SBOSAF1 December 2024 OPA4H199-SP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DYY|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.3.5 Common-Mode Voltage Range
The OPA4H199-SP is a 40V, true rail-to-rail input operational amplifier with an input common-mode range that extends 100mV beyond either supply rail. This wide range is achieved with paralleled complementary N-channel and P-channel differential input pairs, as shown in Figure 6-8. The N-channel pair is active for input voltages close to the positive rail, typically (V+) – 1V to 100mV above the positive supply. The P-channel pair is active for inputs from 100mV below the negative supply to approximately (V+) – 2V. There is a small transition region, typically (V+) – 2V to (V+) – 1V in which both input pairs are turned on. This transition region can vary modestly with process variation, and within this region PSRR, CMRR, offset voltage, offset drift, noise, and THD performance can be degraded compared to operation outside this region.
Figure 5-5 shows this transition region for a typical device in terms of input voltage offset in more detail.
For more information on common-mode voltage range and PMOS/NMOS pair interaction, see the Op amps with complementary-pair input stages: What are the design trade-offs? Analog Design Journal.
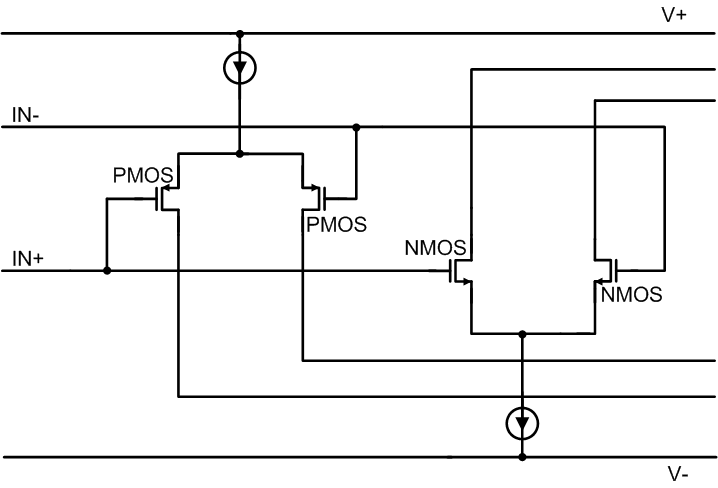 Figure 6-8 Rail-to-Rail Input Stage
Figure 6-8 Rail-to-Rail Input Stage