SBASAU4 March 2024 PCM6140-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Timing Requirements: I2C Interface
- 6.7 Switching Characteristics: I2C Interface
- 6.8 Timing Requirements: SPI Interface
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics: SPI Interface
- 6.10 Timing Requirements: TDM, I2S or LJ Interface
- 6.11 Switching Characteristics: TDM, I2S or LJ Interface
- 6.12 Timing Requirements: PDM Digital Microphone Interface
- 6.13 Switching Characteristics: PDM Digial Microphone Interface
- 6.14 Timing Diagrams
- 6.15 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Serial Interfaces
- 7.3.2 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) and Clock Generation
- 7.3.3 Input Channel Configurations
- 7.3.4 Reference Voltage
- 7.3.5 Programmable Microphone Bias
- 7.3.6
Signal-Chain Processing
- 7.3.6.1 Programmable Channel Gain and Digital Volume Control
- 7.3.6.2 Programmable Channel Gain Calibration
- 7.3.6.3 Programmable Channel Phase Calibration
- 7.3.6.4 Programmable Digital High-Pass Filter
- 7.3.6.5 Programmable Digital Biquad Filters
- 7.3.6.6 Programmable Channel Summer and Digital Mixer
- 7.3.6.7
Configurable Digital Decimation Filters
- 7.3.6.7.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 7.3.6.7.1.1 Sampling Rate: 8 kHz or 7.35 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.2 Sampling Rate: 16 kHz or 14.7 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.3 Sampling Rate: 24 kHz or 22.05 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.4 Sampling Rate: 32 kHz or 29.4 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.5 Sampling Rate: 48 kHz or 44.1 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.6 Sampling Rate: 96 kHz or 88.2 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.7 Sampling Rate: 192 kHz or 176.4 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.8 Sampling Rate: 384 kHz or 352.8 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.9 Sampling Rate 768 kHz or 705.6 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.2 Low-Latency Filters
- 7.3.6.7.3
Ultra-Low-Latency Filters
- 7.3.6.7.3.1 Sampling Rate: 16 kHz or 14.7 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.2 Sampling Rate: 24 kHz or 22.05 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.3 Sampling Rate: 32 kHz or 29.4 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.4 Sampling Rate: 48 kHz or 44.1 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.5 Sampling Rate: 96 kHz or 88.2 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.6 Sampling Rate 192 kHz or 176.4 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.7 Sampling Rate 384 kHz or 352.8 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 7.3.7 Dynamic Range Enhancer (DRE)
- 7.3.8 Automatic Gain Controller (AGC)
- 7.3.9 Digital PDM Microphone Record Channel
- 7.3.10 Interrupts, Status, and Digital I/O Pin Multiplexing
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
-
8 Register Maps
- 8.1
Device Configuration Registers
- 8.1.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.1.1.1 PAGE_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x00) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.2 SW_RESET Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x01) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.3 SLEEP_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x02) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.4 SHDN_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x05) [reset = 5h]
- 8.1.1.5 ASI_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x07) [reset = 30h]
- 8.1.1.6 ASI_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x08) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.7 ASI_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x09) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.8 ASI_CH1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0B) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.9 ASI_CH2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0C) [reset = 1h]
- 8.1.1.10 ASI_CH3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0D) [reset = 2h]
- 8.1.1.11 ASI_CH4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0E) [reset = 3h]
- 8.1.1.12 ASI_CH5 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0F) [reset = 4h]
- 8.1.1.13 ASI_CH6 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x10) [reset = 5h]
- 8.1.1.14 ASI_CH7 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x11) [reset = 6h]
- 8.1.1.15 ASI_CH8 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x12) [reset = 7h]
- 8.1.1.16 MST_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x13) [reset = 2h]
- 8.1.1.17 MST_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x14) [reset = 48h]
- 8.1.1.18 ASI_STS Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x15) [reset = FFh]
- 8.1.1.19 CLK_SRC Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x16) [reset = 10h]
- 8.1.1.20 PDMCLK_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x1F) [reset = 40h]
- 8.1.1.21 PDMIN_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x20) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.22 GPIO_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x21) [reset = 22h]
- 8.1.1.23 GPO_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x22) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.24 GPO_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x23) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.25 GPO_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x24) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.26 GPO_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x25) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.27 GPO_VAL Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x29) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.28 GPIO_MON Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2A) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.29 GPI_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2B) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.30 GPI_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2C) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.31 GPI_MON Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2F) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.32 INT_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x32) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.33 INT_MASK0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x33) [reset = FFh]
- 8.1.1.34 INT_LTCH0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x36) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.35 BIAS_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3B) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.36 CH1_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3C) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.37 CH1_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3D) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.38 CH1_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3E) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.39 CH1_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3F) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.40 CH1_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x40) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.41 CH2_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x41) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.42 CH2_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x42) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.43 CH2_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x43) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.44 CH2_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x44) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.45 CH2_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x45) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.46 CH3_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x46) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.47 CH3_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x47) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.48 CH3_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x48) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.49 CH3_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x49) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.50 CH3_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4A) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.51 CH4_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4B) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.52 CH4_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4C) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.53 CH4_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4D) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.54 CH4_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4E) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.55 CH4_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4F) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.56 CH5_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x52) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.57 CH5_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x53) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.58 CH5_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x54) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.59 CH6_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x57) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.60 CH6_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x58) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.61 CH6_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x59) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.62 CH7_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x5C) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.63 CH7_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x5D) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.64 CH7_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x5E) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.65 CH8_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x61) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.66 CH8_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x62) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.67 CH8_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x63) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.68 DSP_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x6B) [reset = 1h]
- 8.1.1.69 DSP_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x6C) [reset = 40h]
- 8.1.1.70 DRE_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x6D) [reset = 7Bh]
- 8.1.1.71 AGC_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x70) [reset = E7h]
- 8.1.1.72 IN_CH_EN Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x73) [reset = F0h]
- 8.1.1.73 ASI_OUT_CH_EN Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x74) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.74 PWR_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x75) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.75 DEV_STS0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x76) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.76 DEV_STS1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x77) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.77 I2C_CKSUM Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x7E) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.2 Programmable Coefficient Registers
- 8.1
Device Configuration Registers
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Orderable Information
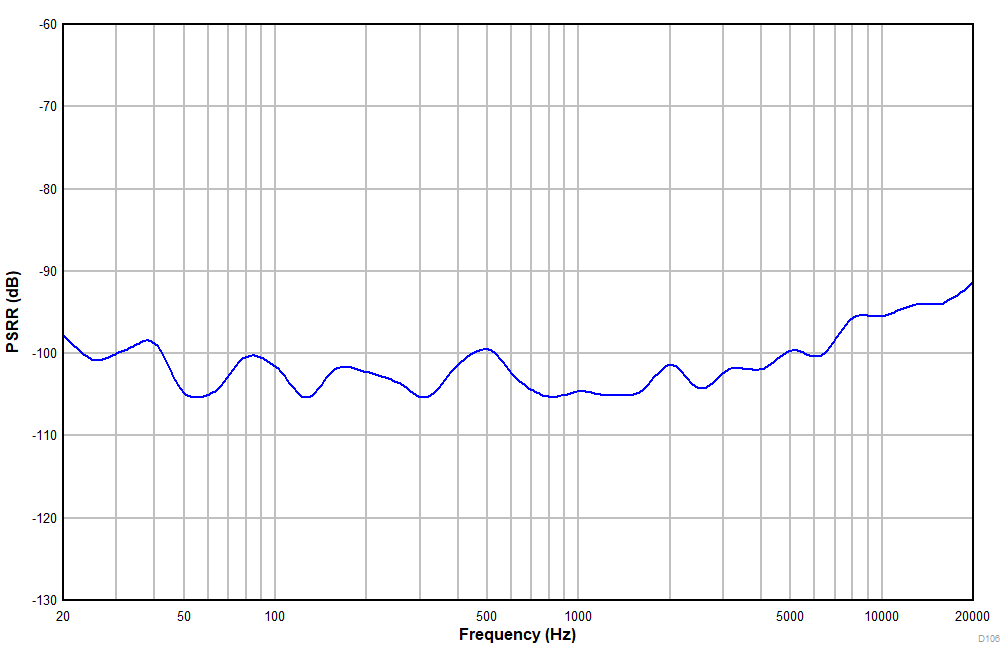
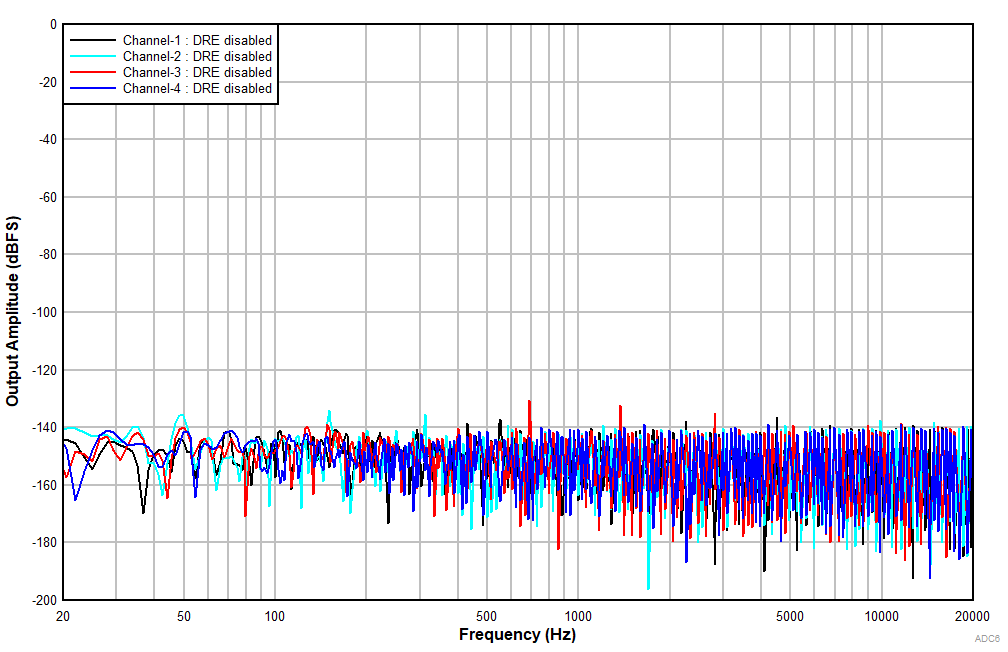
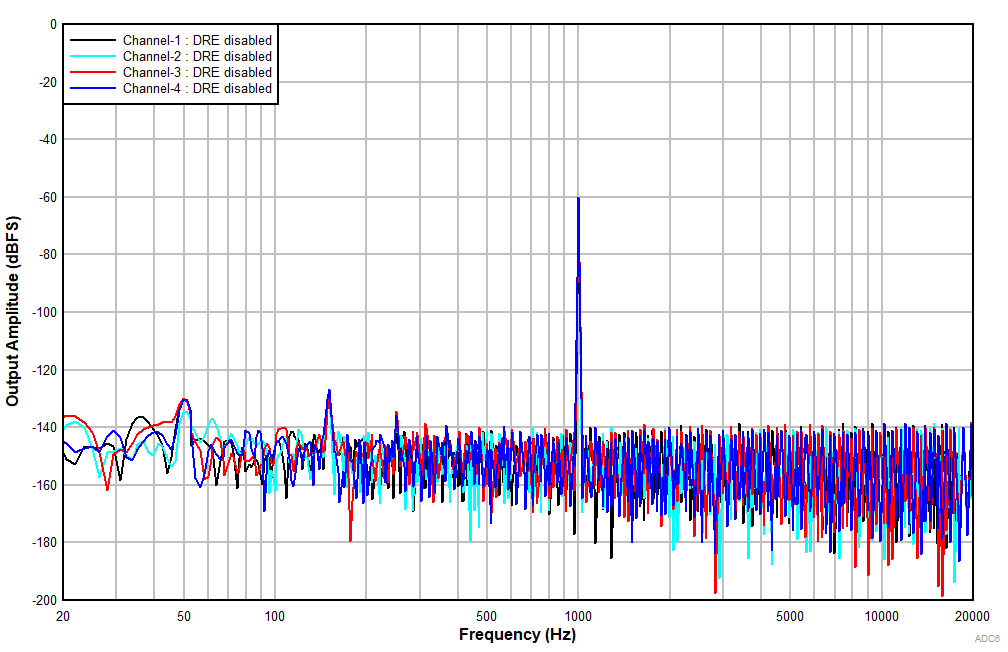
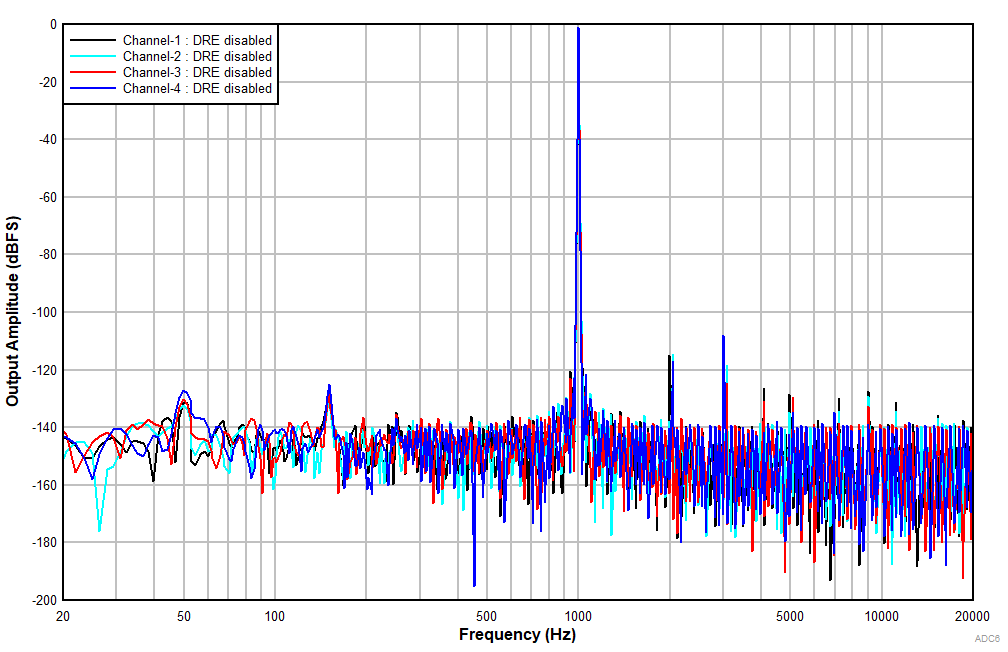
6.15 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, AVDD = 3.3 V, IOVDD = 3.3 V, fIN = 1-kHz sinusoidal signal, fS = 48 kHz, 32-bit audio data, BCLK = 256 × fS, TDM target mode, PLL on, DRE_LVL = –36 dB, channel gain = 0 dB, and linear phase decimation filter (unless otherwise noted); all performance measurements are done with a 20-kHz, low-pass filter, and an A-weighted filter
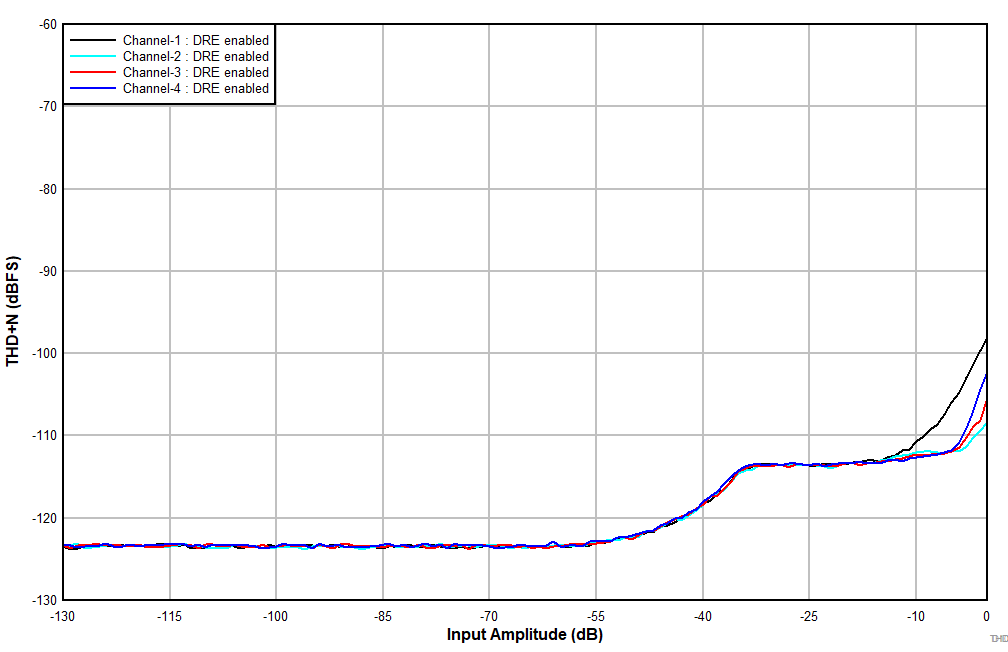
| Differential input |
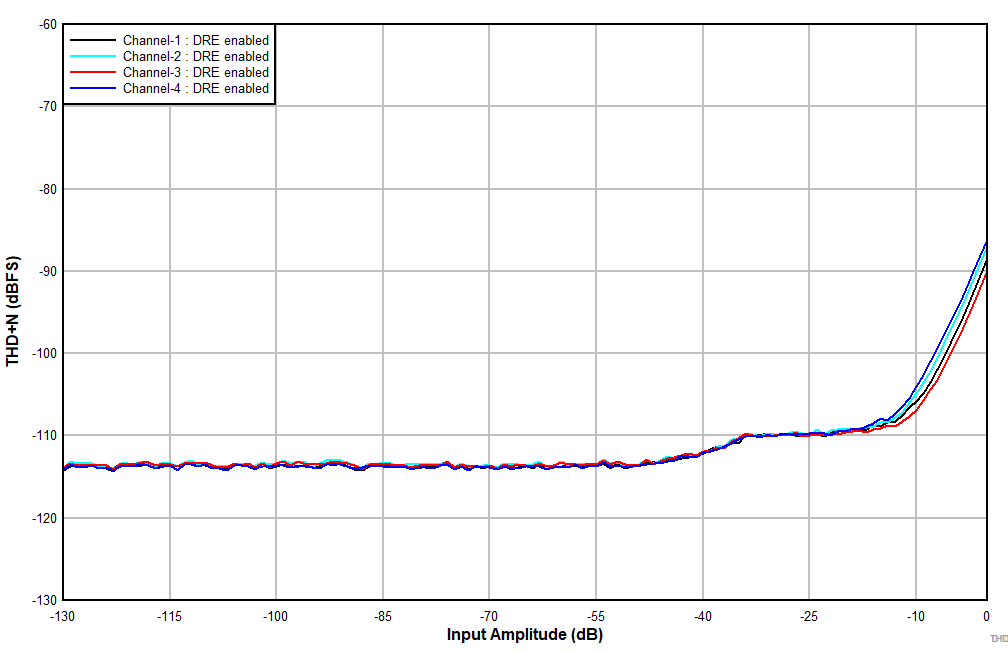
| Single-ended input |
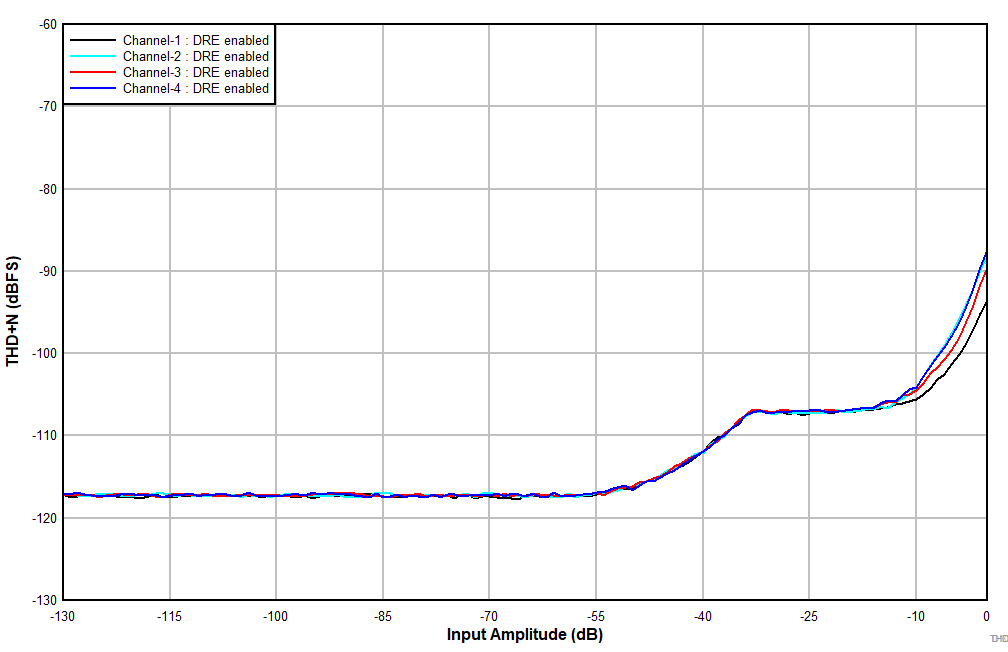
| Differential input with AVDD = 1.8 V and VREF = 1.375 V |
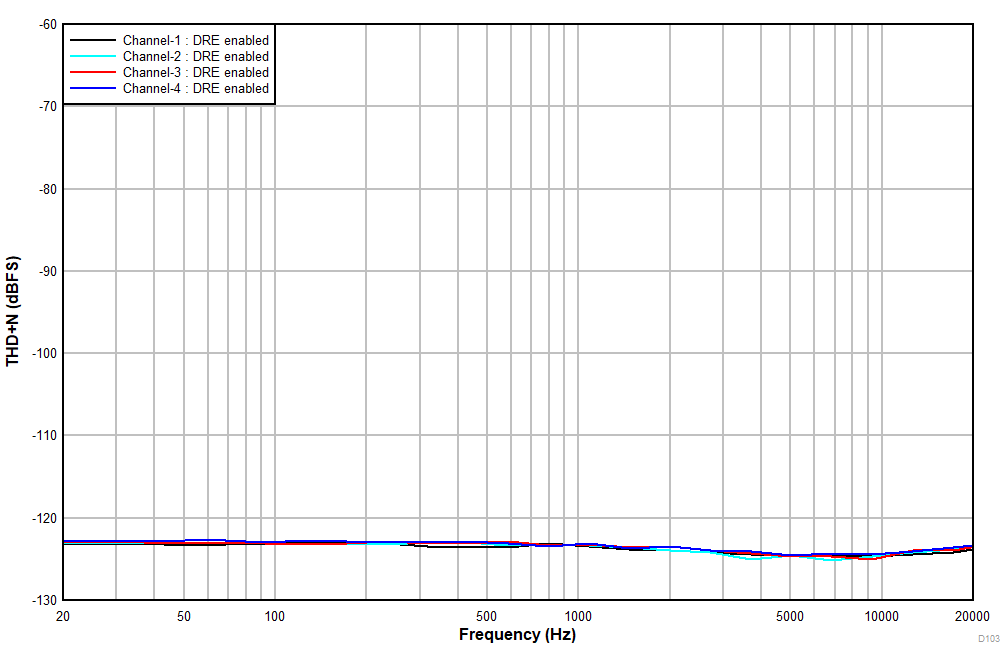
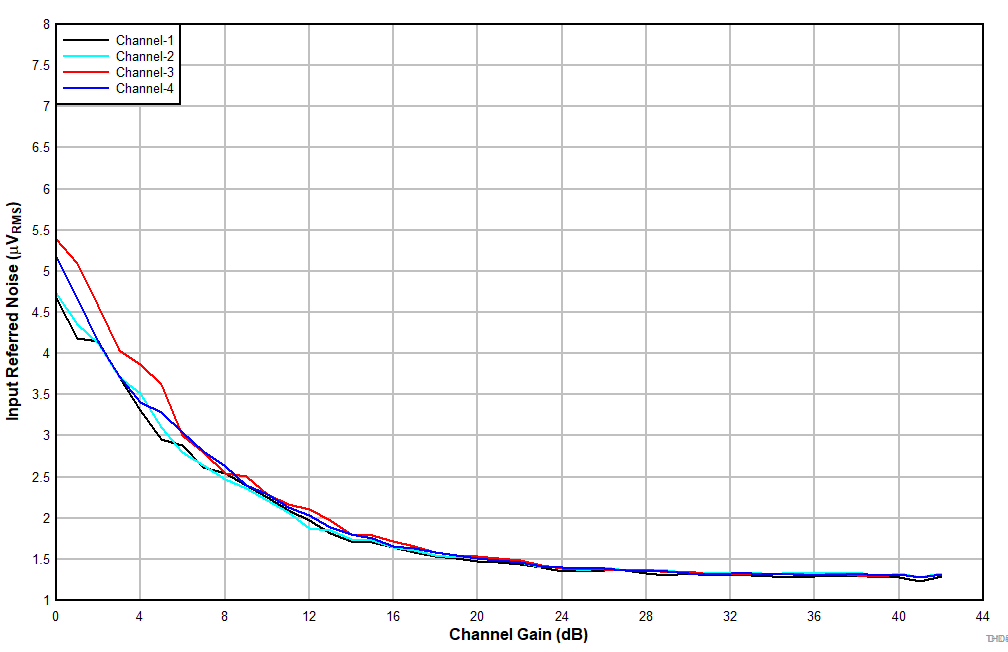
| Differential input |
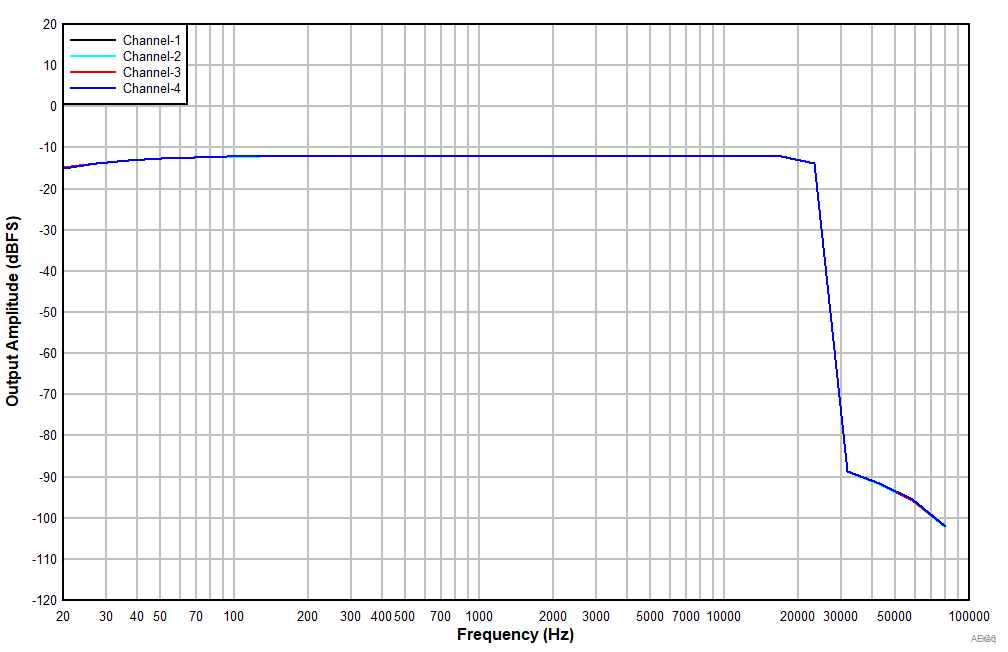
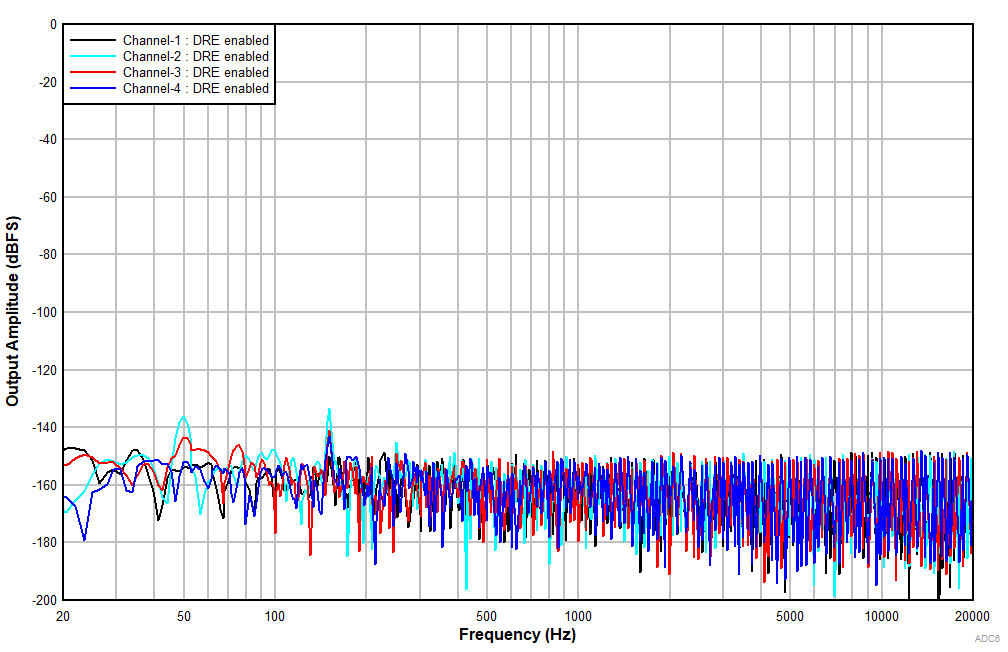
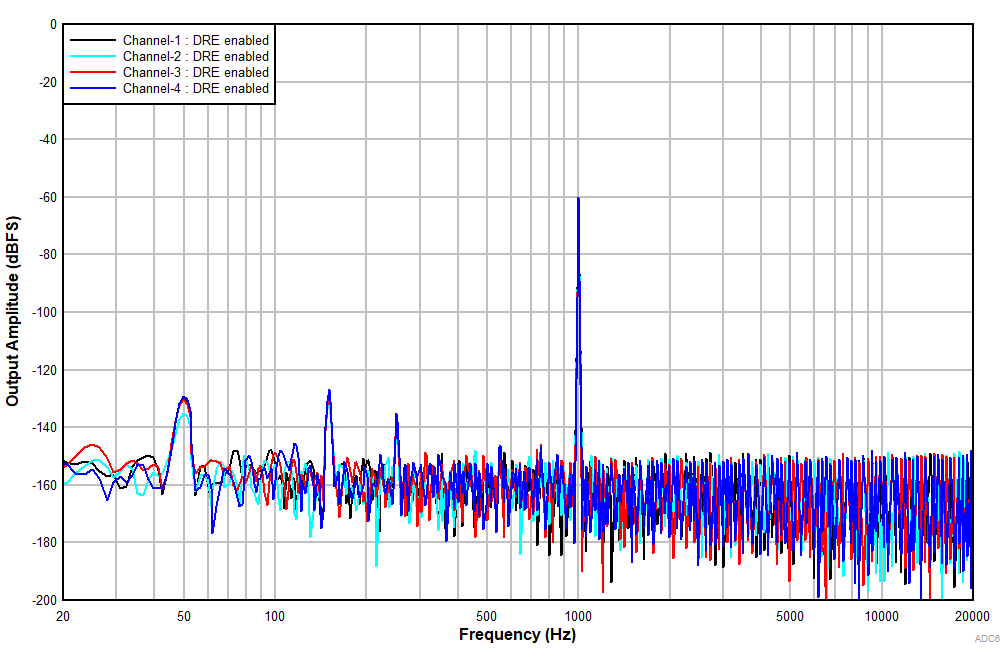
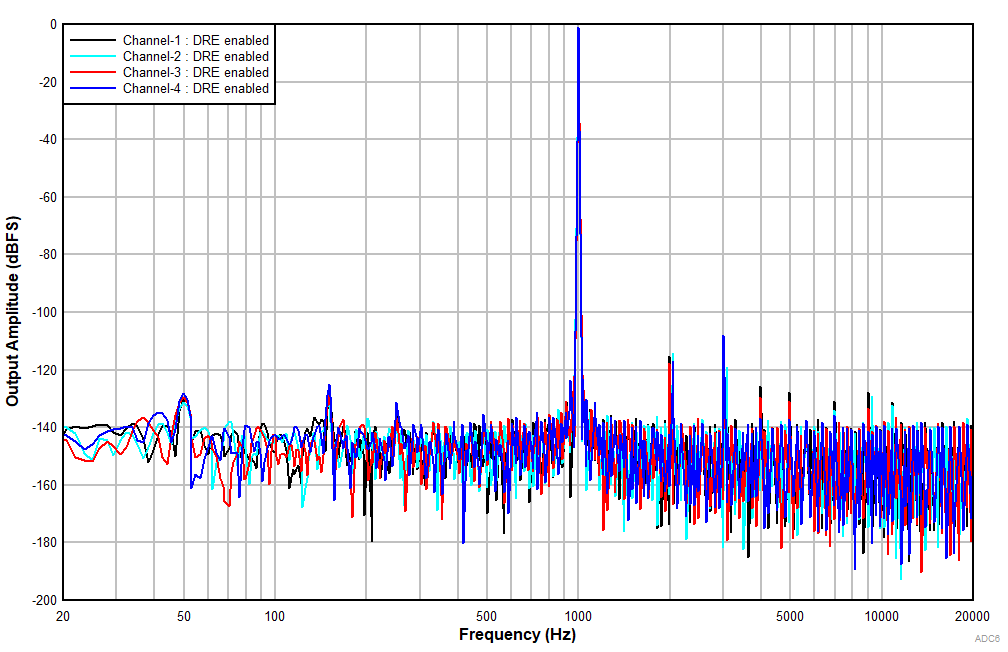
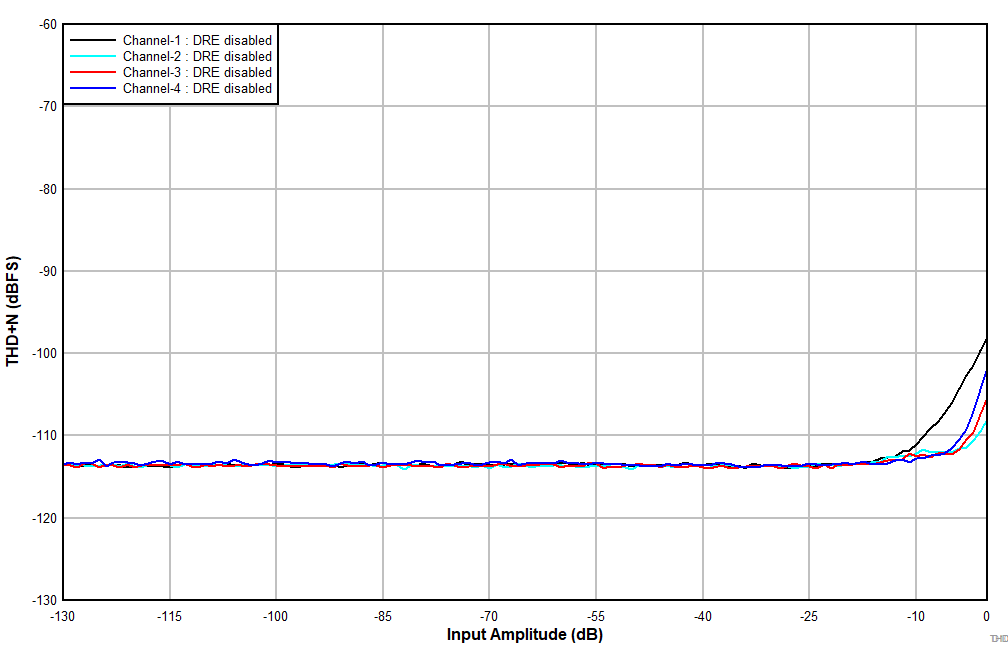
| Differential input |
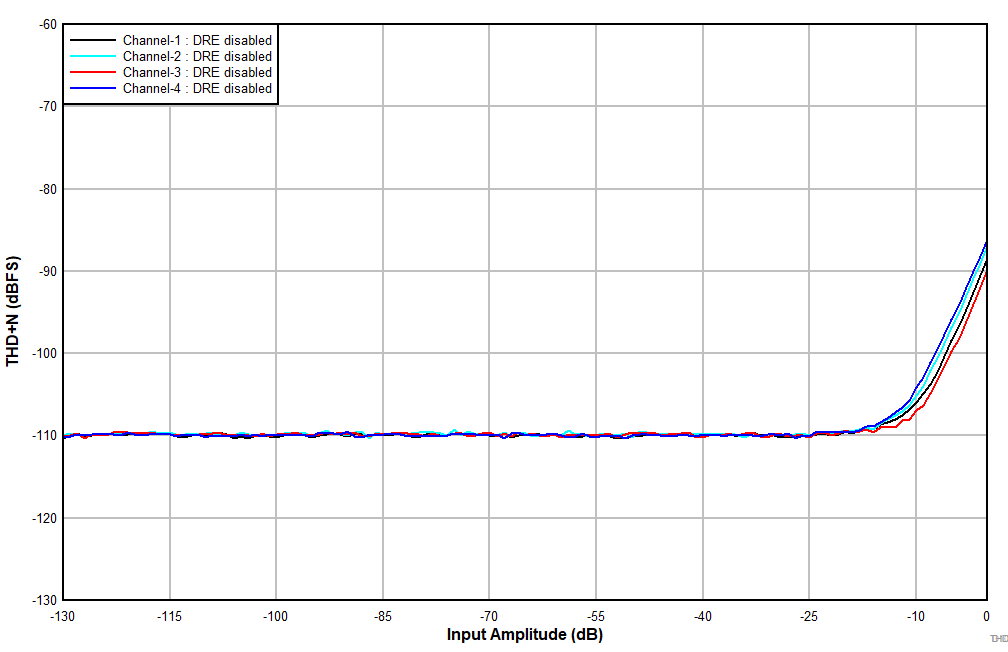
| Single-ended input |
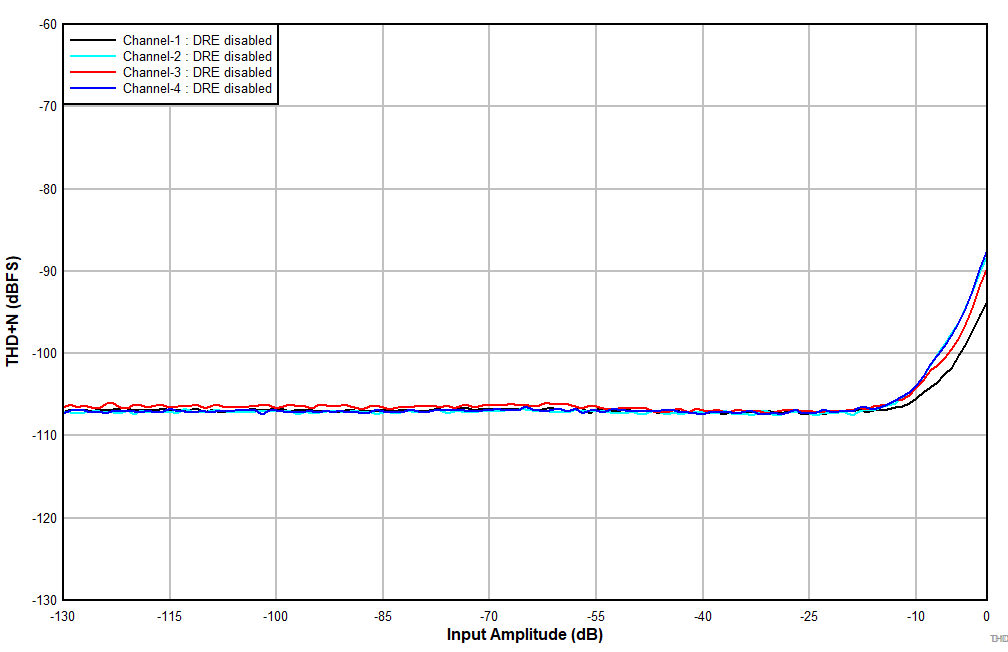
| Differential input with AVDD = 1.8 V and VREF = 1.375 V |
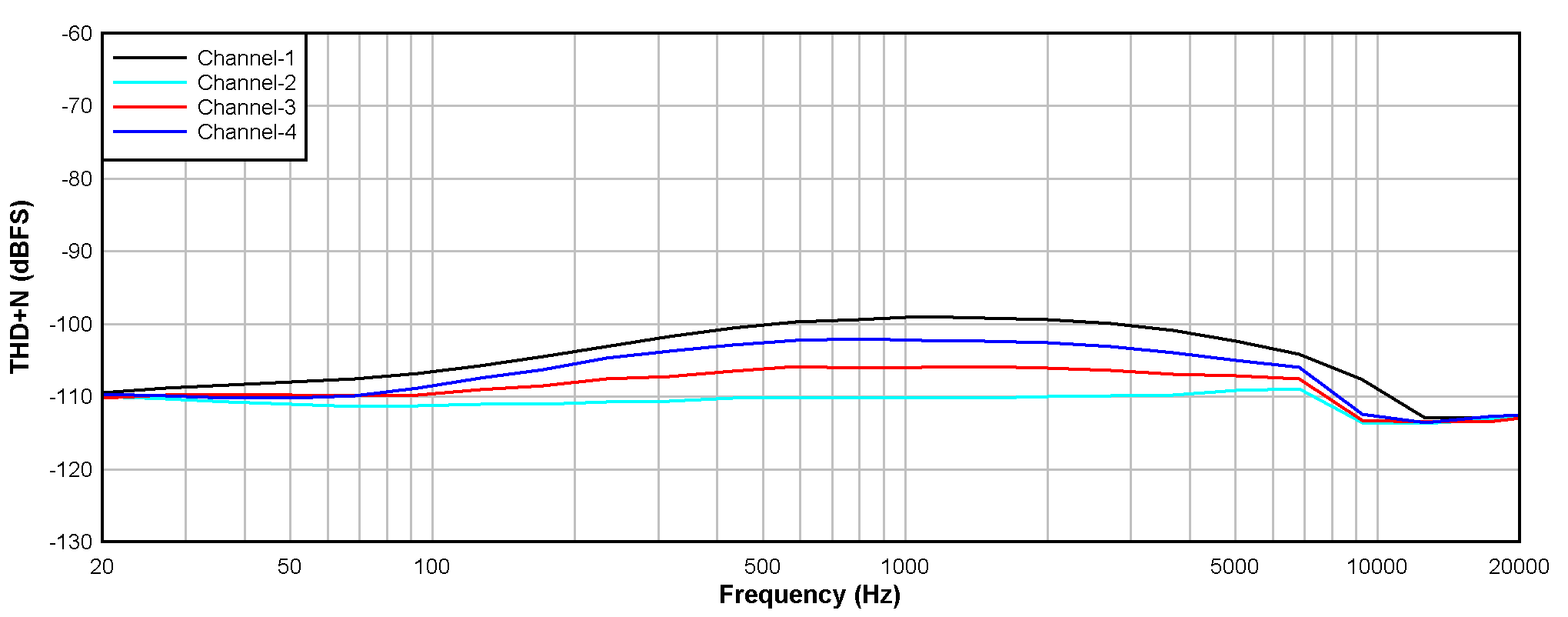
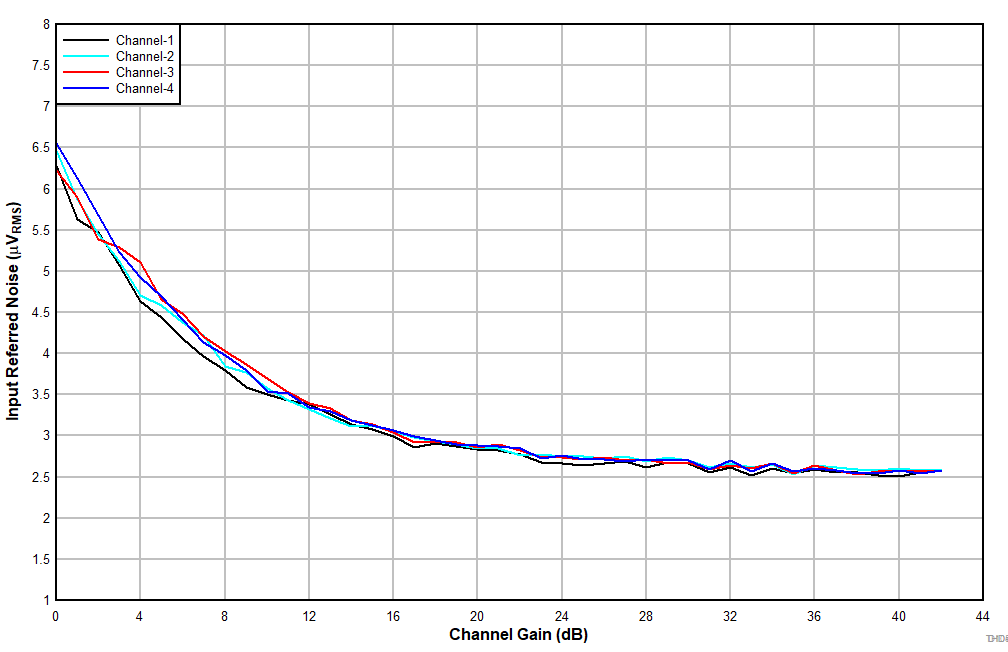
| Single-ended input |