at TA = 25°C, AVDD = 3.3 V,
IOVDD = 3.3 V, BSTVDD = 3.3 V, fIN = 1-kHz sinusoidal signal, fS = 48
kHz, 32-bit audio data, BCLK = 256 × fS, TDM slave mode, PLL on, channel
gain = 0 dB, linear phase decimation filter, and MICBIAS programmed voltage = 8 V
(unless otherwise noted); all performance measurements are done by feeding the device analog input and PDM digital
input signal using audio precision with a 20-kHz, low-pass filter and an
A-weighted filter (unless otherwise noted)
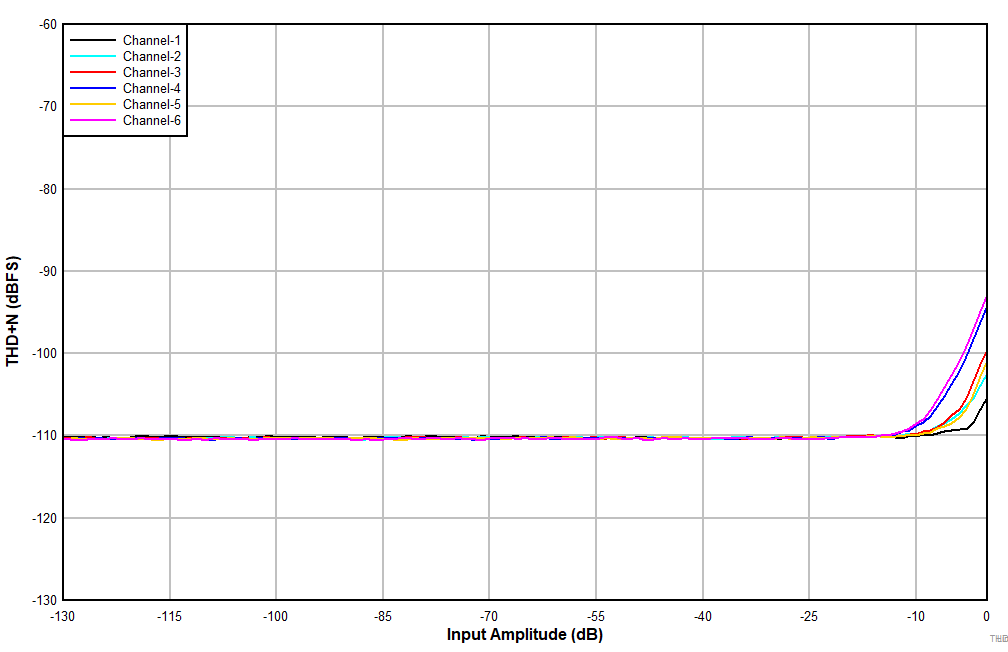
| AC-coupled differential line input |
Figure 7-5 THD+N
vs Input Amplitude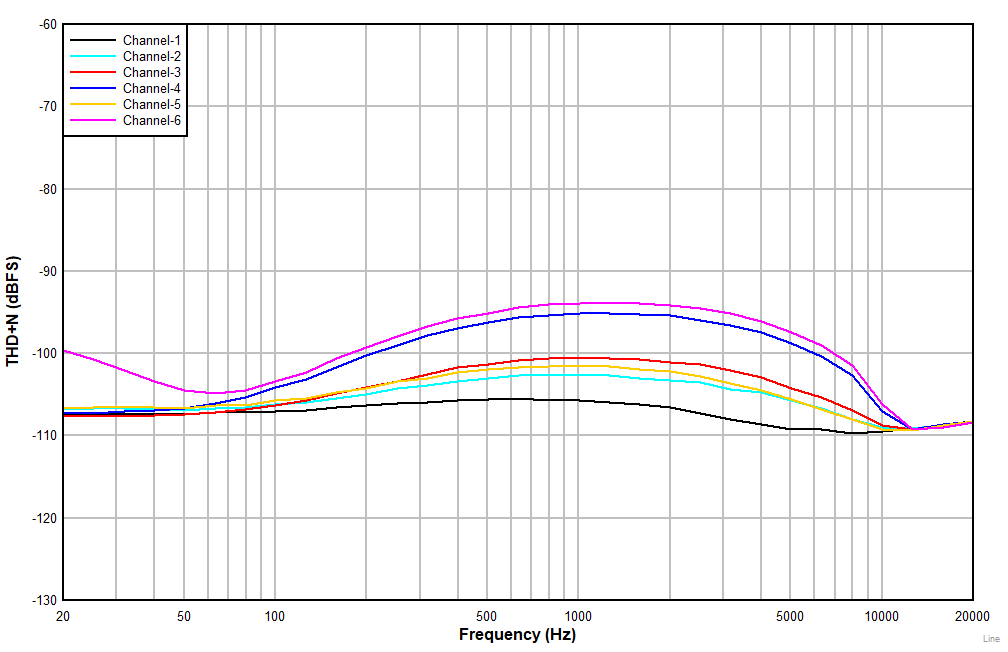
| AC-coupled differential line input |
Figure 7-7 THD+N
vs Input Frequency With a
–1-dBr Input (non
A-weighted)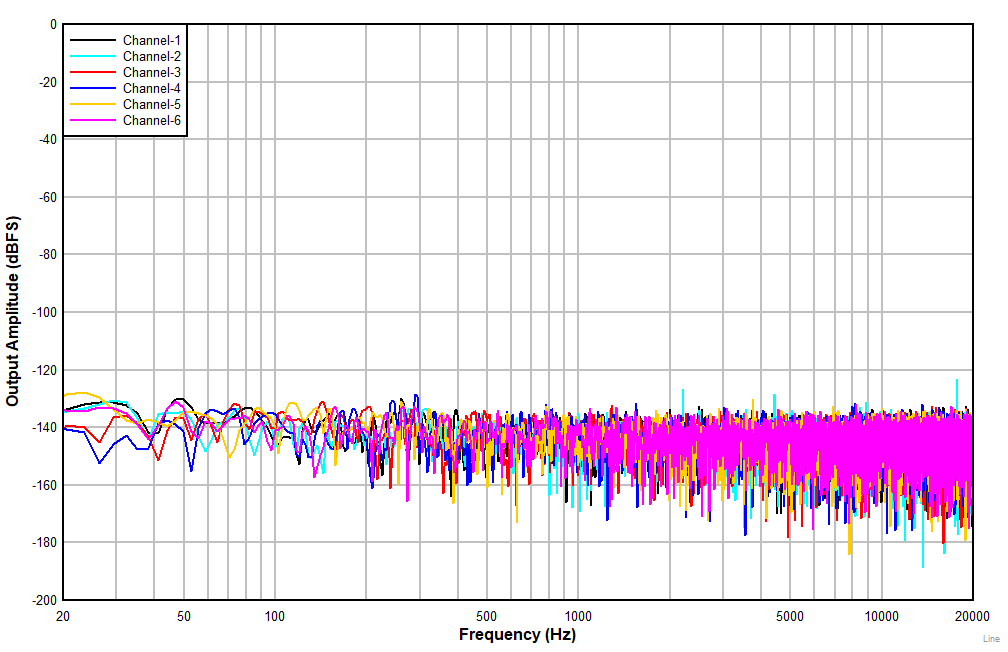
| AC-coupled differential line input |
Figure 7-9 FFT
With Idle Input (non A-weighted)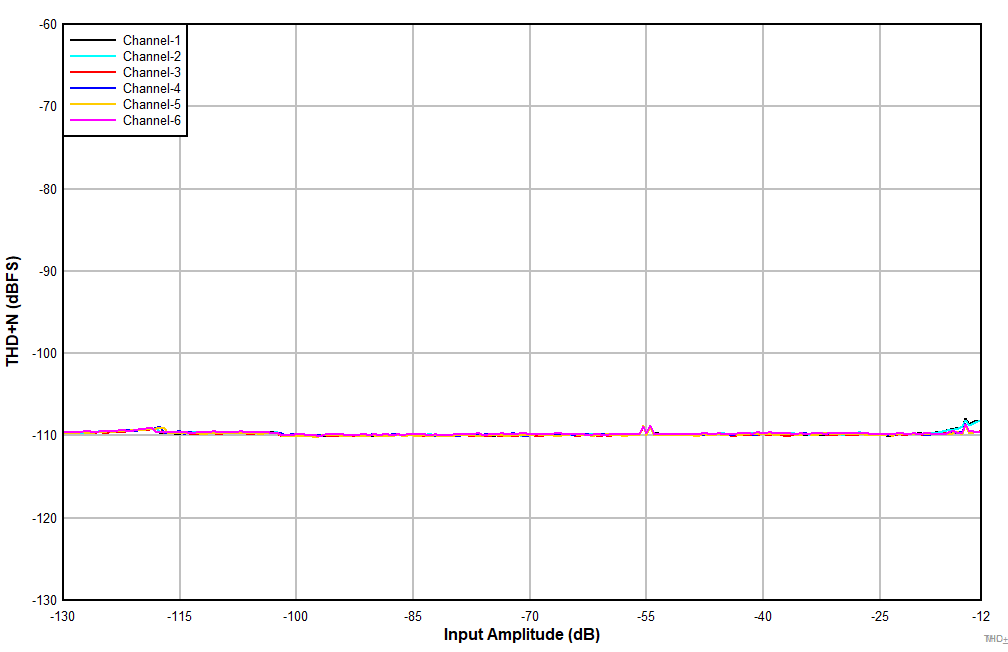
| DC-coupled differential microphone input with DC
common-mode 1NxP = 6 V and INxM = 2 V, high swing mode
enabled |
Figure 7-11 THD+N
vs Input Amplitude
| DC-coupled differential microphone input with DC
common-mode 1NxP = 6 V and INxM = 2 V, High swing mode
enabled |
Figure 7-13 THD+N
vs Input Frequency With a
–15-dBr Input (non
A-weighted)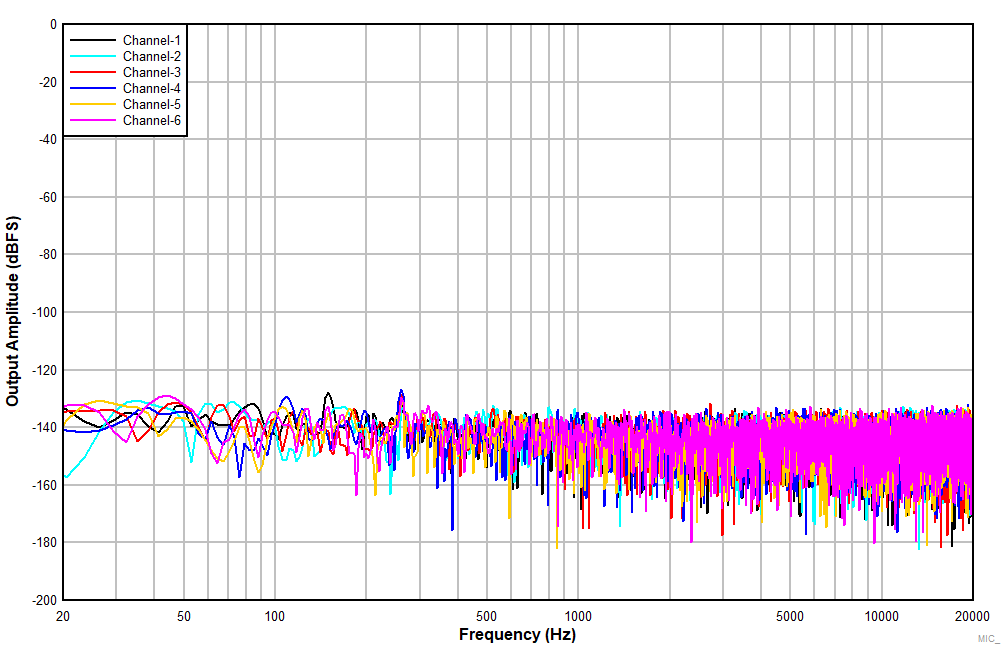
| DC-coupled differential microphone input with DC
common-mode 1NxP = 6 V and INxM = 2 V, high swing mode
enabled |
Figure 7-15 FFT
With Idle Input (non A-weighted)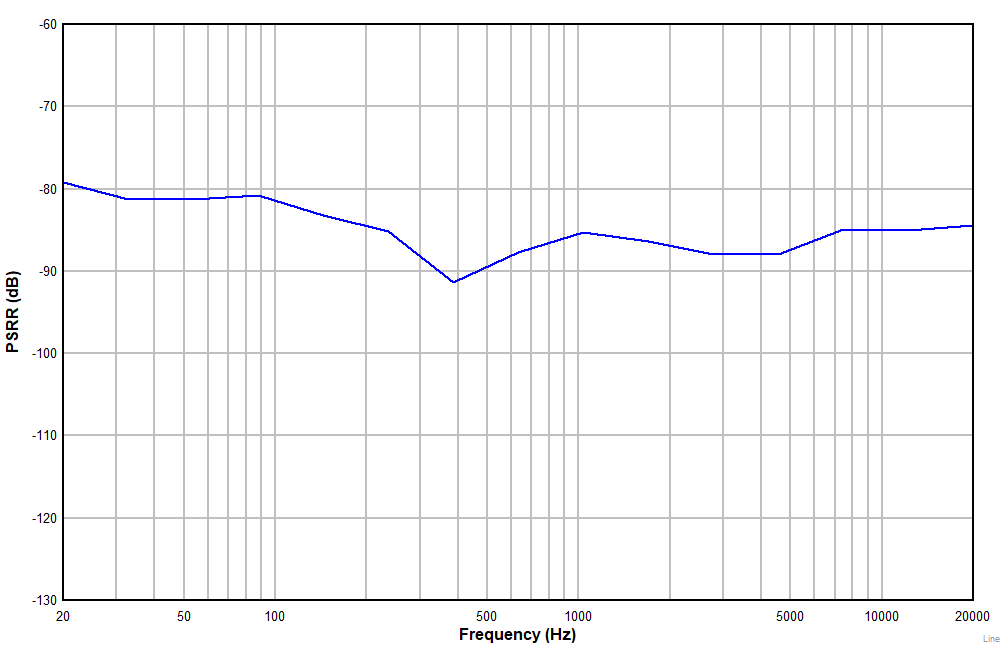
| AC-coupled differential line input |
| |
Figure 7-17 Power-Supply Rejection Ratio vs Ripple Frequency With 1-VPP
Amplitude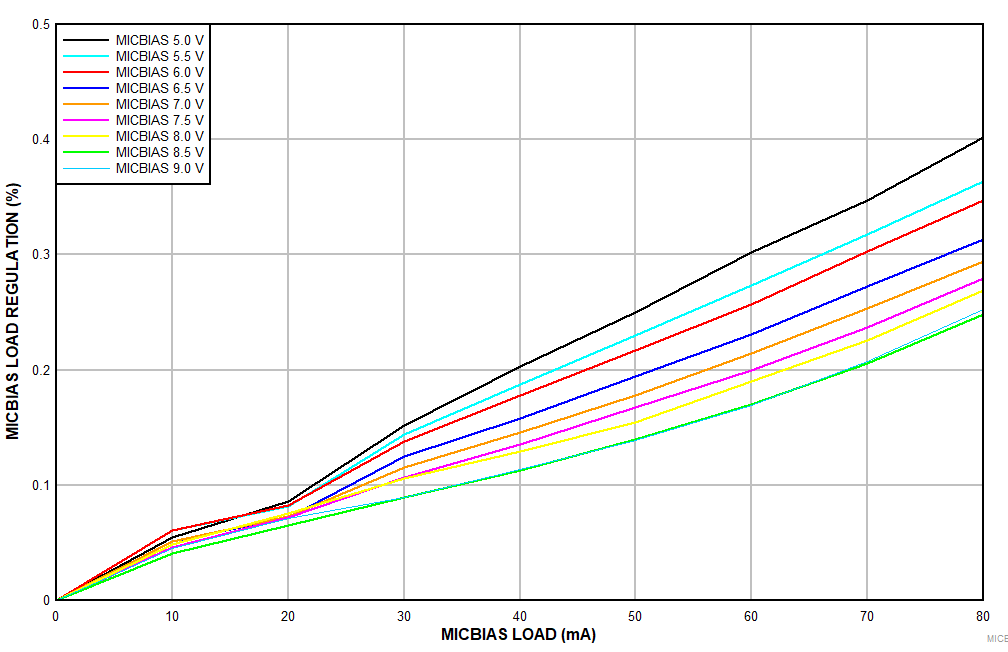
| DC-coupled differential microphone input |
Figure 7-19 MICBIAS Load Regulation vs MICBIAS Load Current
| 4th-order PDM modulator with PDMCLKx = 3.072
MHz |
Figure 7-21 THD+N vs Input
Amplitude
| 4th-order PDM modulator with PDMCLKx = 3.072
MHz |
Figure 7-23 FFT With a –60-dBFS Input
(non A-weighted)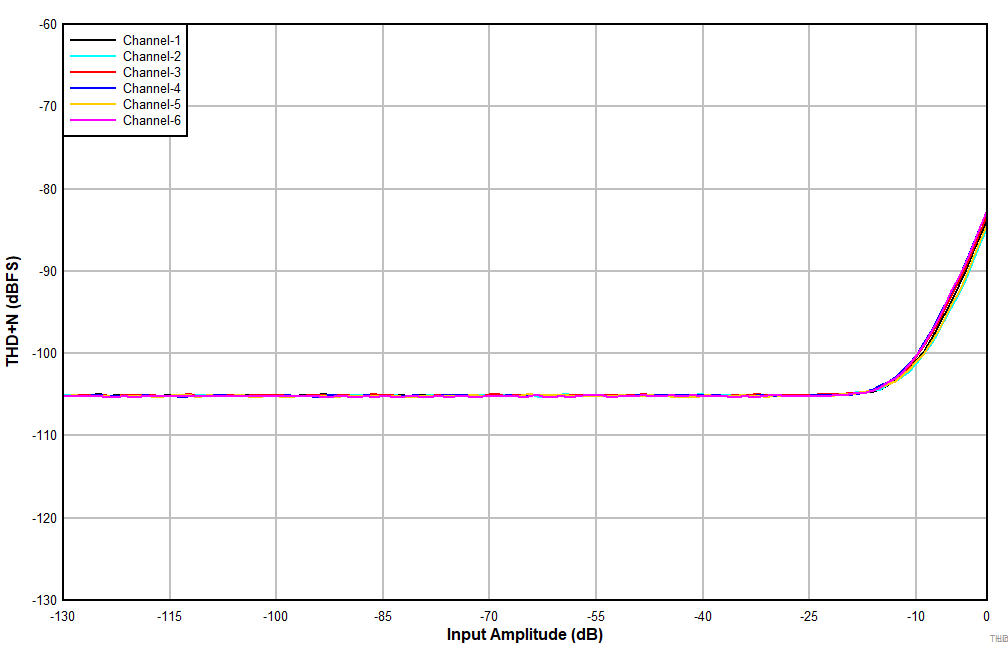
| AC-coupled single-ended line input |
Figure 7-6 THD+N
vs Input Amplitude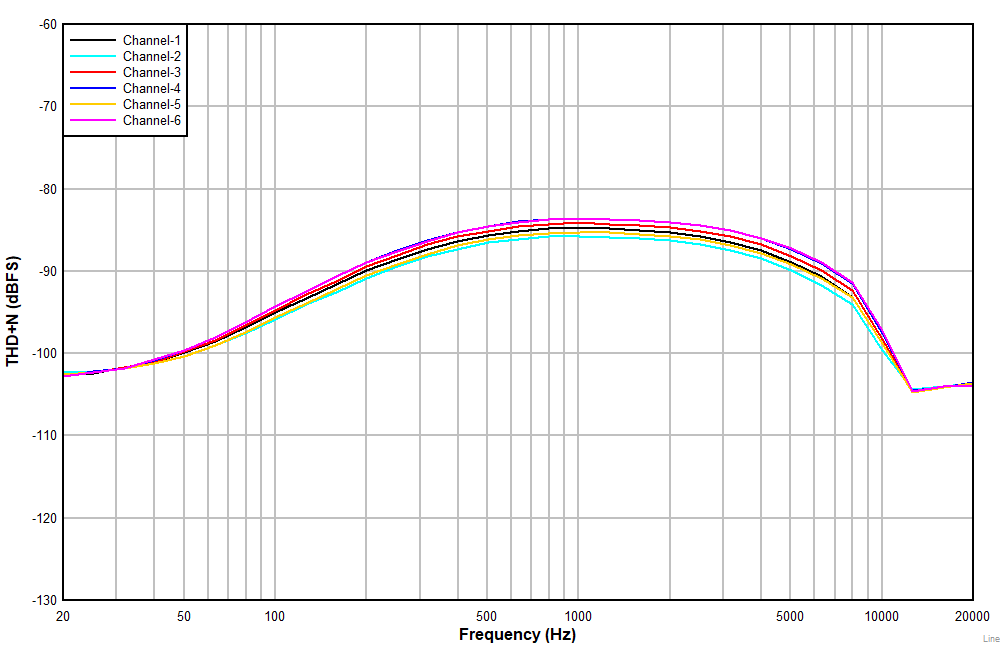
| AC-coupled single-ended line input |
Figure 7-8 THD+N
vs Input Frequency With a
–1-dBr Input (non
A-weighted)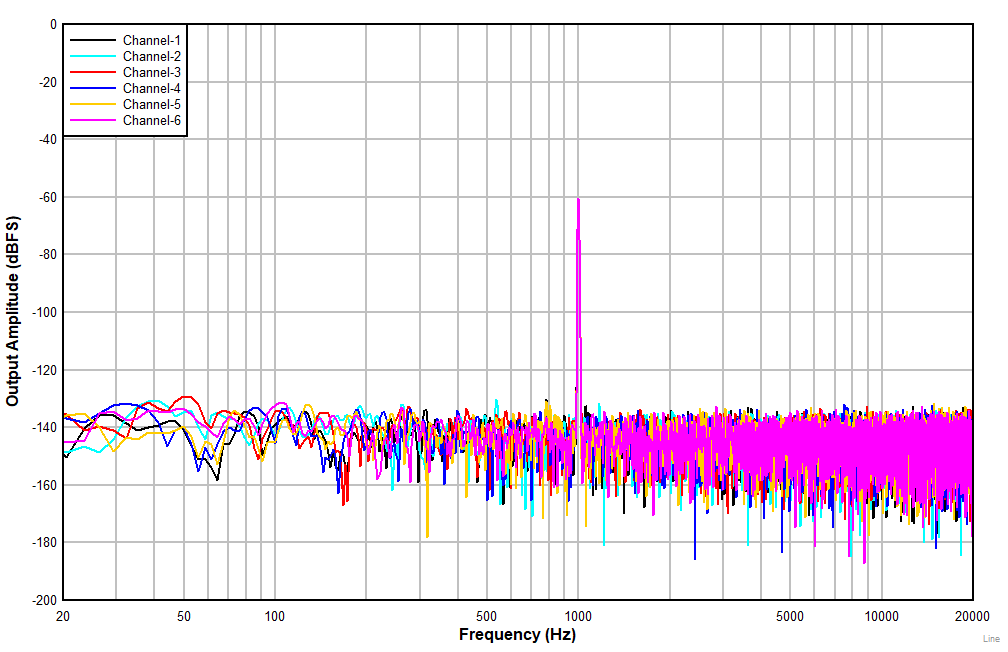
| AC-coupled differential line input |
Figure 7-10 FFT
With a –60-dBr Input (non A-weighted)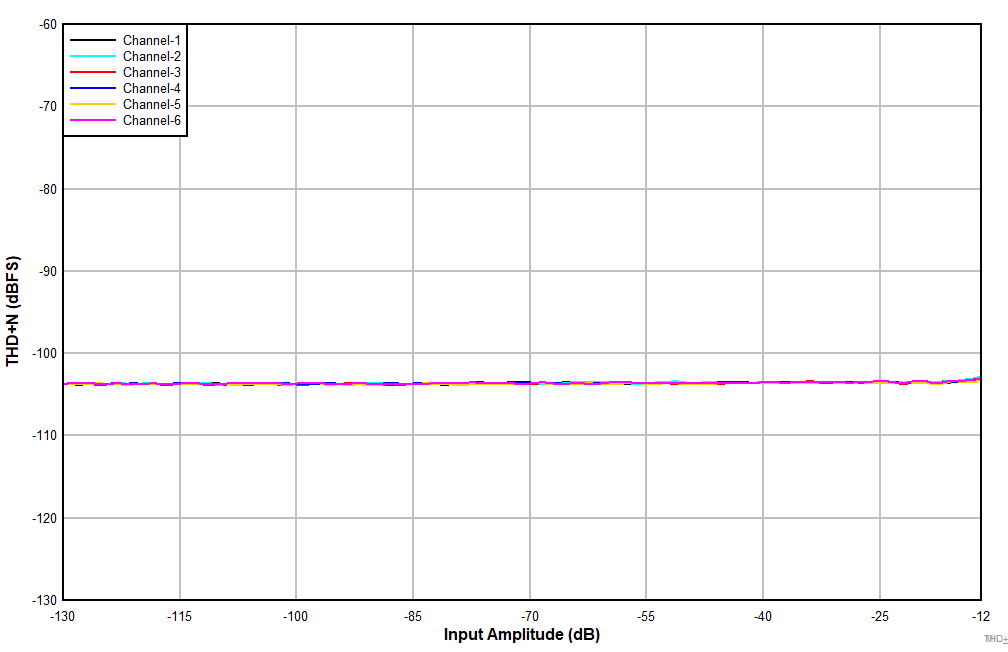
| DC-coupled single-ended microphone input with DC
common-mode 1NxP = 4 V and INxM = 0 V, high swing mode
enabled |
Figure 7-12 THD+N
vs Input Amplitude
| DC-coupled single-ended microphone input with DC
common-mode 1NxP = 4 V and INxM = 0 V, high swing mode
enabled |
Figure 7-14 THD+N
vs Input Frequency With a
–15-dBr Input (non
A-weighted)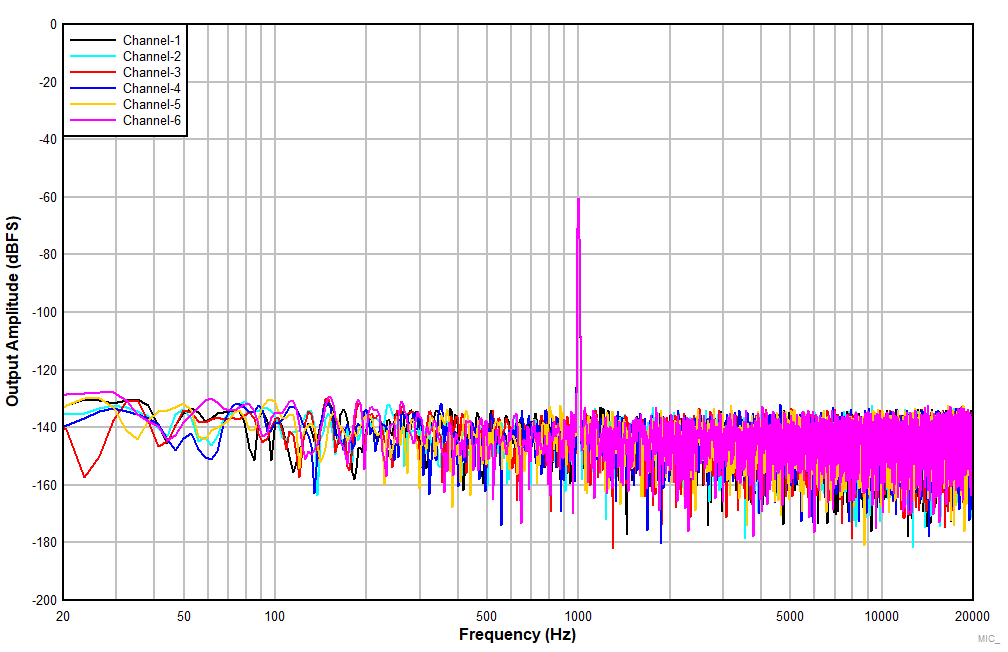
| DC-coupled differential microphone input with DC
common-mode 1NxP = 6 V and INxM = 2 V, high swing mode
enabled |
Figure 7-16 FFT
With a –60-dBr Input (non A-weighted)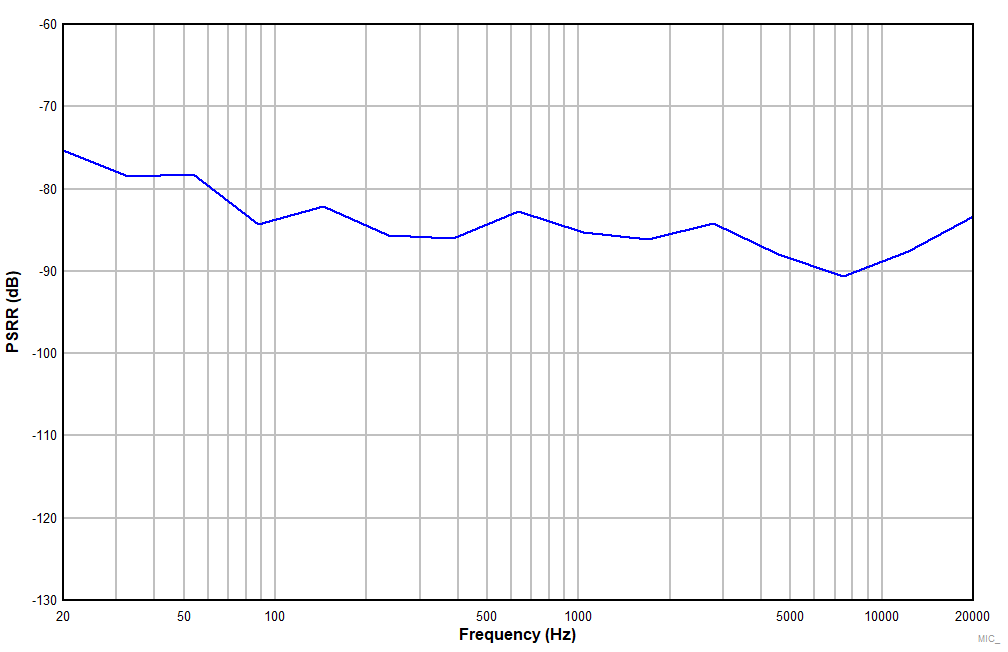
| DC-coupled differential microphone input with DC
common-mode 1NxP = 6 V and INxM = 2 V, high swing mode
enabled |
Figure 7-18 Power-Supply Rejection Ratio vs Ripple Frequency With 1-VPP
Amplitude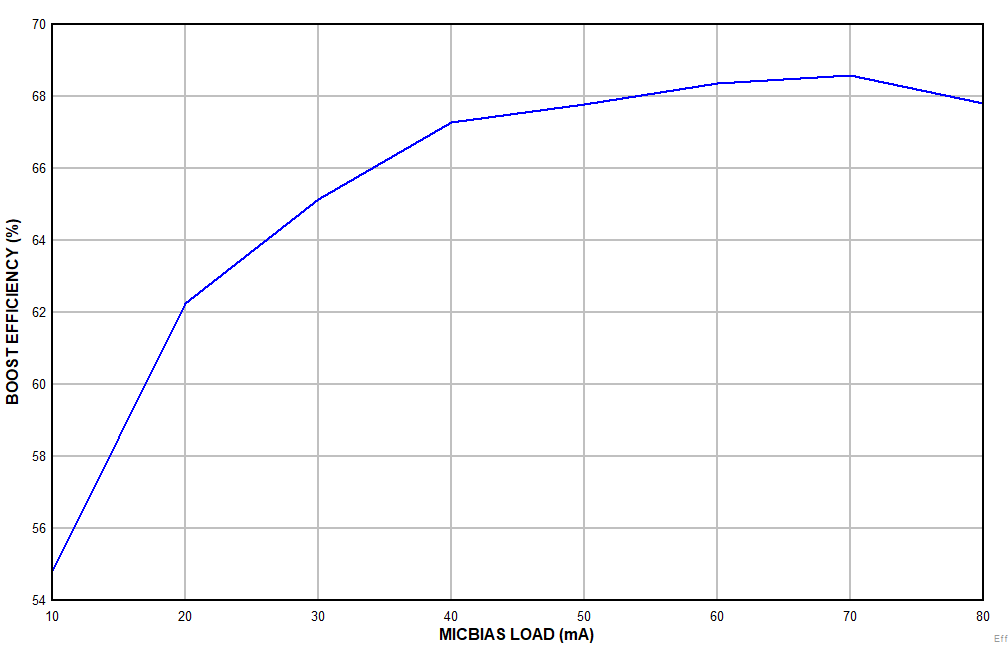
| DC-coupled differential microphone input with DC
common-mode 1NxP = 6 V and INxM = 2 V, high swing mode
enabled |
Figure 7-20 Boost
Efficiency vs MICBIAS Load Current
| 4th-order PDM modulator with PDMCLKx = 3.072
MHz |
Figure 7-22 THD+N vs Input Frequency
With a –20-dBFS Input
| 4th-order PDM modulator with PDMCLKx = 3.072
MHz |
Figure 7-24 Amplitude Response With a
–20-dBFS Input



















