SBOS867D August 2017 – September 2024 OPA838
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics VS = 5 V
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics VS = 3 V
- 6.7 Typical Characteristics: VS = 5 V
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics: VS = 3 V
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: Over Supply Range
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|6
- DCK|5
- DCK|6
- DXB|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
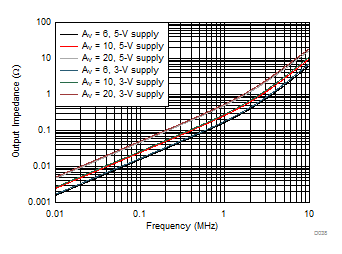
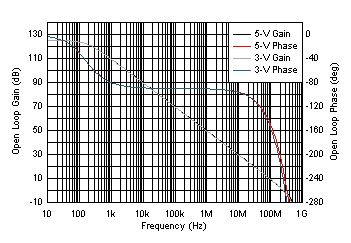
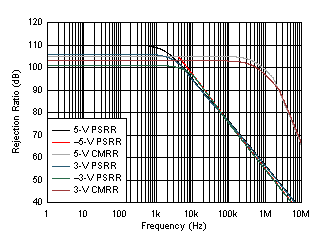
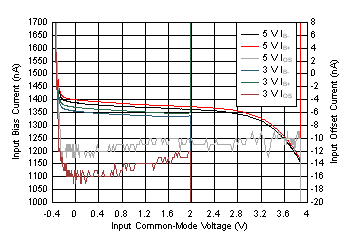
6.9 Typical Characteristics: Over Supply Range
at PD = VS+ and TA = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
| No load, simulation |

| Simulated results |
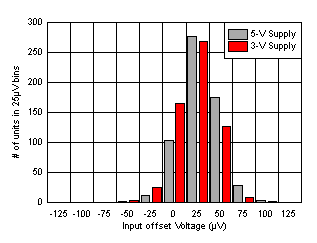
| 600 units at each supply voltage |
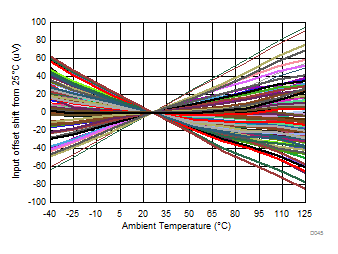
| 51 units at 5-V and 3-V supply |

| 51 units at each supply |
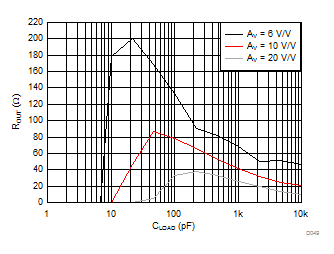
| See Figure 7-6 and Table 8-1 | ||
| small signal, targeting 30° phase margin |
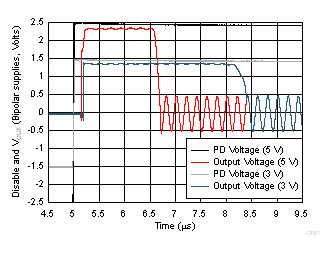
| Single-supply, DC input to produce midscale output (simulation) |
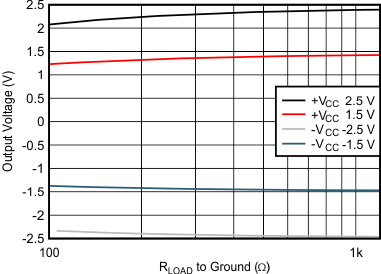
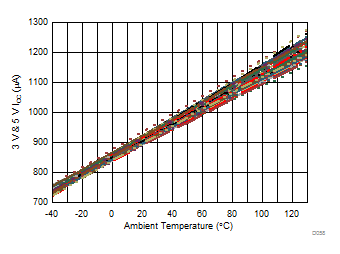
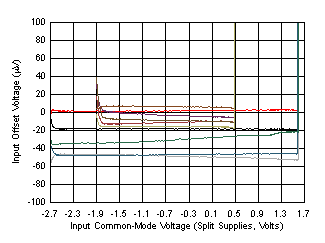
| 5 units, 3-V and 5-V supplies |
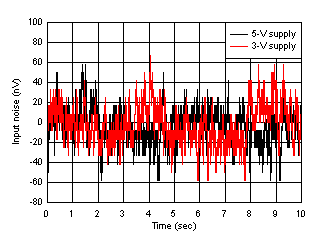
| Input referred |
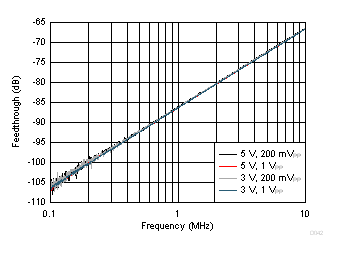
| Measured, AV = 6 V/V, 100-Ω load |
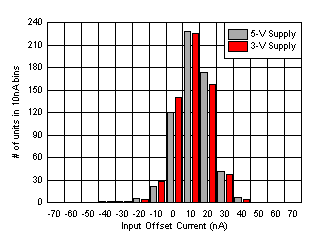
| 600 units at each supply voltage |
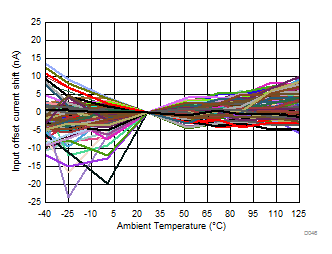
| 51 units at 5-V and 3-V supply |
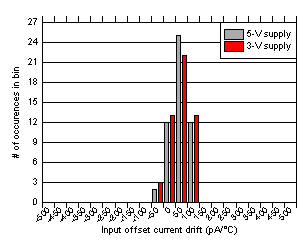
| 51 units at each supply |
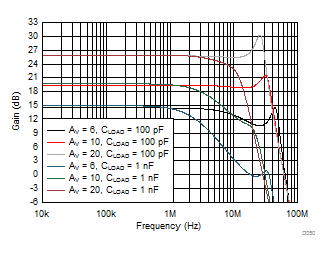
| See Figure 7-6 and Table 8-1 | ||
| 2-kΩ parallel load to C LOAD |
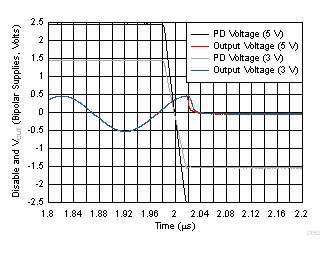
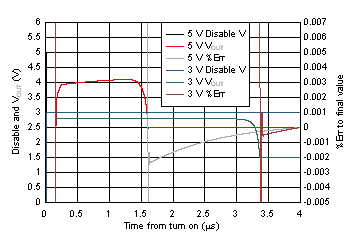
| Single-supply, DC input to produce midscale output (simulation) |

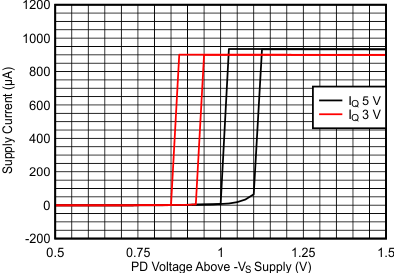
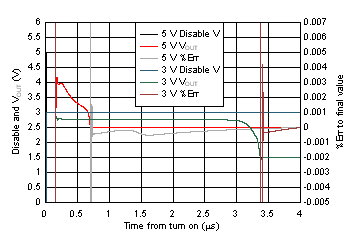
Turn On Higher Than Turn Off
| Measured single device |