SCPS113O october 2004 – september 2023 PCA9306
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Switching Characteristics AC Performance (Translating Down) (EN = 3.3 V)
- 6.7 Switching Characteristics AC Performance (Translating Down) (EN = 2.5 V)
- 6.8 Switching Characteristics AC Performance (Translating Up) (EN = 3.3 V)
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics AC Performance (Translating Up) (EN = 2.5 V)
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1
Overview
- 8.1.1 Definition of threshold voltage
- 8.1.2 Correct Device Set Up
- 8.1.3 Disconnecting an I2C target from the Main I2C Bus Using the EN Pin
- 8.1.4 Supporting Remote Board Insertion to Backplane with PCA9306
- 8.1.5 Switch Configuration
- 8.1.6 Controller on Side 1 or Side 2 of Device
- 8.1.7 LDO and PCA9306 Concerns
- 8.1.8 Current Limiting Resistance on VREF2
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.1
Overview
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.1.5 Switch Configuration
PCA9306 has the capability of being used with its VREF1 voltage equal to VREF2. This essentially turns the device from a translator to a device which can be used as a switch, and in some situations this can be useful. The switch configuration is shown in Figure 8-5 and translation mode is shown in Figure 8-6.
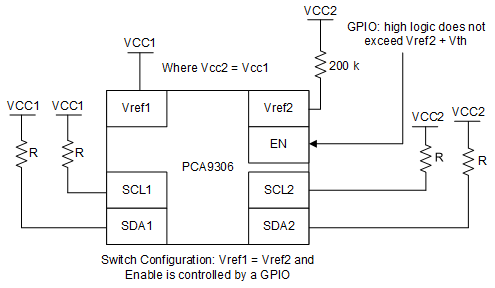 Figure 8-5 Switch
Configuration
Figure 8-5 Switch
Configuration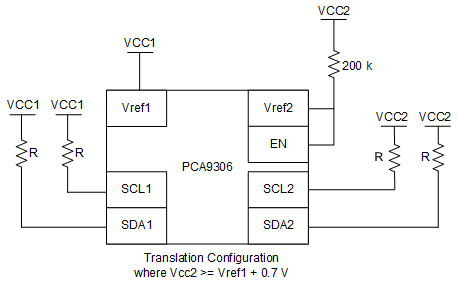 Figure 8-6 Translation Configuration
Figure 8-6 Translation ConfigurationWhen PCA9306 is in the switch configuration (VREF1 = VREF2), the propagation delays are different compared to the translator configuration. Taking a look at the propagation delays, if the pull up resistance and capacitance on both sides of the bus are equal, then in switch mode the PCA9306 has the same propagation delay from side one to two and side two to one. The propagation delays become lower when VCC1/VCC2 is larger. For example, the propagation delay at 1.8 V is longer than at 5 V in the switching configuration. When PCA9306 is in translation mode, side one propagate lows to side two faster than side two can propagate lows to side 1. This time difference becomes larger the larger the difference between VCC2 and VCC1 becomes.