SBBS002B January 1994 – June 2015 OPT101
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power-Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
Make all power connections with short, low impedance connections.
Depending on the application, the design might benefit from having the OPT101 mounted to the opposite side of the board as the other electrical components. Keeping the optical sensor side free from extra components allows for easier mounting of any required optical-mechanical structures around the OPT101.
11.2 Layout Example
The following example shows an external feedback network (R2 and C2) that bypasses the internal feedback network, similar to Figure 19. This example also shows an external feedback network (R1, C1) in series with the internal feedback network, similar to Figure 18. To use only the internal feedback network, load R1 or C1 with a short circuit. This example allows for three different configurations with the same layout. Do not load R1, C1, R2, and C2 simultaneously.
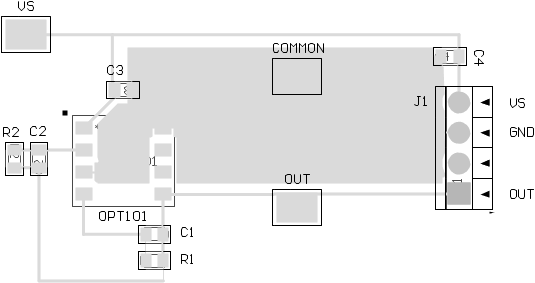 Figure 30. Layout Example
Figure 30. Layout Example