SLLS612F June 2004 – February 2023 SN65HVD485E
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: Driver
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: Receiver
- 7.7 Power Dissipation Characteristics
- 7.8 Supply Current
- 7.9 Switching Characteristics: Driver
- 7.10 Switching Characteristics: Receiver
- 7.11 Dissipation Ratings
- 7.12 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
To protect bus nodes against high-energy transients, the implementation of external transient protection devices is necessary.
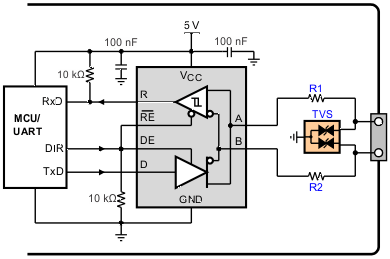 Figure 9-4 Transient Protection Against ESD, EFT, and Surge Transients
Figure 9-4 Transient Protection Against ESD, EFT, and Surge TransientsFigure 9-4 suggests a protection circuit against 10-kV ESD (IEC 61000-4-2), 4-kV EFT (IEC 61000-4-4), and 1-kV surge (IEC 61000-4-5) transients. Table 9-1 shows the associated bill of materials.
Table 9-1 Bill of Materials
| DEVICE | FUNCTION | ORDER NUMBER | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|
| XCVR | 5-V, 10-Mbps RS-485 transceiver | SN65HVD485E | TI |
| R1, R2 | 10-Ω, pulse-proof thick-film resistor | CRCW0603010RJNEAHP | Vishay |
| TVS | Bidirectional 400-W transient suppressor | CDSOT23-SM712 | Bourns |