-
SN65HVD25x Turbo CAN Transceivers for Higher Data Rates and Large Networks Including Features for Functional Safety SLLSEA2D December 2011 – May 2015 SN65HVD255 , SN65HVD256 , SN65HVD257
PRODUCTION DATA.
-
SN65HVD25x Turbo CAN Transceivers for Higher Data Rates and Large Networks Including Features for Functional Safety
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Options
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
SN65HVD25x Turbo CAN Transceivers for Higher Data Rates and Large Networks Including Features for Functional Safety
1 Features
- Meets the Requirements of ISO11898-2
- Turbo CAN:
- Short and Symmetrical Propagation Delay Times and Fast Loop Times for Enhanced Timing Margin
- Higher Data Rates in CAN Networks
- I/O Voltage Range Supports 3.3-V and 5-V MCUs
- Ideal Passive Behavior When Unpowered
- Bus and Logic Pins are High Impedance (No Load)
- Power Up and Power Down With Glitch-Free Operation on Bus
- Protection Features
- HBM ESD Protection Exceeds ±12 kV
- Bus Fault Protection –27 V to 40 V
- Undervoltage Protection on Supply Pins
- Driver Dominant Time Out (TXD DTO)
- SN65HVD257: Receiver-Dominant Time Out (RXD DTO)
- SN65HVD257: FAULT Output Pin
- Thermal Shutdown Protection
- Characterized for –40°C to 125°C Operation
2 Applications
- 1-Mbps Operation in Highly Loaded CAN Networks Down to 10-kbps Networks Using TXD DTO
- Industrial Automation, Control, Sensors, and Drive Systems
- Building, Security, and Climate Control Automation
- Telecom Base Station Status and Control
- SN65HVD257: Functional Safety With Redundant and Multitopology CAN networks
- CAN Bus Standards Such as CANopen, DeviceNet, NMEA2000, ARNIC825, ISO11783, and CANaerospace
3 Description
This CAN transceiver meets the ISO1189-2 High Speed CAN (Controller Area Network) Physical Layer standard. It is designed for data rates in excess of
1 Mbps for CAN in short networks, and enhanced timing margin and higher data rates in long and highly-loaded networks. The device provides many protection features to enhance device and CAN-network robustness. The SN65HVD257 device adds additional features, allowing for easy design of redundant and multitopology networks with fault indication for higher levels of functional safety in the CAN system.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| SN65HVD255 SN65HVD256 SN65HVD257 |
SOIC (8) | 4.90 mm × 3.91 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
Block Diagram
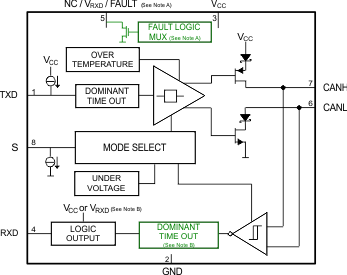
5-V only supply devices (SN65HVD255, SN65HVD257) and driven to VRXD on the output level-shifting device (SN65HVD256).
4 Revision History
Changes from C Revision (September 2013) to D Revision
- Added Pin Configuration and Functions section, ESD Ratings table, Switching Characteristics table, Typical Characteristics section, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation section, Power Supply Recommendations section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information section Go
Changes from B Revision (June 2012) to C Revision
- Added Table 1, Receiver Differential Input Voltage Threshold TestGo
- Added Figure 13, Example Timing Diagram for TXD DTO and FAULT PinGo
- Added Bus Loading, Length, and Number of Nodes subsectionGo
Changes from A Revision (June 2012) to B Revision
- Added SN65HVD257 status to production in Ordering Information tableGo
Changes from * Revision (December 2011) to A Revision
- Updated the Features listGo
- Updated the Applications listGo
- Added text to the Description sectionGo
- Changed Block Diagram - Functional Block Diagram to include HVD257 and Note changes.Go
- Changed the DEVICE OPTIONS tableGo
- Added SN65HVD257 to the D PACKAGE OPTIONS imagesGo
- Added SN65HVD257 FAULT pin to the PIN FUNCTIONS tableGo
- Added SN65HVD257 to the Ordering Information tableGo
- Added SN65HVD257 FAULT pin information to the Abs Max tableGo
- Added FAULT pin information to the ROC tableGo
- changed RID - Differential input resistance value from 3 kΩ to 30 kΩGo
- Added tRXD_DTO - SN65HVD257 informationGo
- Added Figure 4, RXD Dominant Timeout Test Circuit and MeasurementGo
- Added Figure 5, FAULT Test and MeasurementGo
- Added RXD Dominant Timeout (SN65HVD257) sectionGo
- Added FAULT pin informationGo
- Added footnote for SN65HVD257 function to Table 5Go
- Added 5-V VCC with FAULT Open-Drain Output Device (SN65HVD257) sectionGo
- Added Example: Functional Safety Using the SN65HVD257 in a Redundant Physical Layer CAN Network Topology sectionGo
5 Device Options
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
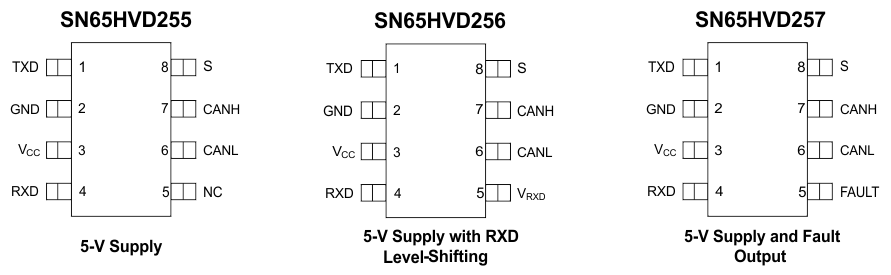
Pin Functions
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings(1)(2)
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | –0.3 | 6.1 | V | |
| VRXD | RXD Output supply voltage | SN65HVD256 | –0.3 | 6 and VRXD ≤ VCC + 0.3 | V |
| VBUS | CAN Bus I/O voltage (CANH, CANL) | –27 | 40 | V | |
| VLogic_Input | Logic input pin voltage (TXD, S) | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| VLogic_Output | Logic output pin voltage (RXD) | SN65HVD255, SN65HVD257 | –0.3 | 6 | V |
| VLogic_Output | Logic output pin voltage (RXD) | SN65HVD256 | –0.3 | 6 and VI ≤ VRXD + 0.3 | V |
| IO(RXD) | RXD (Receiver) output current | 12 | mA | ||
| IO(FAULT) | FAULT output current | SN65HVD257 | 20 | mA | |
| TJ | Operating virtual junction temperature (see Power Dissipation) | –40 | 150 | °C | |
| TA | Ambient temperature (see Power Dissipation) | –40 | 125 | °C | |
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | All pins | ±2500 | V | |
| CAN bus pins (CANH, CANL)(2) | ±12000 | |||||
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(3) | All pins | ±750 | ||||
| Machine model | All pins | ±250 | ||||
| IEC 61400-4-2 according to GIFT-ICT CAN EMC test spec(4) | CAN bus pins (CANH, CANL) to GND | ±8000 | ||||
| ISO7637 Transients according to GIFT - ICT CAN EMC test spec(5) | CAN bus pins (CANH, CANL) | Pulse 1 | –100 | |||
| Pulse 2 | +75 | |||||
| Pulse 3a | –150 | |||||
| Pulse 3b | +100 | |||||
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | 4.5 | 5.5 | V | |
| VRXD | RXD supply (SN65HVD256 only) | 2.8 | 5.5 | ||
| VI or VIC | CAN bus terminal voltage (separately or common mode) | –2 | 7 | ||
| VID | CAN bus differential voltage | -6 | 6 | ||
| VIH | Logic HIGH level input (TXD, S) | 2 | 5.5 | ||
| VIL | Logic LOW level input (TXD, S) | 0 | 0.8 | ||
| IOH(DRVR) | CAN BUS Driver High level output current | –70 | mA | ||
| IOL(DRVR) | CAN BUS Driver Low level output current | 70 | |||
| IOH(RXD) | RXD pin HIGH level output current | –2 | |||
| IOL(RXD) | RXD pin LOW level output current | 2 | |||
| IO(FAULT) | FAULT pin LOW level output current | SN65HVD257 | 2 | ||
| TA | Operational free-air temperature (see Power Dissipation) | –40 | 125 | °C | |
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | SN65HVD25x | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| D (SOIC) | |||
| 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, High-K thermal resistance(2) | 107.5 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 56.7 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 48.9 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 12.1 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 48.2 | °C/W |
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
Over recommended operating conditions, TA = –40°C to 125°C (unless otherwise noted). SN65HVD256 device VRXD = VCC.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP(1) | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUPPLY CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| ICC | 5-V Supply current | Normal Mode (Driving Dominant) | See Figure 6, TXD = 0 V, RL = 50 Ω, CL = open, RCM = open, S = 0 V |
60 | 85 | mA | |
| Normal Mode (Driving Dominant – bus fault) | See Figure 6, TXD = 0 V, S = 0 V, CANH = –12 V, RL = open, CL = open, RCM = open |
130 | 180 | ||||
| Normal Mode (Driving Dominant) | See Figure 6, TXD = 0 V, RL = open (no load), CL = open, RCM = open, S = 0 V |
10 | 20 | ||||
| Normal Mode (Recessive) | See Figure 6, TXD = VCC, RL = 50 Ω, CL = open, RCM = open, S = 0 V |
10 | 20 | ||||
| Silent Mode | See Figure 6, TXD = VCC, RL = 50 Ω, CL = open, RCM = open, S = VCC |
2.5 | 5 | ||||
| IRXD | RXD Supply current (SN65HVD256 only) | All modes | RXD Floating, TXD = 0 V | 500 | µA | ||
| UVVCC | Undervoltage detection on VCC for protected mode | 3.5 | 4.45 | V | |||
| VHYS(UVVCC) | Hysteresis voltage on UVVCC | 200 | mV | ||||
| UVRXD | Undervoltage detection on VRXD for protected mode (SN65HVD256 only) | 1.3 | 2.75 | V | |||
| VHYS(UVRXD) | Hysteresis voltage on UVRXD (SN65HVD256 only) | 80 | mV | ||||
| S PIN (MODE SELECT INPUT) | |||||||
| VIH | HIGH-level input voltage | 2 | V | ||||
| VIL | LOW-level input voltage | 0.8 | V | ||||
| IIH | HIGH-level input leakage current | S = VCC = 5.5 V | 7 | 100 | µA | ||
| IIL | Low-level input leakage current | S = 0 V, VCC = 5.5 V | –1 | 0 | 1 | µA | |
| ILKG(OFF) | Unpowered leakage current | S = 5.5 V, VCC = 0 V, VRXD = 0 V | 7 | 35 | 100 | µA | |
| TXD PIN (CAN TRANSMIT DATA INPUT) | |||||||
| VIH | HIGH level input voltage | 2 | V | ||||
| VIL | LOW level input voltage | 0.8 | V | ||||
| IIH | HIGH level input leakage current | TXD = VCC = 5.5 V | –2.5 | 0 | 1 | µA | |
| IIL | Low level input leakage current | TXD = 0 V, VCC = 5.5 V | –100 | –25 | –7 | µA | |
| ILKG(OFF) | Unpowered leakage current | TXD = 5.5 V, VCC = 0 V, VRXD = 0 V | –1 | 0 | 1 | µA | |
| CI | Input Capacitance | 3.5 | pF | ||||
| RXD PIN (CAN RECEIVE DATA OUTPUT) | |||||||
| VOH | HIGH level output voltage | See Figure 7, IO = –2 mA. For devices with VRXD supply VOH = 0.8 × VRXD | 0.8 × VCC | V | |||
| VOL | LOW level output voltage | See Figure 7, IO = 2 mA | 0.4 | V | |||
| ILKG(OFF) | Unpowered leakage current | RXD = 5.5 V, VCC = 0 V, VRXD = 0 V | –1 | 0 | 1 | µA | |
| DRIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| VO(D) | Bus output voltage (dominant) | CANH | See Figure 15 and Figure 6, TXD = 0 V, S = 0 V, RL = 60 Ω, CL = open, RCM = open |
2.75 | 4.5 | V | |
| CANL | 0.5 | 2.25 | |||||
| VO(R) | Bus output voltage (recessive) | See Figure 15 and Figure 6, TXD = VCC, VRXD = VCC, S = VCC or 0 V (2), RL = open (no load), RCM = open | 2 | 0.5 × VCC | 3 | V | |
| VOD(D) | Differential output voltage (dominant) | See Figure 15 and Figure 6, TXD = 0 V, S = 0 V, 45 Ω ≤ RL ≤ 65 Ω, CL = open, RCM = 330 Ω, –2 V ≤ VCM ≤ 7 V, 4.75 V≤ VCC ≤ 5.25 V |
1.5 | 3 | V | ||
| See Figure 15 and Figure 6, TXD = 0 V, S = 0 V, 45 Ω ≤ RL ≤ 65 Ω, CL = open, RCM = 330 Ω, –2 V ≤ VCM ≤ 7 V, 4.5 V ≤ VCC ≤ 5.5 V |
1.25 | 3.2 | |||||
| VOD(R) | Differential output voltage (recessive) | See Figure 15 and Figure 6, TXD = VCC, S = 0 V, RL = 60 Ω, CL = open, RCM = open |
–0.12 | 0.012 | V | ||
| See Figure 15 and Figure 6, TXD = VCC, S = 0 V, RL = open (no load), CL = open, RCM = open, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ 85°C |
–0.100 | 0.050 | |||||
| VSYM | Output symmetry (dominant or recessive) (VCC – VO(CANH) – VO(CANL)) |
See Figure 15 and Figure 6, S at 0 V, RL = 60 Ω, CL = open, RCM = open |
–0.4 | 0.4 | V | ||
| IOS(SS)_DOM | Short circuit steady-state output current, Dominant | See Figure 15 and Figure 11, VCANH = 0 V, CANL = open, TXD = 0 V | –160 | mA | |||
| See Figure 15 and Figure 11, VCANL = 32 V, CANH = open, TXD = 0 V |
160 | ||||||
| IOS(SS)_REC | Short circuit steady-state output current, Recessive | See Figure 15 and Figure 11, –20 V ≤ VBUS ≤ 32 V, Where VBUS = CANH = CANL, TXD = VCC, Normal and Silent Modes |
–8 | 8 | mA | ||
| CO | Output capacitance | See Input capacitance to ground (CI) in the following Receiver Electrical Characteristics section of this table | |||||
| RECEIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| VIT+ | Positive-going input threshold voltage, normal mode | See Figure 7, Table 5 and Table 1 | 900 | mV | |||
| VIT– | Negative-going input threshold voltage, normal mode | 500 | mV | ||||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage (VIT+ - VIT–) | 125 | mV | ||||
| IIOFF(LKG) | Power-off (unpowered) bus input leakage current | VCANH = VCANL = 5 V, VCC = 0 V, VRXD = 0 V |
5.5 | µA | |||
| CI | Input capacitance to ground (CANH or CANL) | TXD = VCC, VRXD = VCC, VI = 0.4 sin (4E6 π t) + 2.5 V |
25 | pF | |||
| CID | Differential input capacitance | TXD = VCC, VRXD = VCC, VI = 0.4 sin (4E6 π t) |
10 | pF | |||
| RID | Differential input resistance | TXD = VCC = VRXD = 5 V, S = 0 V | 30 | 80 | kΩ | ||
| RIN | Input resistance (CANH or CANL) | 15 | 40 | kΩ | |||
| RIN(M) | Input resistance matching: [1 – RIN(CANH) / RIN(CANL)] × 100% |
V(CANH) = V(CANL), –40°C ≤ TA ≤ 85°C | –3% | 3% | |||
| FAULT PIN (FAULT OUTPUT), SN65HVD257 ONLY | |||||||
| ICH | Output current high level | FAULT = VCC, see Figure 5 | –10 | 10 | µA | ||
| ICL | Output current low level | FAULT = 0.4 V, see Figure 5 | 5 | 12 | mA | ||
7.6 Power Dissipation
| THERMAL METRIC | TEST CONDITIONS | TYP | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD | Average power dissipation | VCC = 5 V, VRXD = 5 V, TJ = 27°C, RL = 60 Ω, S at 0 V, Input to TXD at 250 kHz, 25% duty cycle square wave, CL_RXD = 15 pF. Typical CAN operating conditions at 500 kbps with 25% transmission (dominant) rate. | 115 | mW |
| VCC = 5.5 V, VRXD = 5.5 V, TJ = 150°C, RL = 50 Ω, S at 0 V, Input to TXD at 500 kHz, 50% duty cycle square wave, CL_RXD = 15 pF. Typical high load CAN operating conditions at 1 Mbps with 50% transmission (dominant) rate and loaded network. | 268 | |||
| Thermal shutdown temperature | 170 | °C | ||
| Thermal shutdown hysteresis | 5 | °C | ||
7.7 Switching Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEVICE SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| tPROP(LOOP1) | Total loop delay, driver input (TXD) to receiver output (RXD), recessive to dominant | See Figure 9, S = 0 V, RL = 60 Ω, CL = 100 pF, CL_RXD = 15 pF |
150 | ns | ||
| tPROP(LOOP2) | Total loop delay, driver input (TXD) to receiver output (RXD), dominant to recessive | 150 | ||||
| IMODE | Mode change time, from Normal to Silent or from Silent to Normal | See Figure 8 | 20 | µS | ||
| DRIVER SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| tpHR | Propagation delay time, HIGH TXD to Driver Recessive | See Figure 6, S = 0 V, RL = 60 Ω, CL = 100 pF, RCM = open |
50 | 70 | ns | |
| tpLD | Propagation delay time, LOW TXD to Driver Dominant | 40 | 70 | |||
| tsk(p) | Pulse skew (|tpHR – tpLD|) | 10 | ||||
| tR | Differential output signal rise time | 10 | 30 | |||
| tF | Differential output signal fall time | 17 | 30 | |||
| tR(10k) | Differential output signal rise time, RL = 10 kΩ |
See Figure 6, S = 0 V, RL = 10 kΩ, CL = 10 pF, RCM = open |
35 | ns | ||
| tF(10k) | Differential output signal fall time, RL = 10 kΩ |
100 | ||||
| tTXD_DTO | Dominant timeout(1) | See Figure 10, RL = 60 Ω, CL = open | 1175 | 3700 | µs | |
| RECEIVER SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| tpRH | Propagation delay time, recessive input to high output | See Figure 7, CL_RXD = 15 pF | 70 | 90 | ns | |
| tpDL | Propagation delay time, dominant input to low output | 70 | 90 | ns | ||
| tR | Output signal rise time | 4 | 20 | ns | ||
| tF | Output signal fall time | 4 | 20 | ns | ||
| tRXD_DTO(2) | Receiver dominant time out (SN65HVD257 only) See Figure 4, CL_RXD = 15 pF | 1380 | 4200 | µs | ||
7.8 Typical Characteristics
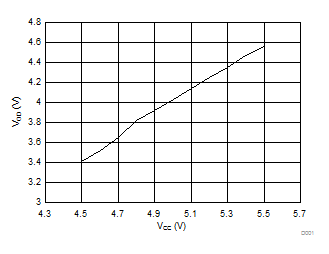 Figure 1. Differential Output Voltage vs Supply Voltage
Figure 1. Differential Output Voltage vs Supply Voltage
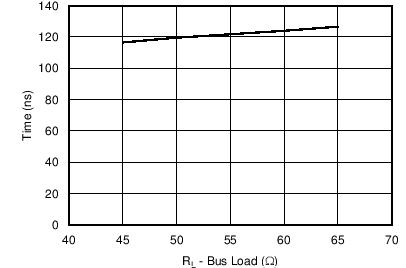 Figure 3. Typical Transceiver Loop Delay vs Bus Loading
Figure 3. Typical Transceiver Loop Delay vs Bus Loading
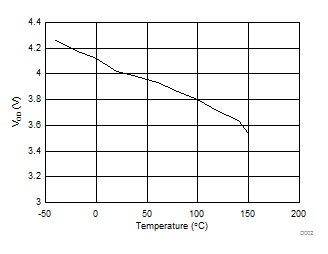 Figure 2. Differential Output Voltage vs Ambient Temperature
Figure 2. Differential Output Voltage vs Ambient Temperature