SBASAU2 May 2024 PCM1841-Q1
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1Features
- 2Applications
- 3Description
- 4Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5Specifications
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Hardware Control
- 6.3.2 Audio Serial Interfaces
- 6.3.3 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) and Clock Generation
- 6.3.4 Input Channel Configurations
- 6.3.5 Reference Voltage
- 6.3.6 Microphone Bias
- 6.3.7
Signal-Chain Processing
- 6.3.7.1 Digital High-Pass Filter
- 6.3.7.2
Configurable Digital Decimation Filters
- 6.3.7.2.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 6.3.7.2.1.1 Sampling Rate: 8kHz or 7.35kHz
- 6.3.7.2.1.2 Sampling Rate: 16kHz or 14.7kHz
- 6.3.7.2.1.3 Sampling Rate: 24kHz or 22.05kHz
- 6.3.7.2.1.4 Sampling Rate: 32kHz or 29.4kHz
- 6.3.7.2.1.5 Sampling Rate: 48kHz or 44.1kHz
- 6.3.7.2.1.6 Sampling Rate: 96kHz or 88.2kHz
- 6.3.7.2.1.7 Sampling Rate: 192kHz or 176.4kHz
- 6.3.7.2.2 Low-Latency Filters
- 6.3.7.2.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 6.3.8 Dynamic Range Enhancer (DRE)
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7Application and Implementation
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Revision History
- Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Orderable Information
5.9 Typical Characteristics
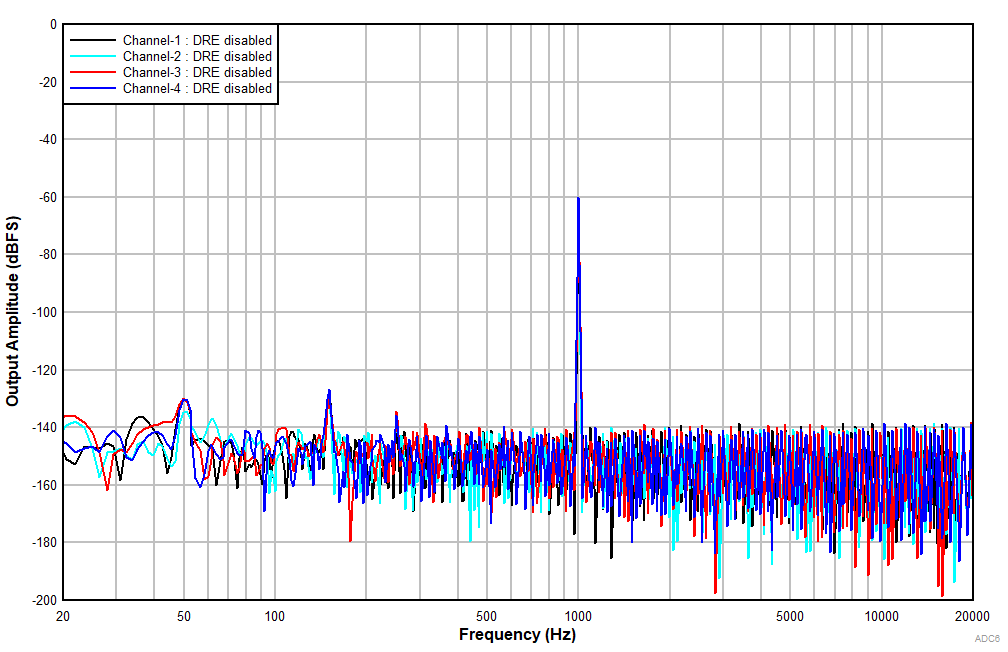
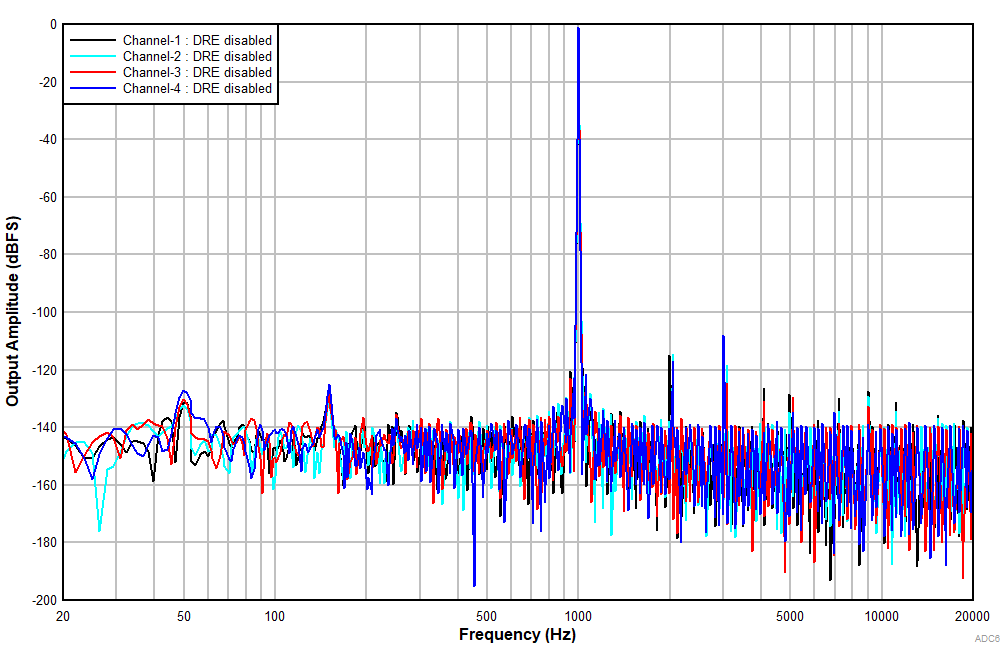
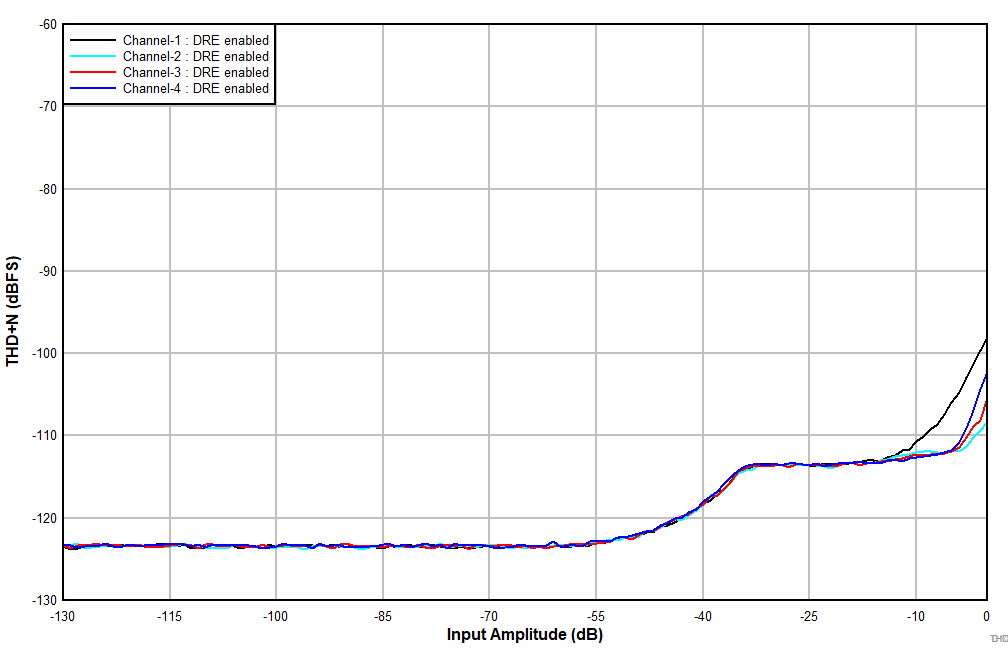
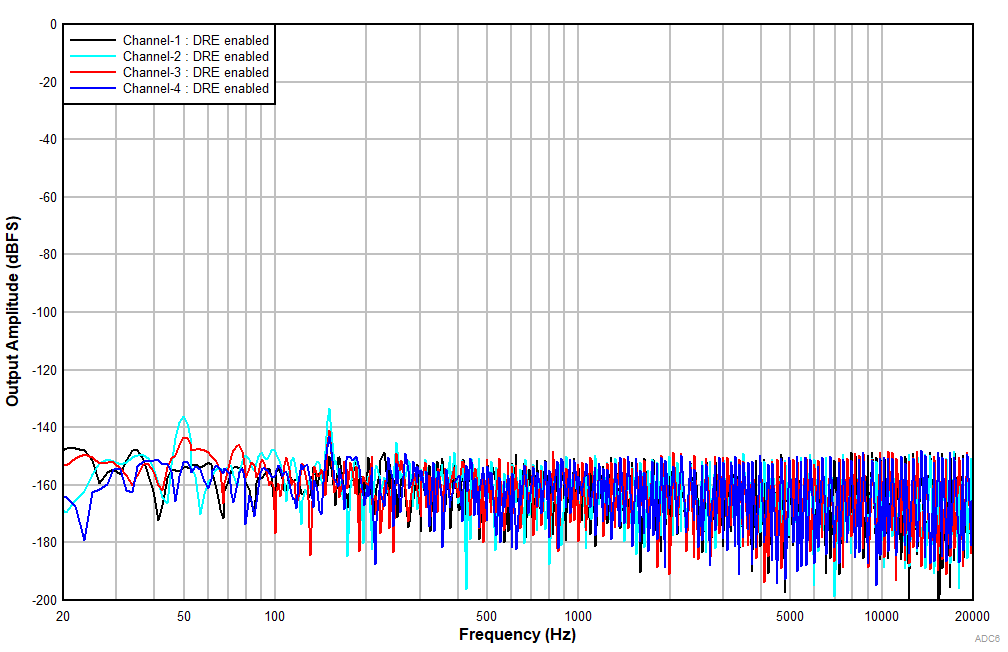
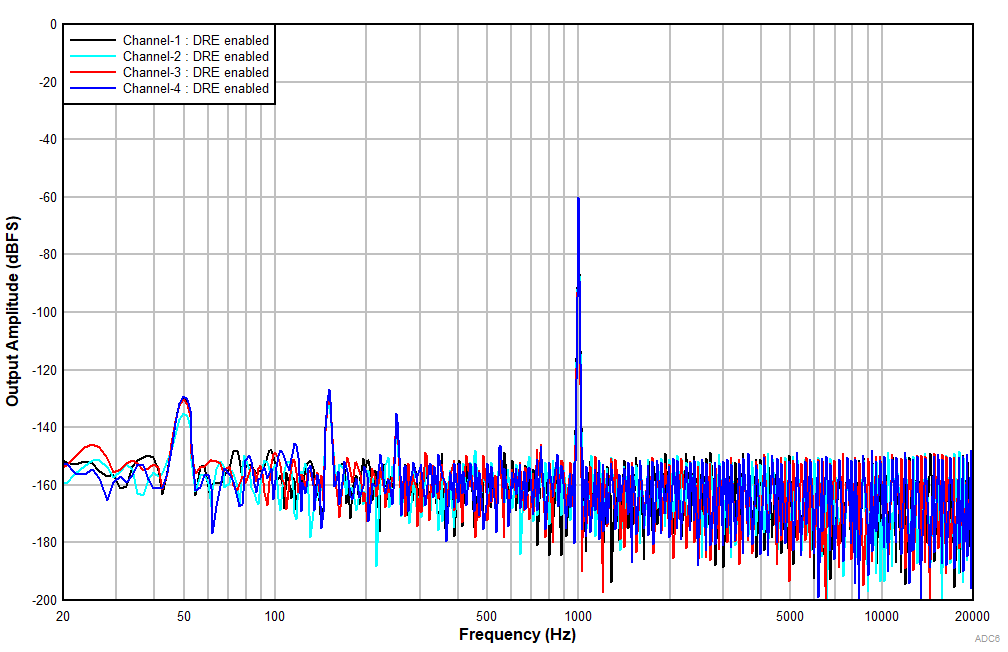
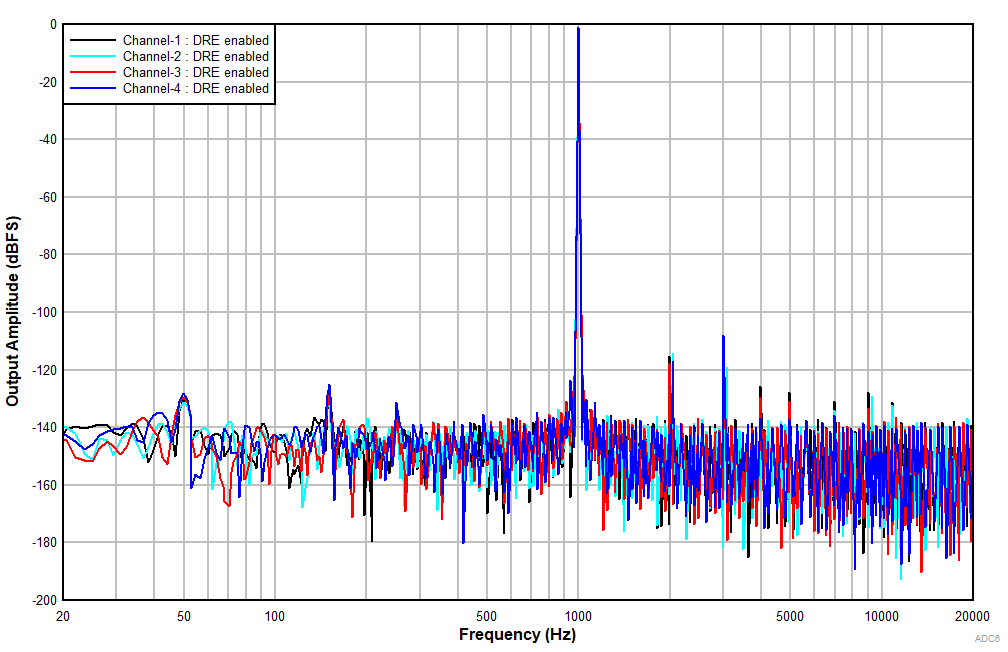
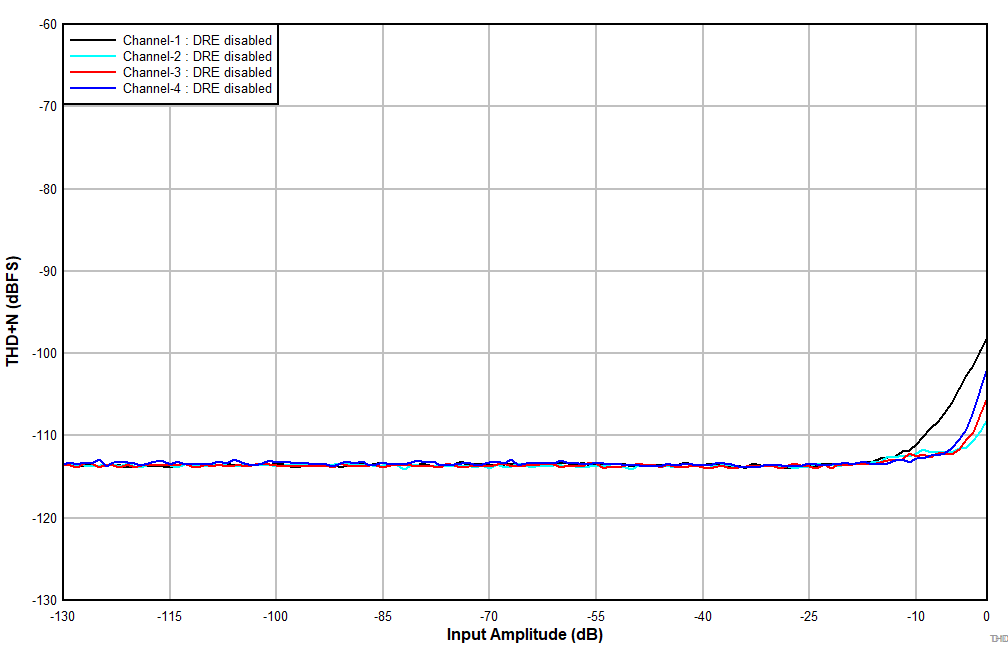
at TA = 25°C, AVDD = 3.3V, IOVDD = 3.3V, fIN = 1kHz sinusoidal signal, fS = 48kHz, 32-bit audio data, BCLK = 256 × fS, TDM target mode, PLL on, DRE_LVL = –36dB, channel gain = 0dB, and linear phase decimation filter (unless otherwise noted); all performance measurements are done with a 20kHz, low-pass filter, and an A-weighted filter
| Differential input |
With DRE Enabled
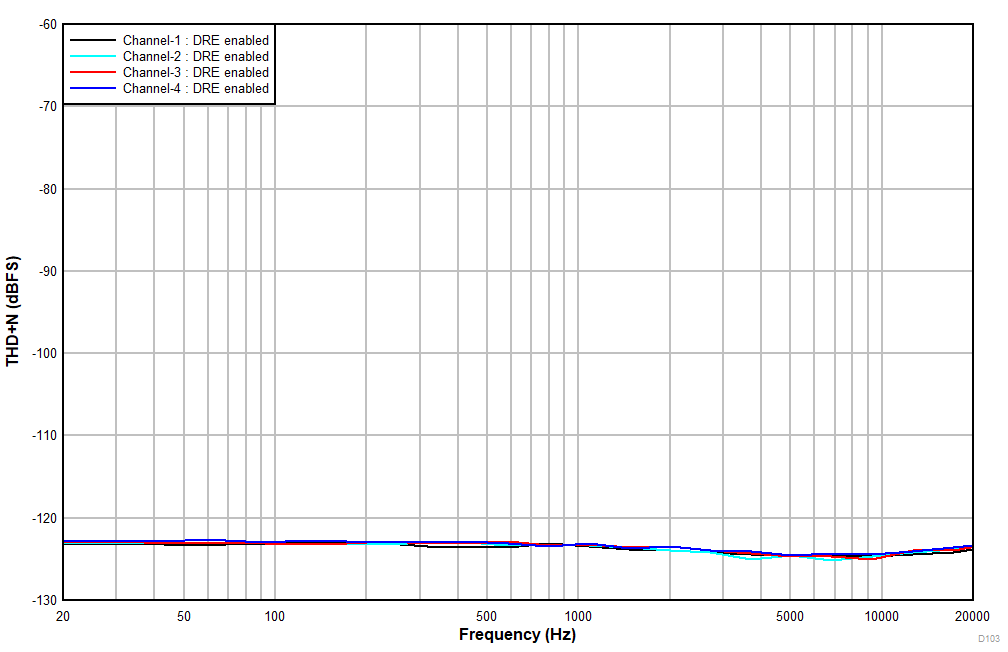
With a –60dBr Input
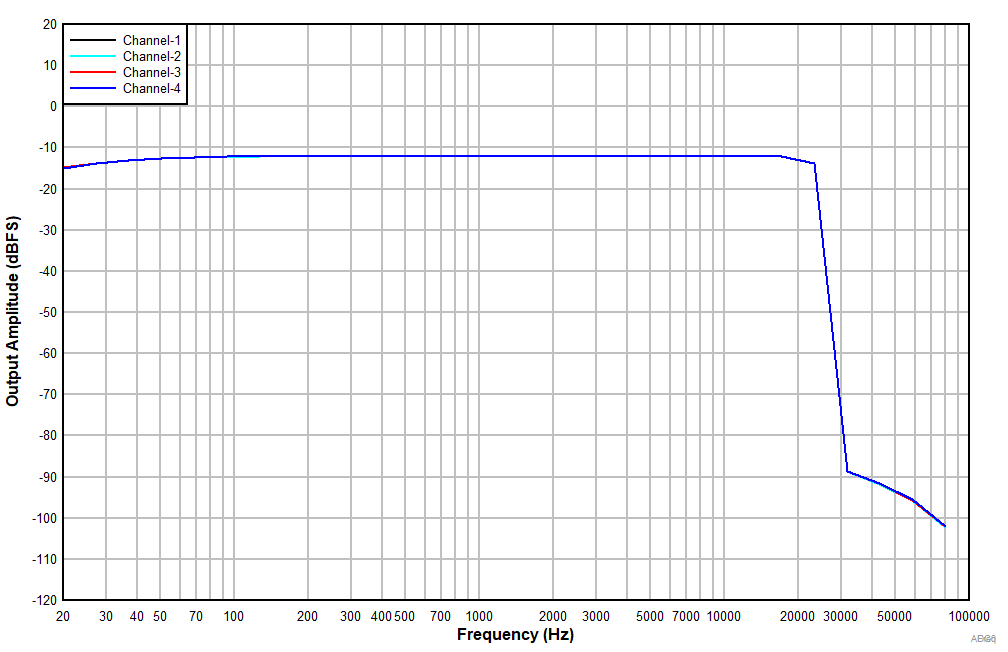
With a –12dBr Input
| Differential input |
With DRE Disabled
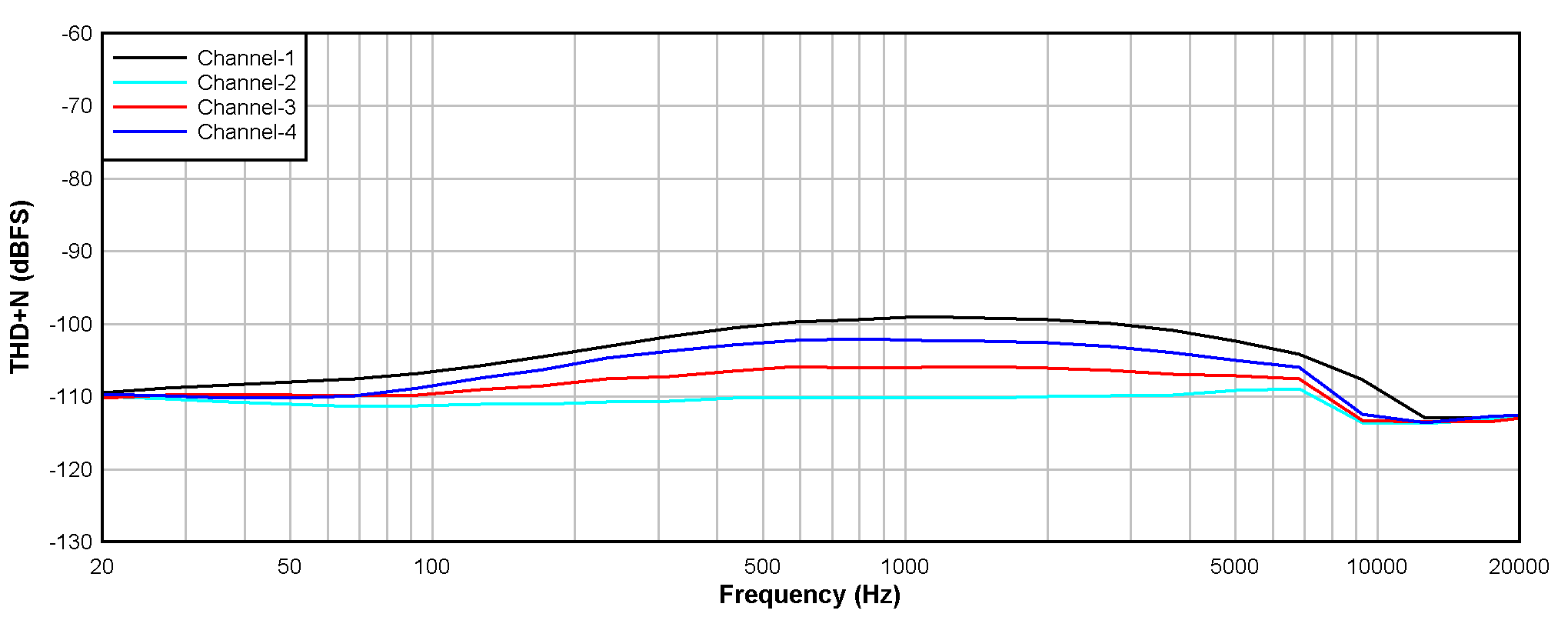
With a –1dBr Input
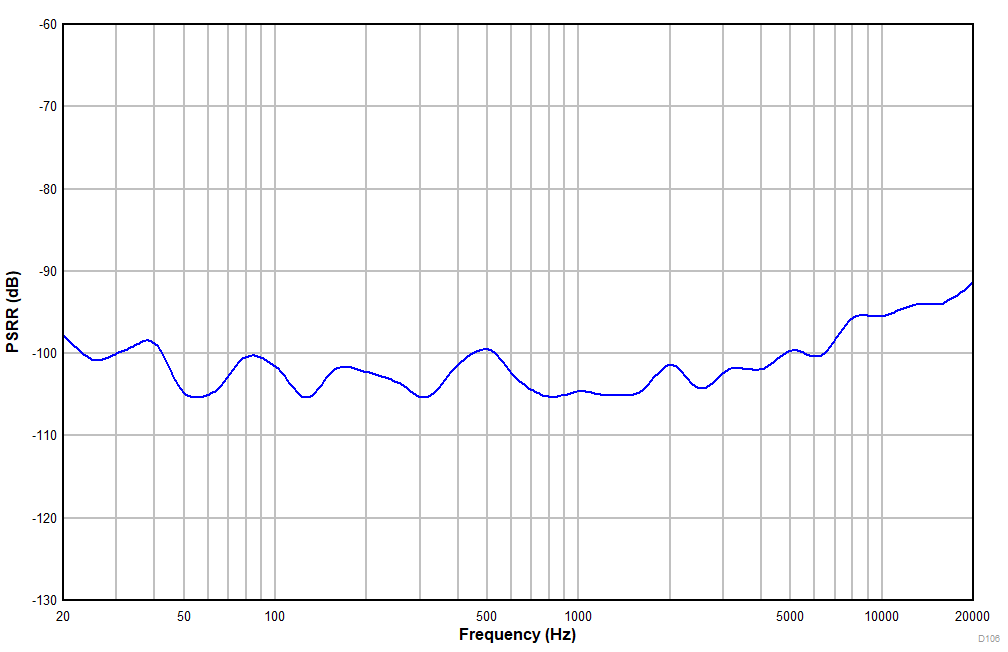
Ripple Frequency With 100mVPP Amplitude