-
SNx4LS24x, SNx4S24x Octal Buffers and Line Drivers With 3-State Outputs
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics - SNx4LS24x
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics - SNx4S24x
- 6.7 Switching Characteristics - SNx4LS24x
- 6.8 Switching Characteristics - SNx4S24x
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
SNx4LS24x, SNx4S24x Octal Buffers and Line Drivers With 3-State Outputs
1 Features
- Inputs Tolerant Down to 2 V, Compatible With
3.3-V or 2.5-V Logic Inputs - Maximum tpd of 15 ns at 5 V
- 3-State Outputs Drive Bus Lines or Buffer Memory Address Registers
- PNP Inputs Reduce DC Loading
- Hysteresis at Inputs Improves Noise Margins
2 Applications
- Servers
- LED Displays
- Network Switches
- Telecom Infrastructure
- Motor Drivers
- I/O Expanders
3 Description
The SNx4LS24x, SNx4S24x octal buffers and line drivers are designed specifically to improve both the performance and density of three-state memory address drivers, clock drivers, and bus-oriented receivers and transmitters. The designer has a choice of selected combinations of inverting and non-inverting outputs, symmetrical, active-low output-control (G) inputs, and complementary output-control (G and G) inputs. These devices feature high fan-out, improved fan-in, and 400-mV noise margin. The SN74LS24x and SN74S24x devices can be used to drive terminated lines down to 133 Ω.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| SN54LS24x, SN54S24x |
CDIP (20) – J | 24.20 mm × 6.92 mm |
| CFP (20) – W | 7.02 mm × 13.72 mm | |
| LCCC (20) – FK | 8.89 mm × 8.89 mm | |
| SN74LS240, SN74LS244 |
SSOP (20) – DB | 7.20 mm × 5.30 mm |
| SN74LS24x, SN74S24x |
SOIC (20) – DW | 12.80 mm × 7.50 mm |
| PDIP (20) – N | 24.33 mm × 6.35 mm | |
| SN74LS24x | SOP (20) – NS | 7.80 mm × 12.60 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
Logic Diagram (Positive Logic)
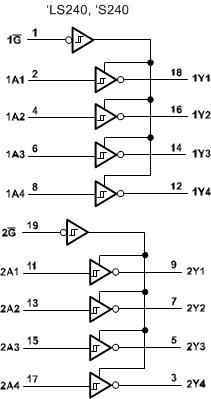
4 Revision History
Changes from C Revision (May 2010) to D Revision
- Added Applications section, ESD Ratings table, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation section, Power Supply Recommendations section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information sectionGo
- Deleted Ordering Information table; see POA at the end of the data sheetGo
- Changed RθJA values in the Thermal Information table from 70 to 94.3 (DB), from 58 to 90.3 (DW), from 69 to 50.6 (N), and from 60 to 76.6 (NS)Go
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| 1 | 1G | I | Channel 1 output enable |
| 2 | 1A1 | I | Channel 1, A side 1 |
| 3 | 2Y4 | O | Channel 2, Y side 4 |
| 4 | 1A2 | I | Channel 1, A side 2 |
| 5 | 2Y3 | O | Channel 2, Y side 3 |
| 6 | 1A3 | I | Channel 1, A side 3 |
| 7 | 2Y2 | O | Channel 2, Y side 2 |
| 8 | 1A4 | I | Channel 1, A side 4 |
| 9 | 2Y1 | O | Channel 2, Y side 1 |
| 10 | GND | — | Ground |
| 11 | 2A1 | I | Channel 2, A side 1 |
| 12 | 1Y4 | O | Channel 1, Y side 4 |
| 13 | 2A2 | I | Channel 2, A side 2 |
| 14 | 1Y3 | O | Channel 1, Y side 3 |
| 15 | 2A3 | I | Channel 2, A side 3 |
| 16 | 1Y2 | O | Channel 1, Y side 2 |
| 17 | 2A4 | I | Channel 2, A side 4 |
| 18 | 1Y1 | O | Channel 1, Y side 1 |
| 19 | 2G/2G(1) | I | Channel 2 output enable |
| 20 | VCC | — | Power supply |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, VCC(2) | 7 | V | ||
| Input voltage, VI | SNx4LS24x | 7 | V | |
| SNx4S24x | 5.5 | |||
| Off-state output voltage | 5.5 | V | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL PACKAGES | ||||
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | 500 | V |
| N PACKAGE | ||||
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | 500 | V |
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage(1) | SN54xS24x | 4.5 | 5 | 5.5 | V |
| SN74xS24x | 4.75 | 5 | 5.25 | |||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 2 | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | SN54LS24x | 0.7 | V | ||
| SN54S24x, SN74xS24x | 0.8 | |||||
| IOH | High-level output current | SN54xS24x | –12 | mA | ||
| SN74xS24x | –15 | |||||
| IOL | Low-level output current | SN54LS24x | 12 | mA | ||
| SN54S24x | 48 | |||||
| SN74LS24x | 24 | |||||
| SN74S24x | 64 | |||||
| External resistance between any input and VCC or ground (SNx4S24x only) | 40 | kΩ | ||||
| TA | Operating free-air temperature(2) | SN54xS24x | –55 | 125 | °C | |
| SN74xS24x | 0 | 70 | ||||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | SN74LS240, SN74LS244 |
SN74LS24x, SN74S24x | SN74LS24x | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB (SSOP) | DW (SOIC) | N (PDIP) | NS (SOP) | |||
| 20 PINS | 20 PINS | 20 PINS | 20 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance(2)(3) | 94.3 | 90.3 | 50.6 | 76.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 55.9 | 45.5 | 37.4 | 42.9 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 49.5 | 48.1 | 31.5 | 44.1 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 21.3 | 19.4 | 24 | 19.2 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 49.1 | 47.6 | 31.4 | 43.7 | °C/W |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics – SNx4LS24x
over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS(1) | MIN | TYP(2) | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIK | VCC = MIN, II = –18 mA | –1.5 | V | ||||
| Hysteresis (VT+ − VT−) |
VCC = MIN | 0.2 | 0.4 | V | |||
| VOH | VCC = MIN, IOH = –3 mA, VIH = 2 V, VIL = MAX | 2.4 | 3.4 | V | |||
| VCC = MIN, IOH = MAX, VIH = 2 V, VIL = 0.5 V | 2 | ||||||
| VOL | VCC = MIN, VIL = MAX, VIH = 2 V | IOL = 12 mA, SN54LS24x | 0.4 | V | |||
| IOL = 24 mA, SN74LS24x | 0.5 | ||||||
| IOZH | VCC = MAX, VIL = MAX, VIH = 2 V, VO = 2.7 V | 20 | µA | ||||
| IOZL | VCC = MAX, VIL = MAX, VIH = 2 V, VO = 0.4 V | –20 | µA | ||||
| II | VCC = MAX, VI = 7 V | 0.1 | mA | ||||
| IIH | VCC = MAX, VI = 2.7 V | 20 | µA | ||||
| IIL | VCC = MAX, VIL = 0.4 V | –0.2 | mA | ||||
| IOS(3) | VCC = MAX | –40 | –225 | mA | |||
| ICC | VCC = MAX, output open | Outputs high | All | 17 | 27 | mA | |
| Outputs low | SNx4LS240 | 26 | 44 | ||||
| SNx4LS241, SNx4LS244 | 27 | 46 | |||||
| Outputs disabled | SNx4LS240 | 29 | 50 | ||||
| SNx4LS241, SNx4LS244 | 32 | 54 | |||||
6.6 Electrical Characteristics – SNx4S24x
over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS(1) | MIN | TYP(2) | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIK | VCC = MIN, II = –18 mA | –1.2 | V | ||||
| Hysteresis (VT+ − VT−) |
VCC = MIN | 0.2 | 0.4 | V | |||
| VOH | VCC = MIN, IOH = –1 mA, VIH = 2 V, VIL = 0.8 V, SN74S24x only | 2.7 | V | ||||
| VCC = MIN, IOH = –3 mA, VIH = 2 V, VIL = 0.8 V | 2.4 | 3.4 | |||||
| VCC = MIN, IOH = MAX, VIH = 2 V, VIL = 0.5 V | 2 | ||||||
| VOL | VCC = MIN, VIL = MAX, VIH = 2 V, IOL = 0.8 V | 0.55 | V | ||||
| IOZH | VCC = MAX, VIL = 0.8 V, VIH = 2 V, VO = 2.4 V | 50 | µA | ||||
| IOZL | VCC = MAX, VIL = MAX, VIH = 2 V, VO = 0.5 V | –50 | µA | ||||
| II | VCC = MAX, VI = 5.5 V | 1 | mA | ||||
| IIH | VCC = MAX, VI = 2.7 V | 50 | µA | ||||
| IIL | VCC = MAX, VIL = 0.5 V | Any A | –400 | µA | |||
| Any G | –2 | mA | |||||
| IOS(3) | VCC = MAX | –50 | –225 | mA | |||
| ICC | VCC = MAX, output open | Outputs high | SN54S240 | 80 | 123 | mA | |
| SN74S240 | 80 | 135 | |||||
| SN54S241, SN54S244 | 95 | 147 | |||||
| SN74S241, SN74S244 | 95 | 160 | |||||
| Outputs low | SN54S240 | 100 | 145 | ||||
| SN74S240 | 100 | 150 | |||||
| SN54S241, SN54S244 | 120 | 170 | |||||
| SN74S241, SN74S244 | 120 | 180 | |||||
| Outputs disabled | SN54S240 | 100 | 145 | ||||
| SN74S240 | 100 | 150 | |||||
| SN54S241, SN54S244 | 120 | 170 | |||||
| SN74S241, SN74S244 | 120 | 180 | |||||
6.7 Switching Characteristics – SNx4LS24x
VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C (see SN54LS24x and SN74LS24x Devices)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPLH | RL = 667 Ω, CL = 45 pF | SNx4LS240 | 9 | 14 | ns | |
| SNx4LS241, SNx4LS244 | 12 | 18 | ||||
| tPHL | RL = 667 Ω, CL = 45 pF | 12 | 18 | ns | ||
| tPZL | RL = 667 Ω, CL = 45 pF | 20 | 30 | ns | ||
| tPZH | RL = 667 Ω, CL = 45 pF | 15 | 23 | ns | ||
| tPLZ | RL = 667 Ω, CL = 5 pF | 10 | 20 | ns | ||
| tPHZ | RL = 667 Ω, CL = 5 pF | 15 | 25 | ns | ||
6.8 Switching Characteristics – SNx4S24x
VCC = 5 V and TA = 25°C (see SN54S24x and SN74S24x Devices)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPLH | RL = 90 Ω, CL = 50 pF | SNx4S240 | 4.5 | 7 | ns | |
| SNx4S241, SNx4S244 | 6 | 9 | ||||
| tPHL | RL = 90 Ω, CL = 50 pF | SNx4S240 | 4.5 | 7 | ns | |
| SNx4S241, SNx4S244 | 6 | 9 | ||||
| tPZL | RL = 90 Ω, CL = 50 pF | 10 | 15 | ns | ||
| tPZH | RL = 90 Ω, CL = 50 pF | SNx4S240 | 6.5 | 10 | ns | |
| SNx4S241, SNx4S244 | 8 | 12 | ||||
| tPLZ | RL = 90 Ω, CL = 5 pF | 10 | 15 | ns | ||
| tPHZ | RL = 90 Ω, CL = 5 pF | 6 | 9 | ns | ||
6.9 Typical Characteristics
VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C, CL = 45 pF, and RL = 667 Ω (unless otherwise noted)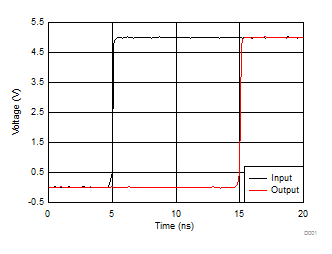 Figure 1. Simulated Propagation Delay From Input to Output
Figure 1. Simulated Propagation Delay From Input to Output
7 Parameter Measurement Information
7.1 SN54LS24x and SN74LS24x Devices
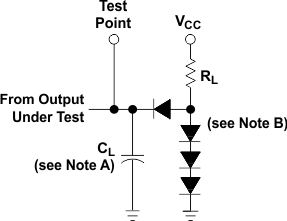 Figure 2. Load Circuit,
Figure 2. Load Circuit,For 2-State Totem-Pole Outputs
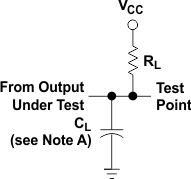 Figure 3. Load Circuit,
Figure 3. Load Circuit,For Open-Collector Outputs
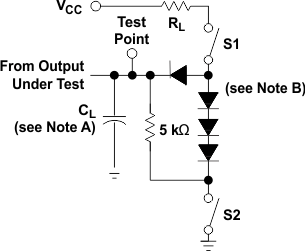 Figure 4. Load Circuit,
Figure 4. Load Circuit,For 3-State Outputs
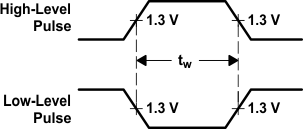 Figure 5. Voltage Waveforms,
Figure 5. Voltage Waveforms,Pulse Durations
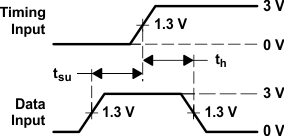 Figure 6. Voltage Waveforms,
Figure 6. Voltage Waveforms,Setup and Hold Times
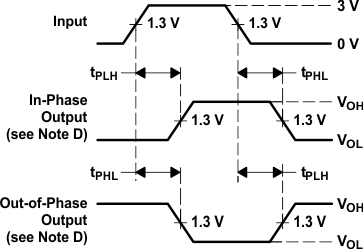 Figure 7. Voltage Waveforms,
Figure 7. Voltage Waveforms,Propagation Delay Times
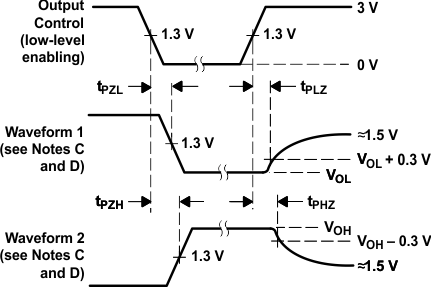
50 Ω, tr ≤ 15 ns, tf ≤ 6 ns.
Enable and Disable Times, 3-State Outputs
7.2 SN54S24x and SN74S24x Devices
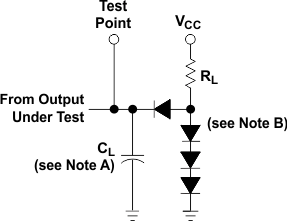 Figure 9. Load Circuit,
Figure 9. Load Circuit,For 2-State Totem-Pole Outputs
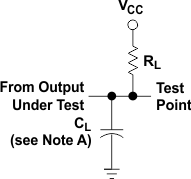 Figure 10. Load Circuit,
Figure 10. Load Circuit,For Open-Collector Outputs
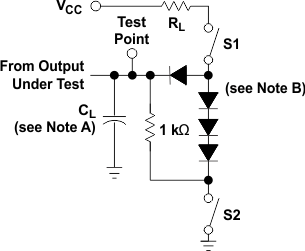 Figure 11. Load Circuit,
Figure 11. Load Circuit,For 3-State Outputs
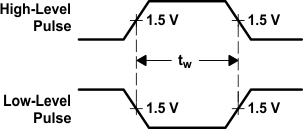 Figure 12. Voltage Waveforms,
Figure 12. Voltage Waveforms,Pulse Durations
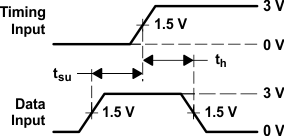 Figure 13. Voltage Waveforms,
Figure 13. Voltage Waveforms,Setup and Hold Times
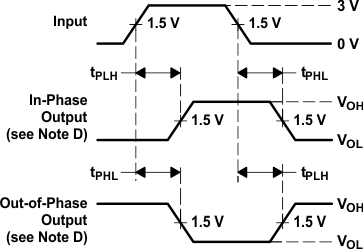 Figure 14. Voltage Waveforms,
Figure 14. Voltage Waveforms,Propagation Delay Times
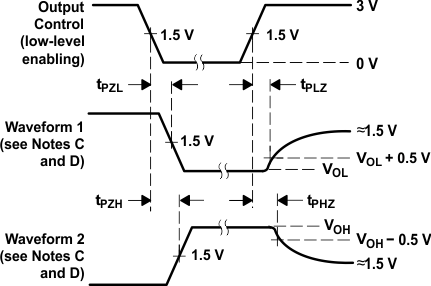
50 Ω; tr and tf ≤ 7 ns for SN54LS24x and SN74LS24x devices, and tr and tf ≤ 2.5 ns for SN54S24x and SN74S24x devices.
Enable and Disable Times, 3-State Outputs
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
This device is organized as two 4-bit buffers and drivers with separate output-enable (G) inputs. When G is low, the device passes data from the A inputs to the Y outputs. When G is high, the outputs are in the high impedance state. Inputs can be driven from either 3.3-V or 5-V devices. This feature allows the use of this device as a translator in a mixed 3.3-V and 5-V system environment. To ensure the high-impedance state during power up or power down, G must be tied to VCC through a pullup resistor; the minimum value of the resistor is determined by the current-sinking capability of the driver.
8.2 Functional Block Diagrams
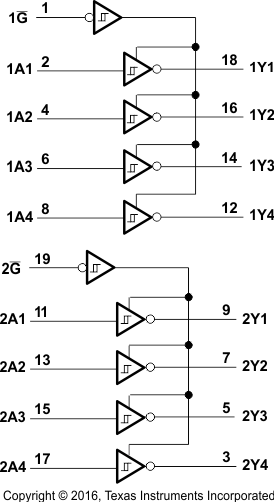
Logic Diagram
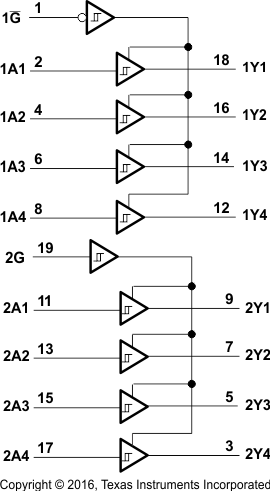
Logic Diagram
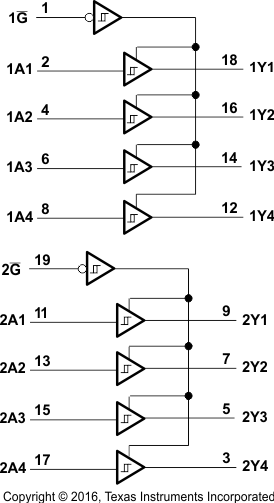
Logic Diagram
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 3-State Outputs
The 3-state outputs can drive bus lines directly. All outputs can be put into high impedance mode through the G pin.
8.3.2 PNP Inputs
This device has PNP inputs which reduce dc loading on bus lines.
8.3.3 Hysteresis on Bus Inputs
The bus inputs have built-in hysteresis that improves noise margins.
8.4 Device Functional Modes
The SNx4LS24x and SNx4S24x devices can be used as inverting and non-inverting bus buffers for data line transmission and can isolate input to output by setting the G pin HIGH. Table 1, Table 2, and Table 3 list the function tables for all devices.
Table 1. SNx4LS240 and SNx4S240
Function Table
| INPUTS | OUTPUTS | |
|---|---|---|
| G | A | Y |
| L | L | H |
| L | H | L |
| H | X | Z |
Table 2. SNx4LS241 and SNx4S241
Function Table
| CHANNEL 1 | CHANNEL 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUTS | OUTPUT | INPUTS | OUTPUT | ||
| 1G | 1A | 1Y | 2G | 2A | 2Y |
| L | L | L | H | L | L |
| L | H | H | H | H | H |
| H | X | Z | L | X | Z |
Table 3. SNx4LS244 and SNx4S244
Function Table
| INPUTS | OUTPUTS | |
|---|---|---|
| G | A | Y |
| L | L | L |
| L | H | H |
| H | X | Z |
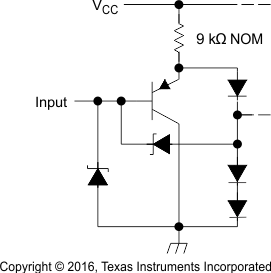 Figure 19. SNx4LS240, SNx4LS241, SNx4LS244
Figure 19. SNx4LS240, SNx4LS241, SNx4LS244Equivalent of Each Input
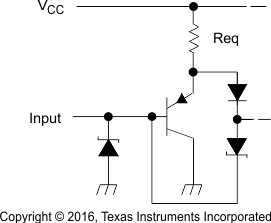
Equivalent of Each Input
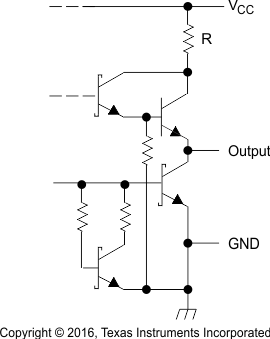
R = 50 Ω NOM
R = 25 Ω NOM
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
The SNx4LS24x, SNx4S24x octal buffers and line drivers are designed to be used for a multitude of bus interface type applications where output drive or PCB trace length is a concern.
9.2 Typical Application
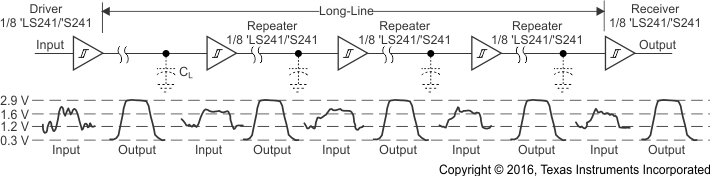 Figure 22. SNx4LS241 and SNx4S241 Used as Repeater or Level Restorer
Figure 22. SNx4LS241 and SNx4S241 Used as Repeater or Level Restorer
9.2.1 Design Requirements
This device uses Schottky transistor logic technology. Take care to avoid bus contention because it can drive currents that would exceed maximum limits. The high drive creates fast edges into light loads, so routing and load conditions must be considered to prevent ringing.
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- Power Supply
- Each device must maintain a supply voltage between 4.5 V and 5.5 V.
- Inputs
- Input signals must meet the VIH and VIL specifications in Electrical Characteristics – SNx4LS24x.
- Inputs leakage values (II, IIH, IIL) from Electrical Characteristics – SNx4LS24x must be considered.
- Outputs
- Output signals are specified to meet the VOH and VOL specifications in Electrical Characteristics – SNx4LS24x as a minimum (the values could be closer to VCC for high signals or GND for low signals).
- TI recommends maintaining output currents as specified in Recommended Operating Conditions.
- The part can be damaged by sourcing or sinking too much current (see Electrical Characteristics – SNx4LS24x for details).
9.2.3 Application Curve
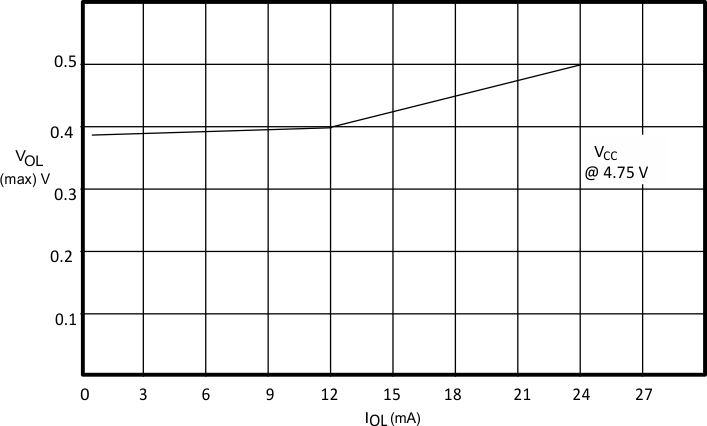 Figure 23. VOL vs IOL
Figure 23. VOL vs IOL
9.3 System Examples
The SNx4LS240 and SNx4S240 devices can be used to buffer signals along a memory bus. The increased output drive helps data transmission reliability. Figure 24 shows a schematic of this example.
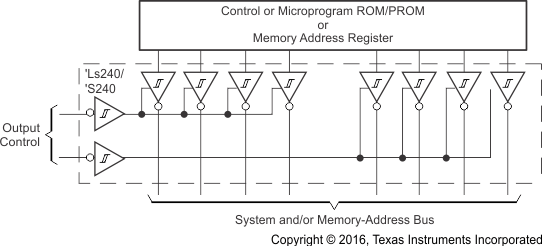
The SNx4LS240 and SNx4S240 devices have two independently controlled 4-bit drivers, and can be used to buffer signals in a bidirectional manner along a data bus. Figure 25 shows the SNx4LS240 or SNx4S240 used in this manner.
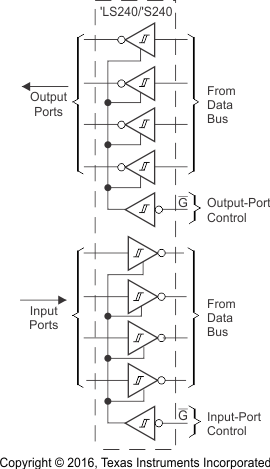 Figure 25. Independent 4-Bit But Drivers/Receivers in a Single Package
Figure 25. Independent 4-Bit But Drivers/Receivers in a Single Package
The enable pins on the SNx4LS241 and SNx4S241 devices can be used to help direct signals along a shared party-line bus. Figure 26 shows a general configuration of how to implement this structure. Take care to ensure that bus contention does not occur.
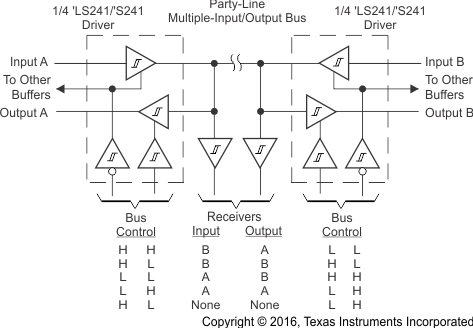 Figure 26. Party-Line Bus System With Multiple Inputs, Outputs, and Receivers
Figure 26. Party-Line Bus System With Multiple Inputs, Outputs, and Receivers