SCPS133K December 2005 – December 2024 PCA9557
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Parameter Measurement Information
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1.1 Minimizing ICC when I/O is Used to Control LED
When an I/O is used to control an LED, normally it is connected to VCC through a resistor as shown in Figure 8-1. The LED acts as a diode so, when the LED is off, the I/O VIN is about 1.2 V less than VCC. The ΔICC parameter in the Section 5.5 table shows how ICC increases as VIN becomes lower than VCC. Designs needing to minimize current consumption, such as battery power applications, should consider maintaining the I/O pins greater than or equal to VCC when the LED is off.
Figure 8-2 shows a high-value resistor in parallel with the LED. Figure 8-3 shows VCC less than the LED supply voltage by at least 1.2 V. Both of these methods maintain the I/O VIN at or above VCC and prevent additional supply-current consumption when the LED is off.
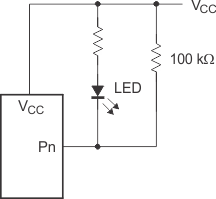 Figure 8-2 High-Value Resistor in Parallel with the LED
Figure 8-2 High-Value Resistor in Parallel with the LED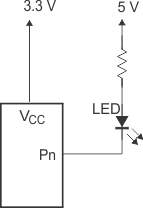 Figure 8-3 Device Supplied by a Low Voltage
Figure 8-3 Device Supplied by a Low Voltage