SLLS563I July 2003 – January 2023 SN65HVD1176 , SN75HVD1176
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2 Typical Application
An RS-485 bus consists of multiple transceivers connecting in parallel to a bus cable. To eliminate line reflections, each cable end is terminated with a termination resistor RT) whose value matches the characteristic impedance (Z0) of the cable. This method, known as parallel termination, allows for higher data rates over longer cable length.
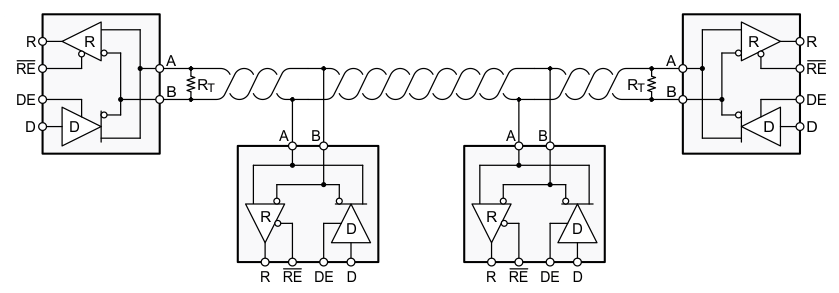 Figure 8-2 Typical
RS-485 Network With Half-Duplex Transceivers
Figure 8-2 Typical
RS-485 Network With Half-Duplex TransceiversThe PROFIBUS standard extends RS-485 by specifying the value of the termination resistor, the characteristic impedance of the bus cable, and the value of fail-safe termination at both ends of the bus.
PROFIBUS requires that 220-Ω termination resistors be placed at both ends of the bus, the bus cable impedance be between 135 Ω and 165 Ω, and that 390-Ω fail-safe resistors be placed on both the A and B lines at both ends of the bus.
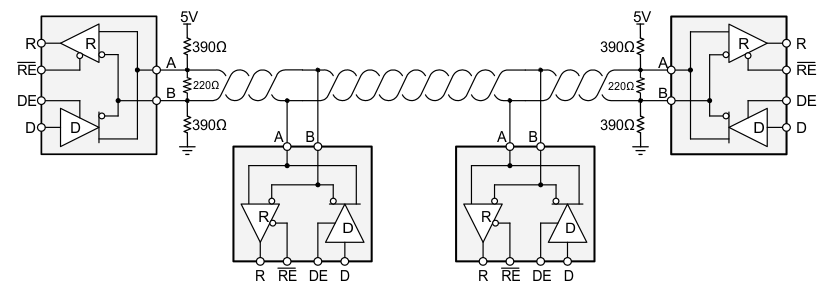 Figure 8-3 Typical PROFIBUS network
Figure 8-3 Typical PROFIBUS network