPA363 , OPA364 , OPA4364
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information: OPA363
- 7.5 Thermal Information: OPA364
- 7.6 Thermal Information: OPA2363
- 7.7 Thermal Information: OPA2364
- 7.8 Thermal Information: OPA4364
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.10 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
In this circuit, the op amp is configured as a transimpedance amplifier which converts the signal current of the microphone into an output voltage. The gain of the circuit is determined by the feedback resistor RFB, which must be calculated according to the microphone sensitivity. For this design, a microphone output current of 8 µA per Pascal (Pa) of air pressure was chosen. Using this value, the output current for a sound pressure level of 100 dBSPL, or 2 Pa air pressure, is calculated in Equation 1.

RFB is then calculated from this current to produce 1-VRMS output for a 100-dBSPL input signal in Equation 2.
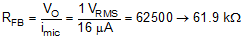
The feedback capacitor (CFB) is calculated to limit the bandwidth of the amplifier to 20 kHz in Equation 3.

RBIAS is required to divert the microphone signal current through capacitor CIN rather than flowing from the power supply, VCC. Larger values of RBIAS allow for a smaller capacitor to be used for CIN and reduce the overall noise of the circuit. However, the maximum value for RBIAS is limited by the microphone bias current and minimum operating voltage.
The value of RBIAS is calculated in Equation 4.
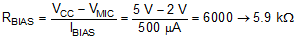
Input capacitor CIN forms a high-pass filter in combination with resistor RBIAS. The filter corner frequency calculation is shown in Equation 5 to place the high-pass corner frequency at 20 Hz.

The voltage divider network at the op amp noninverting input is used to bias the op amp output to the mid-supply point (VCC / 2) to maximize the output voltage range of the circuit. This result is easily achieved by selecting the same value for both resistors in the divider. The absolute value of those resistors is limited by the acceptable power-supply current drawn by the voltage divider. Selecting 25 µA as an acceptable limit of supply current gives a value of 100 kΩ for the resistors in the divider, as Equation 6 shows.

Finally, to minimize the additional noise contribution from the voltage divider, a capacitor is placed at the op amp noninverting input. This capacitor forms a low-pass filter with the parallel combination of the voltage divider resistors. Selecting a filter corner frequency of 20 Hz minimizes the noise contribution of the voltage divider inside the amplifier passband; see Equation 7.
