SNAS809C December 2021 – September 2024 REF35
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|6
- YBH|4
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.4 Thermal Hysteresis
Thermal hysteresis is measured with the REF35 soldered to a PCB, similar to a real-world application. Thermal hysteresis for the device is defined as the change in output voltage after operating the device at 25°C, cycling the device through the specified temperature range, and returning to 25°C. The PCB was baked at 150°C for 30 minutes before thermal hysteresis was measured. Use Equation 2 to calculate the thermal hysteresis:
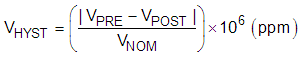
where
- VHYST = thermal hysteresis (in units of ppm)
- VNOM = the specified output voltage
- VPRE = output voltage measured at 25°C pre-temperature cycling
- VPOST = output voltage measured after the device has cycled from 25°C through the specified temperature range of –40°C to +85°C or –40°C to +105°C and returns to 25°C.
The graphs below show the typical thermal hysteresis distribution across various temperature ranges in two cycles.
 Figure 7-7 Thermal Hysteresis Distribution
Figure 7-7 Thermal Hysteresis Distribution –40ºC to 85ºC, Cycle 1
 Figure 7-9 Thermal Hysteresis
Distribution
Figure 7-9 Thermal Hysteresis
Distribution –40ºC to 105ºC, Cycle 1
 Figure 7-8 Thermal Hysteresis
Distribution
Figure 7-8 Thermal Hysteresis
Distribution –40ºC to 85ºC, Cycle 2
 Figure 7-10 Thermal Hysteresis
Distribution
Figure 7-10 Thermal Hysteresis
Distribution –40ºC to 105ºC, Cycle 2