SCLS225G JULY 1995 – November 2016 SN54HCT14 , SN74HCT14
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- J|14
- FK|20
- W|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
When using multiple bit logic devices, inputs must never float. In many cases, functions or parts of functions of digital logic devices are unused, for example, when only two inputs of a triple-input AND gate are used or only three of the four buffer gates are used. Such inputs must not be left unconnected because the undefined voltages at the outside connections result in undefined operational states. All unused inputs of digital logic devices must be connected to a high or low bias to prevent them from floating. The logic level that must be applied to any particular unused input depends on the function of the device. Generally they are tied to GND or VCC, whichever makes more sense or is more convenient. Floating outputs are generally acceptable, unless the part is a transceiver.
11.2 Layout Example
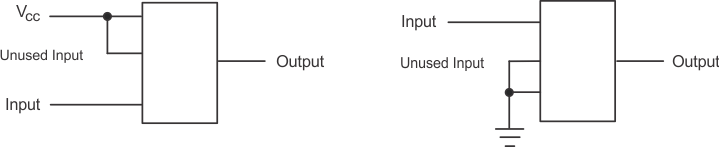 Figure 8. Layout Diagram
Figure 8. Layout Diagram