SLIS128D November 2011 – April 2022 SN65HVDA100-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Description (continued)
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 LIN (Local Interconnect Network) Bus
- 9.3.2 TXD (Transmit Input / Output)
- 9.3.3 RXD (Receive Output)
- 9.3.4 VSUP (Supply Voltage)
- 9.3.5 GND (Ground)
- 9.3.6 EN (Enable Input)
- 9.3.7 NWake (High Voltage Wake Up Input)
- 9.3.8 INH (Inhibit Output)
- 9.3.9 TXD Dominant State Timeout
- 9.3.10 Thermal Shutdown
- 9.3.11 Bus Stuck Dominant System Fault: False Wake-Up Lockout
- 9.3.12 Undervoltage on VSUP
- 9.3.13 Unpowered Device Does Not Affect the LIN Bus
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.3.11 Bus Stuck Dominant System Fault: False Wake-Up Lockout
The device contains logic to detect bus stuck dominant system faults and prevent the device from waking up falsely during this system fault. Upon entering sleep mode, the device detects the state of the LIN bus. If the bus is dominant, the wake-up logic is locked out until a valid recessive on the bus "clears" the bus stuck dominant condition. This logic prevents the potential for a cyclical false wakeup of the system if the bus is stuck dominant, preventing excessive current use. Figure 9-2 and Figure 9-3 show the behavior of this protection feature.
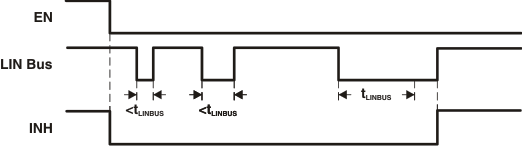 Figure 9-2 No Bus Fault: Entering Sleep Mode With Bus Recessive Condition and Wakeup
Figure 9-2 No Bus Fault: Entering Sleep Mode With Bus Recessive Condition and Wakeup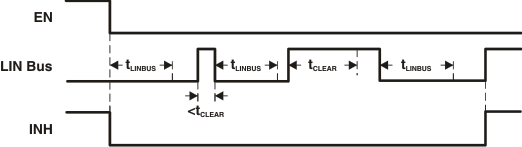 Figure 9-3 Bus Fault: Entering Sleep Mode With Bus Stuck Dominant Fault, Clearing, and Wakeup
Figure 9-3 Bus Fault: Entering Sleep Mode With Bus Stuck Dominant Fault, Clearing, and Wakeup