7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)
|
MIN |
MAX |
UNIT |
| Supply voltage, V+ to V– |
|
7 |
V |
| Output short circuit |
Continuous |
|
| Operating temperature |
–55 |
135 |
°C |
| Junction temperature |
|
150 |
°C |
| Storage temperature, Tstg |
–65 |
150 |
°C |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
7.2 ESD Ratings
|
VALUE |
UNIT |
| V(ESD) |
Electrostatic discharge |
Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) |
±2000 |
V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) |
±1000 |
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
|
MIN |
MAX |
UNIT |
| VIN |
Input voltage |
VREF + 0.05(1) |
5.5 |
V |
| ILOAD |
Load current |
|
25 |
mA |
| TA |
Operating temperature |
–40 |
125 |
°C |
(1) Minimum supply voltage for the REF3112-Q1 is 1.8 V.
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) |
REF31xx-Q1 |
UNIT |
| DBZ (SOT-23) |
| 3 PINS |
| RθJA |
Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance |
292.9 |
°C/W |
| RθJC(top) |
Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance |
124.4 |
°C/W |
| RθJB |
Junction-to-board thermal resistance |
89 |
°C/W |
| ψJT |
Junction-to-top characterization parameter |
11.4 |
°C/W |
| ψJB |
Junction-to-board characterization parameter |
87.6 |
°C/W |
| RθJC(bot) |
Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance |
— |
°C/W |
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, ILOAD = 0 mA, and VIN = 5 V (unless otherwise noted)
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
| REF3312-Q1(1) — 1.25 V |
| VOUT |
Output voltage |
|
1.2475 |
1.25 |
1.2525 |
V |
|
Initial accuracy |
|
–0.2% |
|
0.2% |
|
|
Output voltage noise |
f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz |
|
17 |
|
μVPP |
| f = 10 Hz to 10 kHz |
|
24 |
|
μVRMS |
| REF3120-Q1 — 2.048 V |
| VOUT |
Output voltage |
|
2.0439 |
2.048 |
2.0521 |
V |
|
Initial accuracy |
|
–0.2% |
|
0.2% |
|
|
Output voltage noise |
f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz |
|
27 |
|
μVPP |
| f = 10 Hz to 10 kHz |
|
39 |
|
μVRMS |
| REF3125-Q1 — 2.5 V |
| VOUT |
Output voltage |
|
2.495 |
2.5 |
2.505 |
V |
|
Initial accuracy |
|
–0.2% |
|
0.2% |
|
|
Output voltage noise |
f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz |
|
33 |
|
μVPP |
| f = 1 0Hz to 10 kHz |
|
48 |
|
μVRMS |
| REF3130-Q1 — 3 V |
| VOUT |
Output voltage |
|
2.994 |
3 |
3.006 |
V |
|
Initial accuracy |
|
–0.2% |
|
0.2% |
|
|
Output voltage noise |
f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz |
|
39 |
|
μVPP |
| f = 10 Hz to 10 kHz |
|
57 |
|
μVRMS |
| REF3133-Q1 — 3.3 V |
| VOUT |
Output voltage |
|
3.2934 |
3.3 |
3.3066 |
V |
|
Initial accuracy |
|
–0.2% |
|
0.2% |
|
|
Output voltage noise |
f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz |
|
43 |
|
μVPP |
| f = 10 Hz to 10 kHz |
|
63 |
|
μVRMS |
| REF3140-Q1 — 4.096 V |
| VOUT |
Output voltage |
|
4.0878 |
4.096 |
4.1042 |
V |
|
Initial accuracy |
|
–0.2% |
|
0.2% |
|
|
Output voltage noise |
f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz |
|
53 |
|
μVPP |
| f = 10 Hz to 10 kHz |
|
78 |
|
μVRMS |
| REF31xx-Q1 (REF3112-Q1, REF3120-Q1, REF3125-Q1, REF3130-Q1, REF3133-Q1, REF3140-Q1) |
| dVOUT/dT |
Output voltage temperature drift(2) |
TA = 0°C to 70°C. |
|
5 |
15 |
ppm/°C |
| TA = –40°C to +125°C . |
|
10 |
20 |
|
Long-term stability |
0 to 1000 hours |
|
70 |
|
ppm |
|
Line regulation |
VREF + 0.05(1) ≤ VIN ≤ 5.5 V |
|
20 |
65 |
ppm/V |
| dVOUT/dILOAD |
Load regulation(3) |
Sourcing |
0 mA < ILOAD < 10 mA, VIN = VREF + 250 mV(1) |
|
10 |
30 |
µV/mA |
| Sinking |
–10 mA < ILOAD < 0 mA, VIN = VREF + 100 mV(1) |
|
20 |
50 |
| dT |
Thermal hysteresis(4) |
First Cycle |
|
|
100 |
|
ppm |
| Additional Cycles |
|
|
25 |
|
| VIN – VOUT |
Dropout voltage(1) |
TA = –40°C to +125°C. |
|
5 |
50 |
mV |
| ILOAD |
Output current |
|
–10 |
|
10 |
mA |
| ISC |
Short-circuit current |
Sourcing |
|
|
50 |
|
mA |
| Sinking |
|
|
40 |
|
|
Turnon settling time |
To 0.1% at VIN = +5 V with CL = 0 μF |
|
400 |
|
µs |
| POWER SUPPLY |
| VS |
Voltage |
ILOAD = 0, TA = –40°C to +125°C. |
VREF + 0.05(1) |
|
5.5 |
V |
| IQ |
Quiescent current |
ILOAD = 0, TA = 25°C |
|
100 |
115 |
µA |
| ILOAD = 0, TA = –40°C to +125°C |
|
115 |
135 |
(1) Minimum supply voltage for the REF3112 is 1.8 V.
(2) Box Method used to determine temperature drift.
(3) Typical value of load regulation reflects measurements using force and sense contacts; see
Load Regulation.
7.6 Typical Characteristics
At TA = 25°C, VIN = 5-V power supply, and REF3125-Q1 is used for typical characteristic measurements, unless otherwise noted.
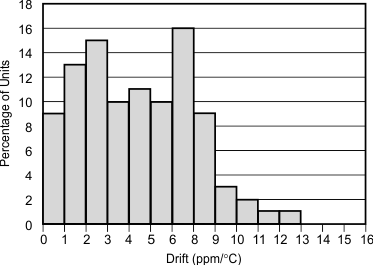 Figure 1. Temperature Drift
Figure 1. Temperature Drift
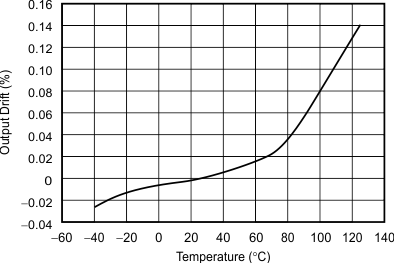 Figure 3. Output Voltage vs Temperature
Figure 3. Output Voltage vs Temperature
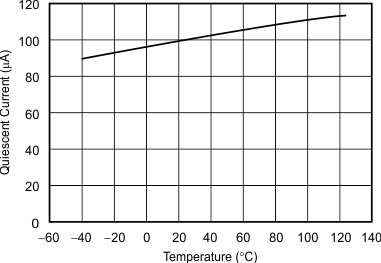 Figure 5. Quiescent Current vs Temperature
Figure 5. Quiescent Current vs Temperature
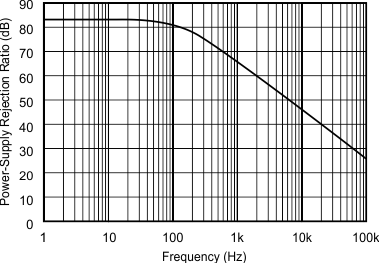 Figure 7. PSRR vs Frequency
Figure 7. PSRR vs Frequency
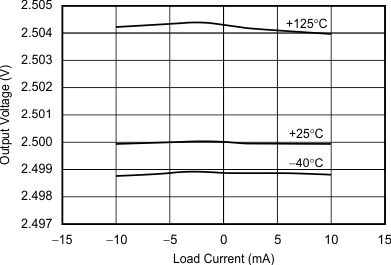 Figure 9. Output Voltage vs Load Current
Figure 9. Output Voltage vs Load Current
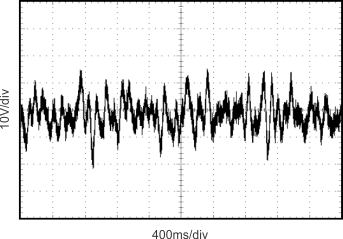 Figure 11. 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Noise
Figure 11. 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Noise
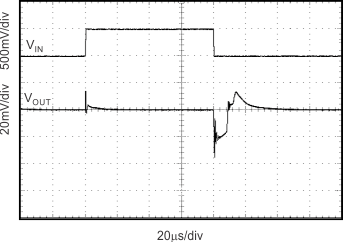 Figure 13. Line Transient
Figure 13. Line Transient
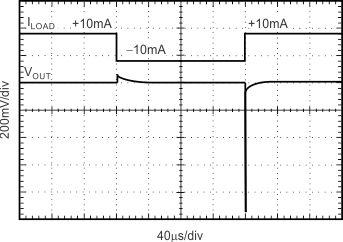
| CL = 0 pF |
±10-mA Output Pulse |
|
Figure 15. Load Transient
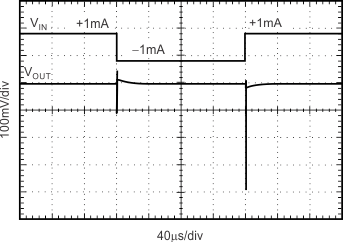
| CL = 0 pF |
±1-mA Output Pulse |
|
Figure 17. Load Transient
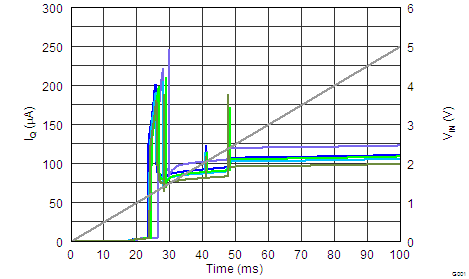 Figure 19. REF3125-Q1 Start-Up
Figure 19. REF3125-Q1 Start-Up
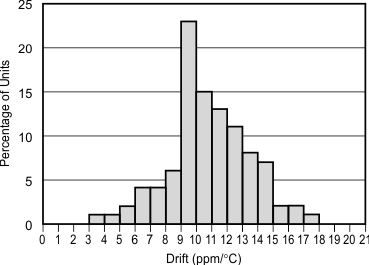 Figure 2. Temperature Drift
Figure 2. Temperature Drift
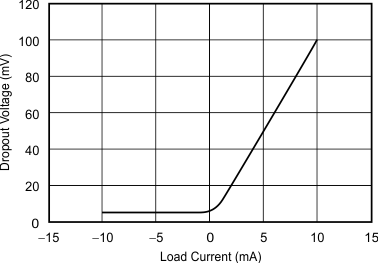 Figure 4. Dropout Voltage vs Load Current
Figure 4. Dropout Voltage vs Load Current
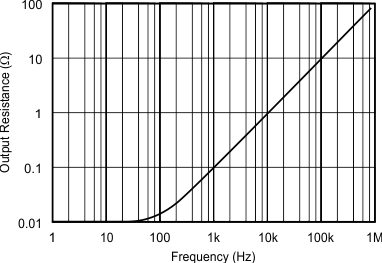 Figure 6. Output Impedance vs Frequency
Figure 6. Output Impedance vs Frequency
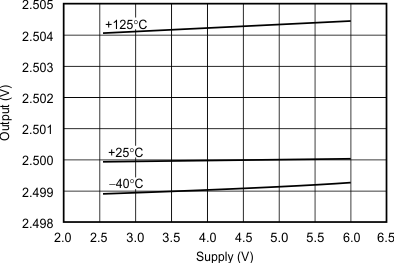 Figure 8. Output vs Supply
Figure 8. Output vs Supply
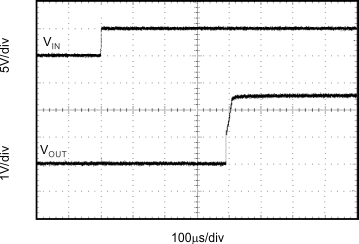 Figure 10. Step Response
Figure 10. Step Response
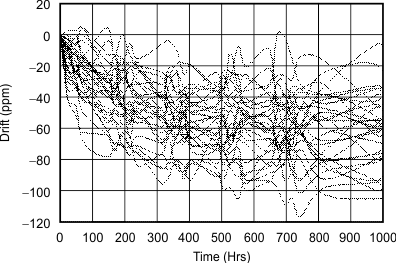 Figure 12. REF3112 Long-Term Stability
Figure 12. REF3112 Long-Term Stability
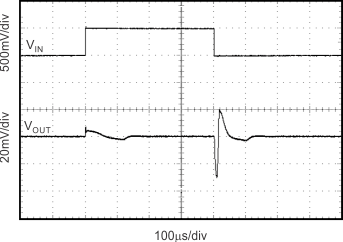 Figure 14. Line Transient
Figure 14. Line Transient
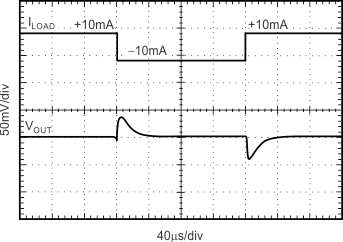
| CL = 1 µF |
±10-mA Output Pulse |
|
Figure 16. Load Transient
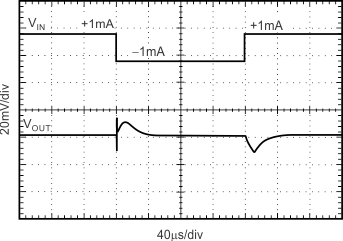
| CL = 1 µF |
±1-mA Output Pulse |
|
Figure 18. Load Transient

 Figure 3. Output Voltage vs Temperature
Figure 3. Output Voltage vs Temperature
 Figure 5. Quiescent Current vs Temperature
Figure 5. Quiescent Current vs Temperature
 Figure 7. PSRR vs Frequency
Figure 7. PSRR vs Frequency

 Figure 11. 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Noise
Figure 11. 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Noise





 Figure 4. Dropout Voltage vs Load Current
Figure 4. Dropout Voltage vs Load Current
 Figure 6. Output Impedance vs Frequency
Figure 6. Output Impedance vs Frequency
 Figure 8. Output vs Supply
Figure 8. Output vs Supply

 Figure 12. REF3112 Long-Term Stability
Figure 12. REF3112 Long-Term Stability


