SLTS278J November 2010 – March 2020 PTH08T250W
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1
Typical Application
- 9.1.1
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.1.1.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 9.1.1.2
Capacitor Recommendations for the PTH08T250W Power Module
- 9.1.1.2.1 Capacitor Technologies
- 9.1.1.2.2 Input Capacitor (Required)
- 9.1.1.2.3 Input Capacitor Information
- 9.1.1.2.4 Output Capacitor (Required)
- 9.1.1.2.5 Output Capacitor Information
- 9.1.1.2.6 TurboTrans Output Capacitance
- 9.1.1.2.7 Non-TurboTrans Output Capacitance
- 9.1.1.2.8 Designing for Fast Load Transients
- 9.1.1.2.9 Capacitor Table
- 9.1.1.3 TurboTrans™ Technology
- 9.1.1.4 TurboTrans™ Selection
- 9.1.1.5 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 9.1.1.6 On/Off Inhibit
- 9.1.1.7 Current Sharing
- 9.1.1.8 Prebias Startup Capability
- 9.1.1.9 SmartSync Technology
- 9.1.1.10 Auto-Track™ Function
- 9.1.1
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.1
Typical Application
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- BCU|22
- ECT|22
- ECU|22
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3 Typical Characteristics (VI = 12 V)
(1)(2)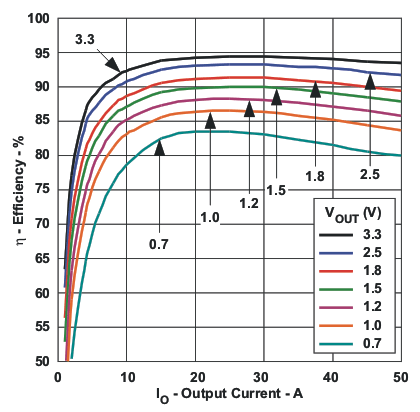 Figure 1. Efficiency versus Output Current
Figure 1. Efficiency versus Output Current 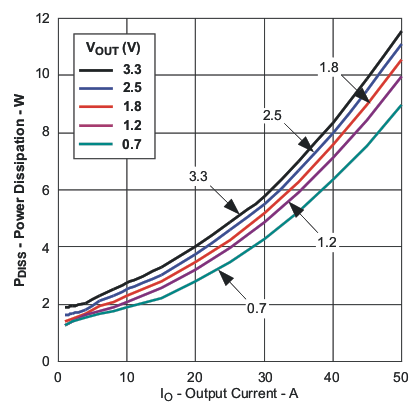 Figure 3. Power Dissipation versus Output Current
Figure 3. Power Dissipation versus Output Current 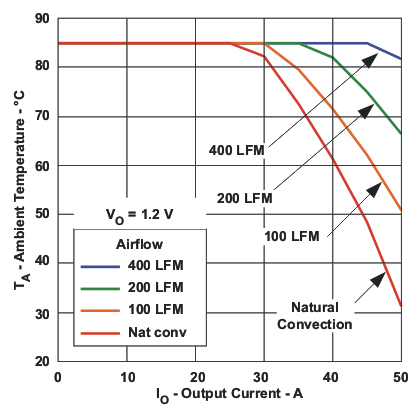 Figure 5. Ambient Temperature versus Output Current
Figure 5. Ambient Temperature versus Output Current 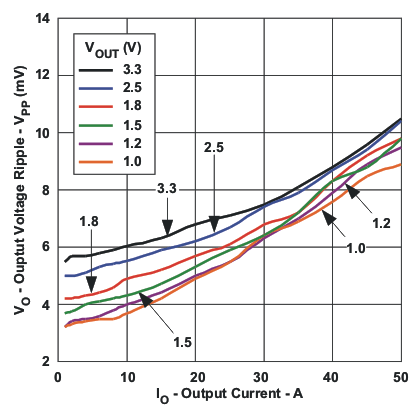 Figure 2. Output Ripple versus Output Current
Figure 2. Output Ripple versus Output Current 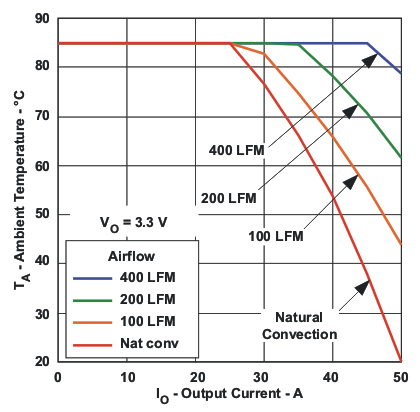 Figure 4. Ambient Temperature versus Output Current
Figure 4. Ambient Temperature versus Output Current