SBASAU4 March 2024 PCM6140-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Timing Requirements: I2C Interface
- 6.7 Switching Characteristics: I2C Interface
- 6.8 Timing Requirements: SPI Interface
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics: SPI Interface
- 6.10 Timing Requirements: TDM, I2S or LJ Interface
- 6.11 Switching Characteristics: TDM, I2S or LJ Interface
- 6.12 Timing Requirements: PDM Digital Microphone Interface
- 6.13 Switching Characteristics: PDM Digial Microphone Interface
- 6.14 Timing Diagrams
- 6.15 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Serial Interfaces
- 7.3.2 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) and Clock Generation
- 7.3.3 Input Channel Configurations
- 7.3.4 Reference Voltage
- 7.3.5 Programmable Microphone Bias
- 7.3.6
Signal-Chain Processing
- 7.3.6.1 Programmable Channel Gain and Digital Volume Control
- 7.3.6.2 Programmable Channel Gain Calibration
- 7.3.6.3 Programmable Channel Phase Calibration
- 7.3.6.4 Programmable Digital High-Pass Filter
- 7.3.6.5 Programmable Digital Biquad Filters
- 7.3.6.6 Programmable Channel Summer and Digital Mixer
- 7.3.6.7
Configurable Digital Decimation Filters
- 7.3.6.7.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 7.3.6.7.1.1 Sampling Rate: 8 kHz or 7.35 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.2 Sampling Rate: 16 kHz or 14.7 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.3 Sampling Rate: 24 kHz or 22.05 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.4 Sampling Rate: 32 kHz or 29.4 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.5 Sampling Rate: 48 kHz or 44.1 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.6 Sampling Rate: 96 kHz or 88.2 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.7 Sampling Rate: 192 kHz or 176.4 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.8 Sampling Rate: 384 kHz or 352.8 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1.9 Sampling Rate 768 kHz or 705.6 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.2 Low-Latency Filters
- 7.3.6.7.3
Ultra-Low-Latency Filters
- 7.3.6.7.3.1 Sampling Rate: 16 kHz or 14.7 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.2 Sampling Rate: 24 kHz or 22.05 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.3 Sampling Rate: 32 kHz or 29.4 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.4 Sampling Rate: 48 kHz or 44.1 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.5 Sampling Rate: 96 kHz or 88.2 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.6 Sampling Rate 192 kHz or 176.4 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.3.7 Sampling Rate 384 kHz or 352.8 kHz
- 7.3.6.7.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 7.3.7 Dynamic Range Enhancer (DRE)
- 7.3.8 Automatic Gain Controller (AGC)
- 7.3.9 Digital PDM Microphone Record Channel
- 7.3.10 Interrupts, Status, and Digital I/O Pin Multiplexing
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
-
8 Register Maps
- 8.1
Device Configuration Registers
- 8.1.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.1.1.1 PAGE_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x00) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.2 SW_RESET Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x01) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.3 SLEEP_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x02) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.4 SHDN_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x05) [reset = 5h]
- 8.1.1.5 ASI_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x07) [reset = 30h]
- 8.1.1.6 ASI_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x08) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.7 ASI_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x09) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.8 ASI_CH1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0B) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.9 ASI_CH2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0C) [reset = 1h]
- 8.1.1.10 ASI_CH3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0D) [reset = 2h]
- 8.1.1.11 ASI_CH4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0E) [reset = 3h]
- 8.1.1.12 ASI_CH5 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0F) [reset = 4h]
- 8.1.1.13 ASI_CH6 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x10) [reset = 5h]
- 8.1.1.14 ASI_CH7 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x11) [reset = 6h]
- 8.1.1.15 ASI_CH8 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x12) [reset = 7h]
- 8.1.1.16 MST_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x13) [reset = 2h]
- 8.1.1.17 MST_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x14) [reset = 48h]
- 8.1.1.18 ASI_STS Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x15) [reset = FFh]
- 8.1.1.19 CLK_SRC Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x16) [reset = 10h]
- 8.1.1.20 PDMCLK_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x1F) [reset = 40h]
- 8.1.1.21 PDMIN_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x20) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.22 GPIO_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x21) [reset = 22h]
- 8.1.1.23 GPO_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x22) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.24 GPO_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x23) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.25 GPO_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x24) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.26 GPO_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x25) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.27 GPO_VAL Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x29) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.28 GPIO_MON Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2A) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.29 GPI_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2B) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.30 GPI_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2C) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.31 GPI_MON Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2F) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.32 INT_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x32) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.33 INT_MASK0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x33) [reset = FFh]
- 8.1.1.34 INT_LTCH0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x36) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.35 BIAS_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3B) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.36 CH1_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3C) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.37 CH1_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3D) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.38 CH1_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3E) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.39 CH1_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3F) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.40 CH1_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x40) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.41 CH2_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x41) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.42 CH2_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x42) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.43 CH2_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x43) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.44 CH2_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x44) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.45 CH2_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x45) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.46 CH3_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x46) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.47 CH3_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x47) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.48 CH3_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x48) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.49 CH3_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x49) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.50 CH3_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4A) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.51 CH4_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4B) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.52 CH4_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4C) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.53 CH4_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4D) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.54 CH4_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4E) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.55 CH4_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4F) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.56 CH5_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x52) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.57 CH5_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x53) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.58 CH5_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x54) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.59 CH6_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x57) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.60 CH6_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x58) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.61 CH6_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x59) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.62 CH7_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x5C) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.63 CH7_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x5D) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.64 CH7_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x5E) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.65 CH8_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x61) [reset = C9h]
- 8.1.1.66 CH8_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x62) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.67 CH8_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x63) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.68 DSP_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x6B) [reset = 1h]
- 8.1.1.69 DSP_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x6C) [reset = 40h]
- 8.1.1.70 DRE_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x6D) [reset = 7Bh]
- 8.1.1.71 AGC_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x70) [reset = E7h]
- 8.1.1.72 IN_CH_EN Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x73) [reset = F0h]
- 8.1.1.73 ASI_OUT_CH_EN Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x74) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.74 PWR_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x75) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.75 DEV_STS0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x76) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1.76 DEV_STS1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x77) [reset = 80h]
- 8.1.1.77 I2C_CKSUM Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x7E) [reset = 0h]
- 8.1.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.2 Programmable Coefficient Registers
- 8.1
Device Configuration Registers
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Orderable Information
7.3.6 Signal-Chain Processing
The PCM6140-Q1 signal chain is comprised of very-low-noise, high-performance, and low-power analog blocks and highly flexible and programmable digital processing blocks. The high performance and flexibility combined with a compact package makes the PCM6140-Q1 optimized for a variety of end-equipments and applications that require multichannel audio capture. Figure 7-16 shows a conceptual block diagram that highlights the various building blocks used in the signal chain, and how the blocks interact in the signal chain.
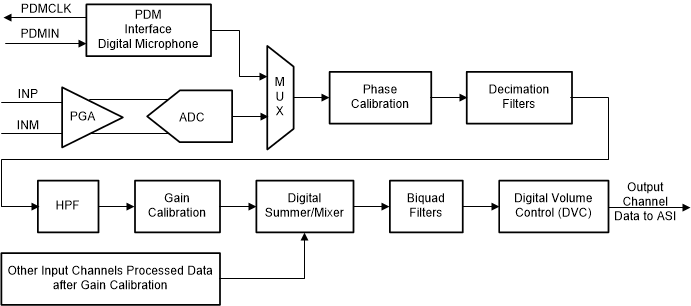 Figure 7-16 Signal-Chain Processing Flowchart
Figure 7-16 Signal-Chain Processing FlowchartThe front-end PGA is very low noise, with a 120-dB dynamic range performance. Along with a low-noise and low-distortion, multibit, delta-sigma ADC, the front-end PGA enables the PCM6140-Q1 to record a far-field audio signal with very high fidelity, both in quiet and loud environments. Moreover, the ADC architecture has inherent antialias filtering with a high rejection of out-of-band frequency noise around multiple modulator frequency components. Therefore, the device prevents noise from aliasing into the audio band during ADC sampling. Further on in the signal chain, an integrated, high-performance multistage digital decimation filter sharply cuts off any out-of-band frequency noise with high stop-band attenuation.
The device also has an integrated programmable biquad filter that allows for custom low-pass, high-pass, or any other desired frequency shaping. Thus, the overall signal chain architecture removes the requirement to add external components for antialiasing low-pass filtering, and thus saves drastically on the external system component cost and board space. See the TLV320ADCx140 Integrated Analog Antialiasing Filter and Flexible Digital Filter application report for further details.
The signal chain also consists of various highly programmable digital processing blocks such as phase calibration, gain calibration, high-pass filter, digital summer or mixer, biquad filters, and volume control. The details on these processing blocks are discussed further in this section. The device also supports up to eight digital PDM microphone recording channels when the analog record channels are not used. Channels 1 to 4 in the signal chain block diagram of Figure 7-16 are as described in this section, however, channels 5 to 8 only support the digital microphone recording option and do not support the digital summer or mixer option.
The desired input channels for recording can be enabled or disabled by using the IN_CH_EN (P0_R115) register, and the output channels for the audio serial interface can be enabled or disabled by using the ASI_OUT_EN (P0_R116) register. In general, the device supports simultaneous power-up and power-down of all active channels for simultaneous recording. However, based on the application needs, if some channels must be powered-up or powered-down dynamically when the other channel recording is on, then that use case is supported by setting the DYN_CH_PUPD_EN, P0_R117_D4 register bit to 1'b1 but do not power-down channel 1 in this mode of operation.
The device supports an input signal bandwidth up to 80 kHz, which allows the high-frequency non-audio signal to be recorded by using a 176.4-kHz (or higher) sample rate.
For output sample rates of 48 kHz or lower, the device supports all features for 8-channel recording and various programmable processing blocks. However, for output sample rates higher than 48 kHz, there are limitations in the number of simultaneous channel recordings supported and the number of biquad filters and such. See the TLV320ADCx140 Sampling Rates and Programmable Processing Blocks Supported application report for further details.