SLLS632C December 2005 – February 2015 SN65HVD1050
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (Continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Driver Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Receiver Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Device Switching Characteristics
- 7.8 Driver Switching Characteristics
- 7.9 Receiver Switching Characteristics
- 7.10 Supply Current
- 7.11 S-Pin Characteristics
- 7.12 VREF-Pin Characteristics
- 7.13 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8 Parameter Measurement Information
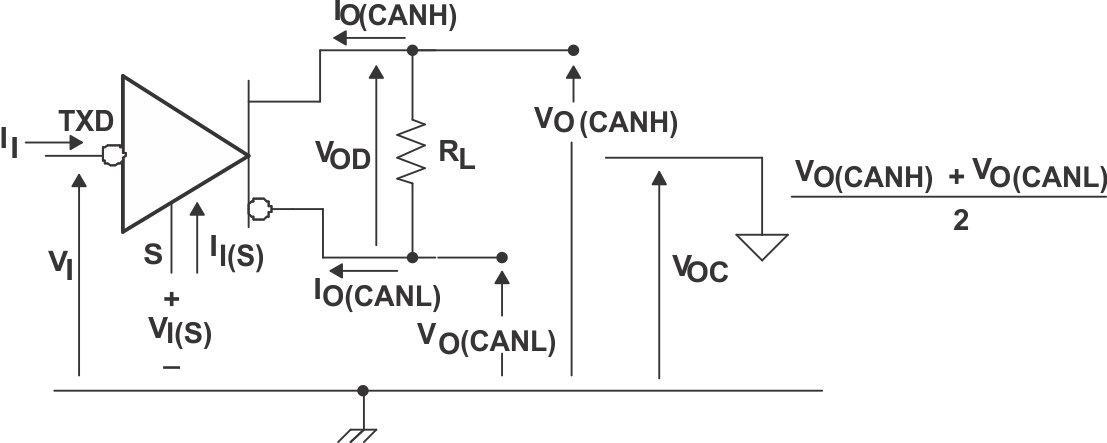
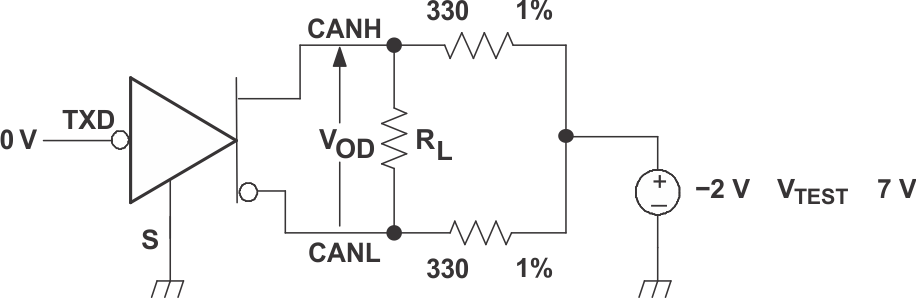
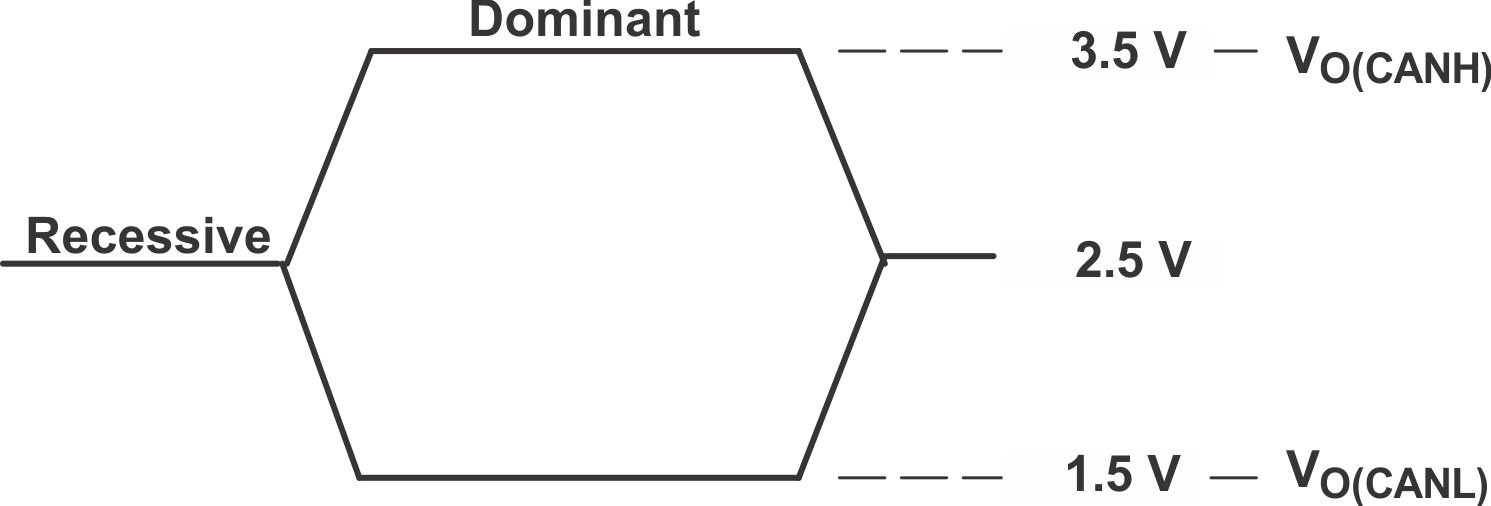
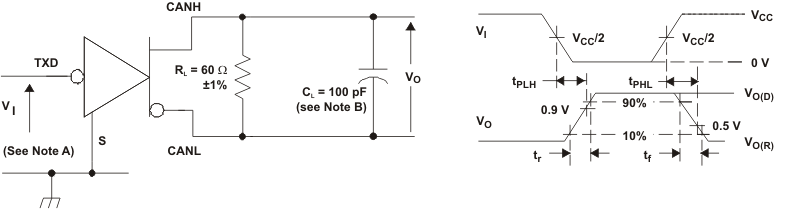 Figure 14. Driver Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
Figure 14. Driver Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
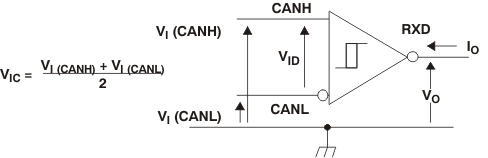 Figure 15. Receiver Voltage and Current Definitions
Figure 15. Receiver Voltage and Current Definitions
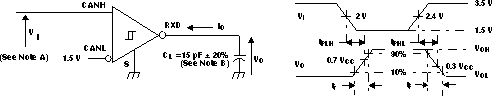
A. The input pulse is supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: PRR ≤ 125 kHz, 50% duty cycle, tr ≤ 6 ns, tf ≤ 6ns, ZO = 50 Ω.
B. CL includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within ±20%.
Figure 16. Receiver Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
Table 1. Differential Input Voltage Threshold Test
| INPUT | OUTPUT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCANH | VCANL | |VID| | R | |
| –11.1V | –12V | 900 mV | L | VOL |
| 12V | 11.1V | 900 mV | L | |
| –6V | –12V | 6V | L | |
| 12V | 6V | 6V | L | |
| –11.5V | –12V | 500 mV | H | VOH |
| 12V | 11.5V | 500 mV | H | |
| –12V | –6V | 6V | H | |
| 6V | 12V | 6V | H | |
| Open | Open | X | H | |
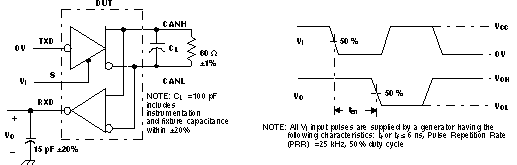 Figure 17. TEN Test Circuit and Waveform
Figure 17. TEN Test Circuit and Waveform
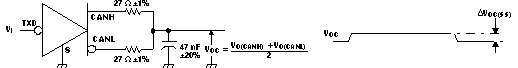
NOTE:
All VI input pulses are from 0V to VCC and supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤ 6 ns. Pulse Repetition Rate (PRR) = 125 kHz, 50% duty cycle.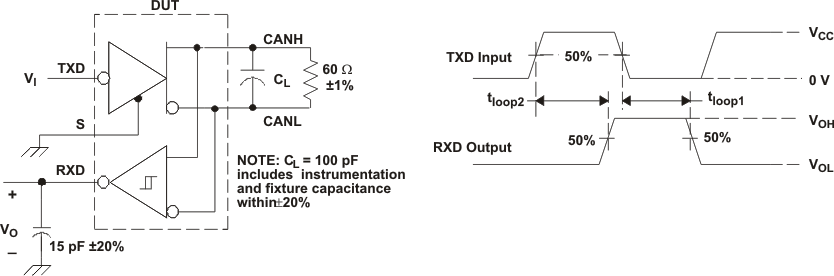
A. All VI input pulses are from 0V to VCC and supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤ 6 ns. Pulse Repetition Rate (PRR) = 125 kHz, 50% duty cycle.
Figure 19. T(LOOP) Test Circuit and Waveform
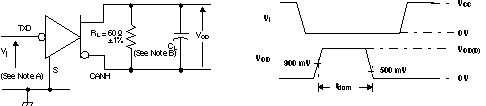
A. All VI input pulses are from 0 V to VCC and supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤ 6 ns. Pulse Repetition Rate (PRR) = 500 Hz, 50% duty cycle.
B. CL = 100 pF includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within ±20%.
Figure 20. Dominant Time-Out Test Circuit and Waveforms
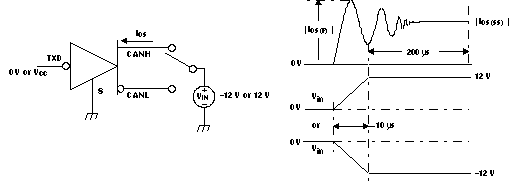 Figure 21. Driver Short-Circuit Current Test and Waveform
Figure 21. Driver Short-Circuit Current Test and Waveform