SCPS127F September 2006 – March 2021 PCA9554A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Description
- 3 Revision History
- 4 Description (Continued)
- 5 Pin Configuration And Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application Information Disclaimer
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.8 Typical Characteristics
TA = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)

| fSCL = 400 kHz | I/Os = High or Low Inputs |

| fSCL = 400 kHz | I/Os = High or Low Inputs | TA = 25°C |

| TA = 25°C |

| TA = 25°C |

| VCC = 5 V |
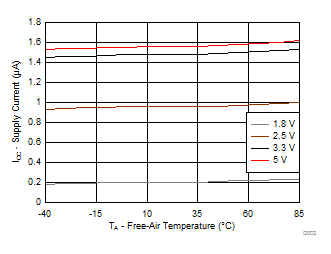
| fSCL = 0 kHz | I/Os = High Inputs |
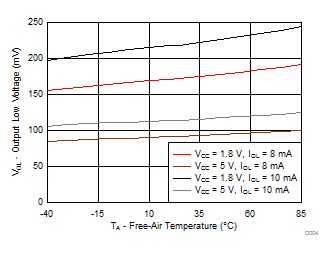
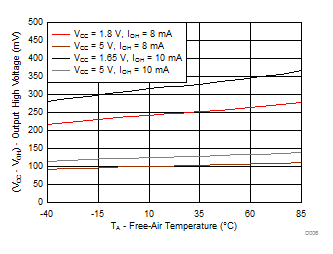 Figure 6-6 Output High Voltage (VCC – VOH) vs Temperature (TA) for P-Ports
Figure 6-6 Output High Voltage (VCC – VOH) vs Temperature (TA) for P-Ports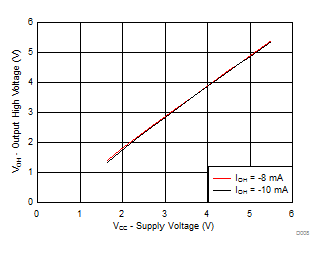
| TA = 25°C |
 Figure 6-10 Δ ICC vs Temperature for Different VCC (VI = VCC – 0.6 V)
Figure 6-10 Δ ICC vs Temperature for Different VCC (VI = VCC – 0.6 V)