SCPS124H September 2006 – March 2021 PCA9534
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Description
- 3 Revision History
- 4 Description (Continued)
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application Information Disclaimer
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.3.2.4.1 Writes
Data is transmitted to the PCA9534 by sending the device address and setting the least significant bit (LSB) to a logic 0 (see Figure 9-6 for device address). The command byte is sent after the address and determines which register receives the data that follows the command byte (see Figure 9-8 and Figure 9-9). There is no limitation on the number of data bytes sent in one write transmission.
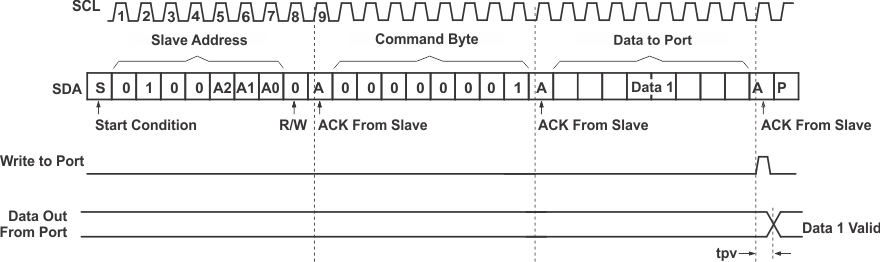 Figure 9-8 Write To Output Port Register
Figure 9-8 Write To Output Port Register Figure 9-9 Write To Configuration Or Polarity Inversion Registers
Figure 9-9 Write To Configuration Or Polarity Inversion Registers